Plant-based meat to substitute the real meat in the U.S.
What is plant-based meat?
Plant-based meat is a processed product based on proteins from plants, vegetables, or fruit, which mimics real meat’s taste and texture. Unlike the vegan hamburger patties and sausages made with ground chickpeas or tofus, Plant-based meat aims to mimic the real meat as much as possible, even the animal fat texture and reddish color of raw beef. This meatless meat’s key ingredients are coconut oils, soy leghemoglobin, seitan, and yeast extract.

Source: Epicurious
The number of people that consume meatless meat is at the highest level than ever before. Since 2014, when the plant-based food industry’s investment officially kicked off, the investment amount has almost tripled up every year, eventually hitting $10 billion by the 2018/19 season. Along with the rapid expansion of the industry, meatless meat consumption has been increasing significantly since then. It is projected to occupy 25% of the total meat market, including processed and fresh meat, by 2040, while the real meat market share is forecasted to fall from 90% to 40%. Some people argue that the fake meat industry started to substitute the real meat industry partially and will have more influence on dairy, eggs, and even the seafood industry. Meanwhile, there are still some unanswered questions on the sustainability of high-cost ingredients, the long-term effect on human health, and the possibility of coexistence with the real meat industry.
[Forecasted global market value of plant-based meat, 2019-2027]
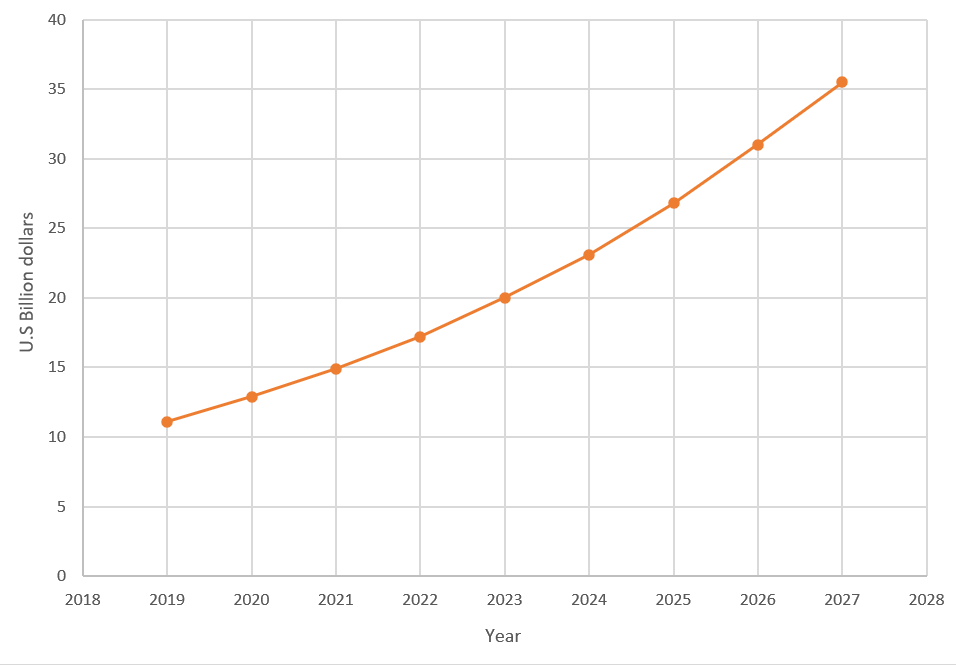
Source: Statista, Polaris Market Research
Plant-based meat craze continues
According to the United States Department of Agriculture(USDA), the carbon intensity of eating beef amount to 14.1g/kcal, higher than Dairy(4.5g/kcal), Fruit(4.6g/kcal), and vegetables(2.2g/kcal) due to CO2 and Methane gas emission accompanied with meat production. Also, water waste is considered a critical issue in the major meat-producing countries wherein, in the US, nearly 50% of the total water is used for meat production. While producing one pound of corn and wheat only requires 108 gallons and 138 gallons of water, raising pork requires 800 gallons of water, and beef, surprisingly, 1800 gallons. As more people become aware of meat consumption’s negative environmental effect, the world witnessed a global movement towards consuming less meat and rapid growth in the plant-based industry.
COVID-19 is also playing a big part in the booming meatless meat consumption. The supply chain for conventional meat production has been disrupted and confirmed cases of deteriorated production volume after the pandemic outbreak. Particularly, in the US, More than 35,000 workers in meat production plants have tested positive for Covid-19. Consequently, as consumers confront unprecedented meat shortages and high prices, they started to look beyond meat for alternative protein sources. On top of that, as consumers started to pursue healthier lifestyles than the pre-pandemic after the lockdown, more people became keen on plant-based meat, believing that plant-based meat can reduce the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases or type 2 diabetes caused by animal fat. When the US government took the lockdown measurement in March, the demand for plant-based meat surged 264% during nine weeks until May.
Can meatless meat substitute real meat?
Since the International Paris Climate Agreement in 2015, the global society has started acting together to achieve the common goal of protecting the planet from climate change and global warming. In its climate-change report, the United Nations recommended replacing the real meat component of meat-based meals with plant-based foods for environmental sustainability, since meat production is highly associated with CO2 and Methane emission, water waste, and even deforestation that harm biodiversity. In line with this trend, it seems crucial to reduce meat consumption, and finding an alternative source of protein, and plant-based meat can be the solution for long-term sustainability.
Above all, producing plant-based meat requires less greenhouse gas emission and water usage. According to Good Food Institute(GFI), producing plant-based meat can save up to 95% of water usage, 88% of greenhouse gas emissions, and 93% of land use, compared to making the same amount of beef burger. Also, Plant-based meat is considered healthier than meat since it does not have cholesterol which can cause a high prevalence of hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes. Although some people argue that plant-based meat is not always lighter than real meat due to its high composition of fat, sodium, and seasoning, it is much better to eat plant-based meat, according to Dr. Michael Eisen, the official advisor for Impossible Foods, one of the World’s largest plant-meat production companies.
However, the cost of plant-based meat production could be a hindrance to the development of the industry. In the retail store, the cost of plant-based meat patties(12 USD) is more than double of regular meat patties(5 USD), and the cost gap in the restaurant is even larger, making consumers consider plant-based meat as a pricy option. The main reason is that mass production of meat is available worldwide, and processing and packing facilities are better established than the plant-based meat industry, which is smaller in scale.
On top of that, it is hard to say that plant-based meat is always lighter than regular meat due to the high contents of sodium, carb, and oils. When looking into the calorie table of Plant-based meat burger and regular meat burger, there is not much difference between the two products. Here is an example below.
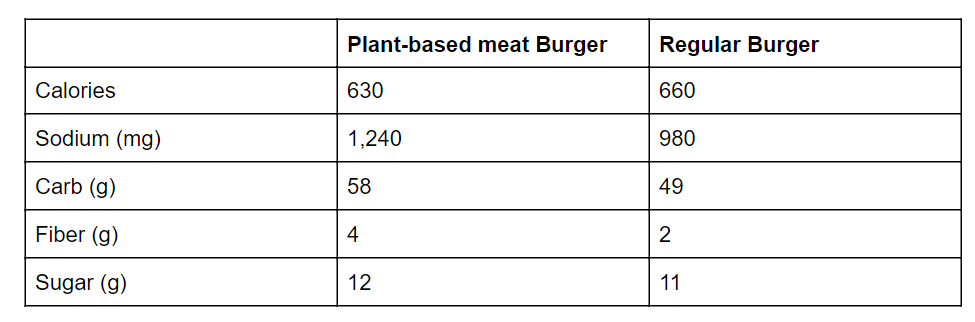
Although there are unclear aspects regarding plant-based meat, and its advantages and disadvantages, it is undeniable that plant-based meat is the key solution for the current situation that global society encounters. Since it’s in the initial stage, it’s difficult to affirm that plant-based meat production is economically feasible and sustainable in the long term. However, if more environmental awareness boosts its demand which then promotes well-established infrastructures in the supply chain, plant-based meat will soon play a key role.
Sources:
- Beyond Meat
- MarketandMarkets, "Future Business Opportunities in the Plant-based Meat Market"
- The New York Times, "Fake Meat vs. Real Meat"
- The New York Times, "Plant-Based ‘Meats’ Catch On in the Pandemic"
- The New York Times, "How Do They Make Plant-Based Meat Behave Like Beef?"
- The Spoon, "GFI: Investment in Plant-Based Meat, Eggs, and Dairy Hits $16 Billion, No Sign of Slowing"
- Good Food Institute(GFI), "Just how sustainable is plant-based meat?"
- Green matters, "What Is Heme? Impossible Foods’ Magic Ingredient Has Caused Some Controversy"
- Oxford Business Group, "Plant-based meat: a Covid-19 boom industry?"
- CBI Insights, "Our Meatless Future: How The $2.7T Global Meat Market Gets Disrupted"
- Nature, "Eat less meat: UN climate-change report calls for change to human diet"
- NBC, "Is fake meat better for you, or the environment?"
- Water Footprint Calculator, "Beef: The “King” of the Big Water Footprints"




