
1. Weekly News
Moldova
Moldovan Apple Exports to EU Surged by Over 100% YoY in 2024
Moldova significantly expanded its apple exports to the European Union (EU), reaching USD 12.4 million (MDL 228 million) from Jan-24 to Oct-24, more than double the exports during the same period last year. This growth reflects the efforts of Moldovan farmers and the impact of extended trade liberalization with the EU, which has provided broader market access. The share of Moldovan apple exports to EU countries has surged from 0.4% in 2021 to 18% in 2024, highlighting the rising quality and competitiveness of Moldova's apple production on the global stage.
Russia
Russia Expects Apple Production to Increase in 2025
Russia’s apple production is forecast to reach 1.987 million tons in 2025, an increase from 1.601 million tons in 2024, overcoming challenges from May frosts. The Ministry of Agriculture targets self-sufficiency in apple production by 2028, aiming for 2.4 million tons and expanding orchards by 30 thousand hectares (ha) by 2030. Plans prioritize high-yield intensive orchards in the Southern and North Caucasian Federal Districts, aligning with broader initiatives to enhance fruit and berry production.
Ukraine
Ukrainian Apple Exports Face Challenges From Reduced Quality
Due to unfavorable weather, Ukraine's apple exports are under pressure this 2024/25 season, leading to a one-third reduction in export-quality apples. While there is interest in exports, local demand remains strong, and increasing logistical complexities and costs, especially for exports to the Middle East and Asia, further hinder exports. Additionally, the size of apples, such as the Gala variety, has decreased compared to last year, reflecting the impact of adverse weather conditions.
Peru
Peru Tightens Import Regulations for Brazilian Apples
Peru's National Agrarian Health Service (SENASA) introduced stringent phytosanitary requirements for importing fresh apples from Brazil. Effective November 21, 2024, shipments must include a phytosanitary certificate from Brazil's Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock (MAPA), verifying compliance with Peru's export work plan and confirming the absence of specific pests. Additional measures include mandatory pre-shipment cold treatment, detailed documentation of the process, and sealed, contaminant-free, and properly labeled packaging. All imports will undergo rigorous inspections upon arrival in Peru to ensure adherence to these standards.
Poland
Challenging Apple Season in Poland Affects Quality and Prices
Polish apple growers faced a challenging 2024 season due to adverse weather, including spring frosts, summer heat, and drought, which impacted apple quality. Despite these difficulties, export demand remains strong in key markets such as Germany, the Czech Republic, and the United Kingdom (UK), with higher volumes shipped this year. The predominant apple size for export is medium (70 to 90 millimeters), ideal for international markets, though smaller sizes are less abundant. Apple prices are approximately 20% year-on-year (YoY) higher than last season, with steady demand and potential for further growth as the market stabilizes.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
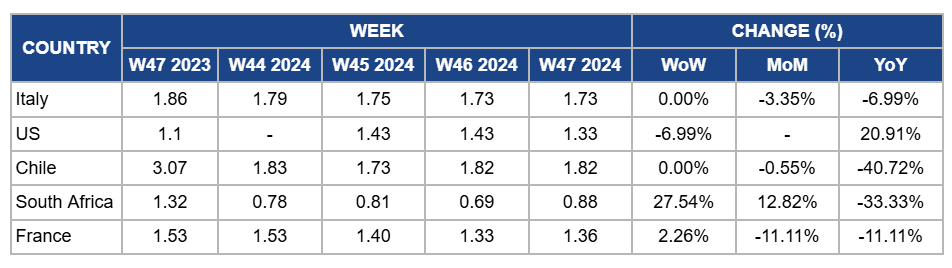
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W47 2023 to W47 2024)
Italy
In W47, apple prices in Italy remained unchanged at USD 1.73/kg, with a 3.35% MoM drop and a 6.99% YoY decrease. This continued decline despite the end of the peak harvest period in Oct-24 suggests lingering market pressures, including high stock levels from the earlier harvest and competition from other apple-producing regions. Demand has remained steady but not strong enough to absorb the abundant supply fully, which has kept prices under pressure. Prices are expected to stabilize or increase as the market works through excess inventory and seasonal demand patterns shift.
United States
Apple prices in the United States (US) dropped by 6.99% WoW to USD 1.33/kg in W47, with a 20.91% YoY decrease. Despite the end of the peak harvest period in mid-Nov-24, this unexpected price drop likely reflects lingering high stock levels from the abundant harvest, which are still being cleared in the market. Additionally, increased competition from alternative fruit options during the holiday season and logistical bottlenecks may have contributed to the downward pressure on prices. While demand remains steady, the YoY decline contrasts with the higher base prices observed last year due to a smaller crop. Prices are expected to stabilize in the coming weeks as inventory levels normalize and seasonal demand strengthens.
Chile
Chile's apple prices held steady at USD 1.82/kg in W47, showing only a 0.55% MoM drop. However, YoY pricing showed a significant 40.72% decrease. This stability is due to the market balancing after earlier inventory adjustments in the previous months, as processors and exporters cleared stocks to manage high supply levels. The continued high supply, primarily from new orchard plantings and favorable harvest yields in the current season, has kept prices under pressure. The substantial YoY decrease reflects a combination of oversupply in this season, with a larger production volume than last year, and weaker export demand, which has persisted since earlier in the season due to increased competition from other producing countries and logistical challenges in key export markets.
South Africa
South Africa's apple prices surged by 27.54% WoW to USD 0.88/kg in W47, with a 12.82% MoM increase due to stronger local demand, and a slight reduction in supply during the week. This seasonal boost in domestic consumption helped support prices. However, there is a decrease of 33.33% YoY due to the continued oversupply of red apple varieties, along with persistent export disruptions, including the suspension of shipments to Taiwan, which has impacted overall market conditions compared to last year.
France
In France, apple prices increased by 2.26% WoW in W47 due to a slight reduction in supply and some recovery in domestic demand following the seasonal oversupply that peaked during the harvest period in Oct-24. Despite the WoW increase, MoM and YoY prices both declined by 11.11% due to the continued impact of oversupply from the peak harvest season and ongoing competition from imported apples. The MoM and YoY declines reflect the sustained pressure on prices from high volumes still available in the market, particularly given the large harvest in the previous year.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Focus on Export-Grade Apple Supply
Polish apple growers should meet export demand by prioritizing medium-sized apples for primary international markets like Germany, the Czech Republic, and the UK. To capitalize on strong demand and higher prices, growers can optimize sorting and grading processes, ensure consistent quality, and leverage strategic partnerships with exporters to maintain market momentum despite weather-related challenges.
Optimize Supply Chain and Storage for Apple Price Stability
Italian apple producers should focus on improving supply chain efficiency and storage capabilities to manage the influx of apples during the harvest season. By investing in better storage facilities and enhancing distribution strategies, such as developing regional distribution hubs and utilizing advanced logistics software, producers can ensure a steady supply to the market while avoiding price pressure. Leveraging partnerships with retailers and wholesalers for dynamic routing and just-in-time delivery can also reduce waste and improve market responsiveness. Additionally, they should explore targeted marketing to emphasize premium varieties like Fuji and Annurca, helping to sustain demand and mitigate seasonal price fluctuations.
Sources: Tridge, Agromeat, AgroPeru, Eastfruit, Freshplaza, InformateAgrario, Interfax, Mxfruit





