
1. Weekly News
Colombia
Rain Delays Tomato Harvest in Eastern Antioquia, Driving Prices Up 30% in Northern Colombia
During W25, tomato growers postponed farming activities due to rains in Eastern Antioquia, Colombia. As a result, wholesale markets in several cities in Northern Colombia experienced a substantial 30% week-on-week (WoW) price increase. The current price for tomatoes rose to USD 0.80 per kilogram (kg), reflecting the supply disruption from this key producing area.
Mexico
US Lifts Four-Year Restrictions on Fresh Mexican Tomato Imports, Easing Export Process
According to Mexico's Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (SADER), the United States (US) government has lifted restrictions on the free entry of fresh Mexican tomatoes after four years, initially imposed due to the Tomato brown rugose fruit virus (ToBRFV). Starting June 17, Mexican tomato exports to the US will no longer require an inspection certificate, which has been mandatory since June 3, 2020. This certificate previously needed to include details such as the inspection date, name, title, and signature of the inspector, as well as the producer and packer's names and addresses. This decision will facilitate and expedite border crossings. The National Service for Health, Safety, and Agri-Food Quality (SENASICA) clarified that the restriction only applies to propagative material for tomatoes and peppers, including seeds, but excludes fresh produce. SENASICA maintains that fresh fruit is not a means of spreading the virus, as it is for consumption rather than reproduction. Tomatoes with virus symptoms pose no risk to human health and do not reduce the harvest's value.
Mexico's Tomato Production Forecasted to Reach 3.30 MMT in 2024 Amid Export Demand Growth
Mexico's tomato production is expected to increase to 3.30 million metric tons (mmt) in 2024, up 2% year-on-year (YoY) despite the drought that caused an 8% YoY drop in production in 2023. The Sinaloa region leads with 22% of total production, and the top five states contribute over half of Mexico's total output. Mexico has maintained its status as the world's top tomato exporter since surpassing the Netherlands in 2016, showing resilience and continued growth in export demand.
Russia
Belgorod Region Tomato Prices Dropped 39% MoM
According to departmental monitoring information from the Ministry of Agriculture of Russia, agricultural producers in the Belgorod region reduced selling prices for tomatoes from May 15 to June 12 by 39% month-on-month (MoM). Prices dropped from USD 1,057.01 per metric ton (RBL 91,960/mt) to USD 642.36 (RBL 55,885/mt)
Spain
Spanish Tomato Exports Surged 19% YoY in Apr-24
According to Spanish Federation of Associations of Producers and Exporters of Fruits, Vegetables (FEPEX) data, Spanish exports of fresh fruits and vegetables in Apr-24 rose 14% in volume and 10% YoY, reaching 1.1 mmt and USD 1903.44 million. Specifically, vegetable exports amounted to 573,707 mt, an 8% YoY increase, with a value of USD 871.09 million, up by 2%. Lettuce, tomatoes, and cabbage were the most exported vegetables. Tomato exports totaled 81,392 mt, marking a 19% YoY increase.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
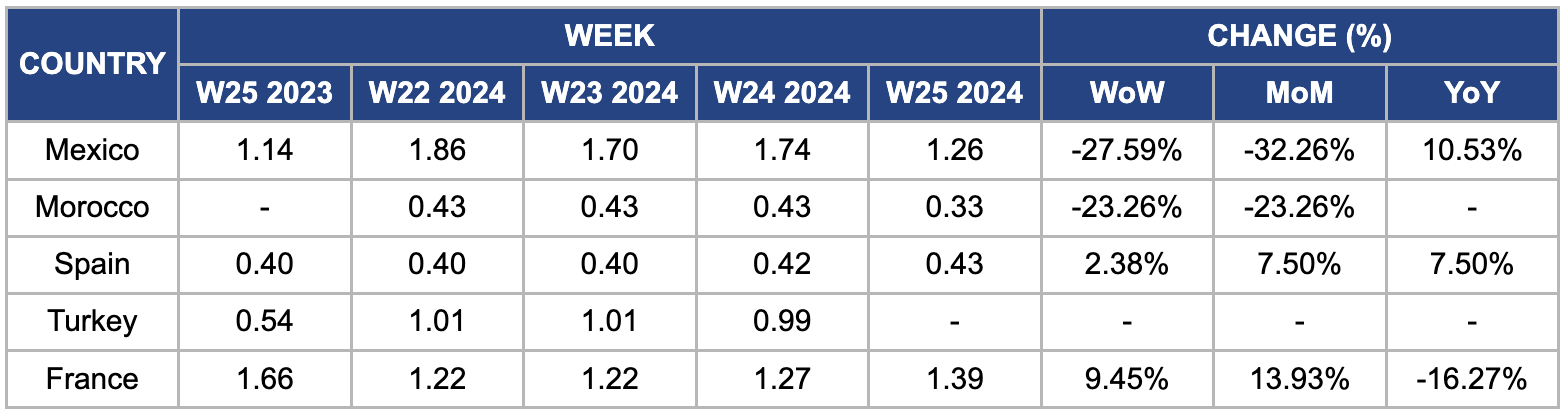
* Varieties: All tomato pricing is for round tomatoes.
Yearly Change in Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (W25 2023 to W25 2024)
* Varieties: All tomato pricing is for round tomatoes.
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
Mexico
Tomato prices in Mexico dropped significantly by 27.59% WoW to USD 1.26/kg, with a 32.26% MoM decline. In Northern Mexico, Roma tomatoes are in full production, continuing shipments until mid-July-24. The round tomato program, delayed by about a month, began in Jun-24. Initially, robust demand sustained higher prices, but increased production due to warmer weather has softened markets recently. The market is expected to stabilize in the coming weeks, possibly correcting after the current production surge.
Morocco
Moroccan tomato prices declined by 23.26% WoW and MoM to USD 0.33/kg, primarily due to lower demand and high supply. The Moroccan tomato season has concluded for most varieties, except for late varieties exported in summer. Challenges this season included an early heatwave that delayed the season by a month and an average price drop of 30%. There has been increased scrutiny against Moroccan tomatoes in France and Spain due to heightened hostility.
Spain
Tomato prices in Spain rose by 2.38% WoW and 7.50% MoM to USD 0.3/kg. The persistent drought across much of Spain is causing significant issues, affecting water supplies for domestic use and critical sectors like agriculture and livestock. This lack of rainfall has directly impacted activities such as tomato cultivation. For instance, the Las Nieves Cooperative Society in Seville has reduced its tomato planting by 50% YoY in 2024 due to the drought, opting for caution in uncertain water availability.
France
In France, tomato prices surged 9.45% WoW to USD 1.39/kg in W25. This increase follows a trend of rising prices since W22. As the production cycle concluded,the market faced insufficient supply compared to demand and crops were uprooted in preparation for the next season. According to a producer and exporter, this supply shortage is the primary factor driving the price increase in the tomato market.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Sustainable Agriculture Initiatives in Spain
Spain's tomato market is facing price increases attributed to persistent drought conditions, necessitating sustainable water management solutions and resilient farming practices. To optimize resource use and minimize environmental impact, stakeholders should prioritize investments in water-efficient irrigation systems, soil health management, and climate-smart technologies. Collaborative initiatives among industry players, research institutions, and government agencies can promote sustainable agriculture practices that enhance productivity and resilience in Spain's tomato production sector.
Sustainable Agriculture Initiatives in Spain
With the removal of restrictions on Mexican tomato exports to the US, effective June 17, 2024, Mexico's tomato industry is poised for accelerated growth in export volumes and market penetration. This regulatory change streamlines trade processes and enhances market efficiency, presenting a prime opportunity for stakeholders to expand their market footprint. To capitalize on this momentum, stakeholders should focus on enhancing logistical capabilities and ensuring compliance with quality standards. Collaborative efforts between producers, exporters, and regulatory bodies can optimize supply chain efficiency and sustain Mexico's position as a leading global tomato exporter.
Strategic Market Positioning in France
In France, the recent surge in tomato prices reflects supply shortages as the production cycle concludes, presenting an opportunity for producers to enhance strategic market positioning. Stakeholders should leverage this scarcity to explore innovative cultivation techniques, such as vertical farming and precision agriculture, to boost yield resilience and meet growing market demand. By diversifying distribution channels and investing in branding and marketing initiatives, producers can strengthen their market presence and capitalize on premium pricing opportunities in the tomato segment.
Sources: Specagro, Elperiodicodemexico, Financialfood, Eastfruit, Fresh Plaza, HortiDaily, Le360






