
1. Weekly News
Global
Global Avocado Production Threatened by Climate Change
Avocado production is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change due to its high water requirements and sensitivity to temperature fluctuations. The report by the United Kingdom (UK) charity Christian Aid highlights this vulnerability, suggesting that climate change could lead to a significant reduction in avocado-growing areas by 14% to 41% by 2050. This prediction is contingent upon global efforts to reduce emissions, emphasizing the urgency of addressing climate change to safeguard avocado production and food security.
This poses particular concerns for Mexico, as it faces prospects of a hotter, drier climate, potentially affecting local avocado communities and job markets. Additionally, the report underscores the environmental strain of avocado cultivation, notably its substantial water requirements. Other avocado-producing nations like Spain, Peru, Chile, and Burundi also face challenges such as heat waves and droughts. To address these issues, the report recommends measures such as increasing climate financing, reducing emissions, and transitioning to renewable energy sources.
Australia
Premium Avocados from Western Australia Reached India
Western Australia (WA) has exported over 320 metric tons (mt) of avocados, valued at more than USD 1.6 million, to India, with the majority originating from Delroy Orchards in the Southern Forests region. This export surge follows the removal of a 30% tariff on Australian Hass avocados as part of the Australia-India Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement. There is a growing demand for Western Australian avocados in India, the Middle East, and Asia. The avocado sector stands out as the most lucrative fruit industry in Western Australia, with projections reaching an unprecedented production milestone of 65 thousand mt in 2023/24.The WA Government is organizing a promotional event in India to highlight the state's avocados and to promote trade.
Brazil
Avocado Production in Brazil Surges by 50%
Brazil's avocado production has seen a remarkable 50% surge since the last survey, making it the sixth largest producer globally. This growth is driven by both international demand and increasing domestic consumption. Despite facing challenges such as climate fluctuations, the sector remains attractive, with efforts to expand cultivation areas and explore by-product opportunities. While the Southeast regions, particularly São Paulo and Minas Gerais, dominate production, other areas like Ceará also show promise, indicating potential for expanded export opportunities.
Peru
Peruvian Avocado Exports Surpassed USD 217 Million in Q1-24
In Q1-24, Peru held the position as the world's second-largest exporter of avocados, following Mexico. Peru exported a total of 95.5 thousand tons of avocados, generating a value of over USD 217 million. The majority of the shipments were for the Hass variety, with the remaining 13% for other varieties. Among the export regions, Lima led with 51 thousand tons, followed by Ica and Lambayeque. Notably, the exports in Q1-24 constituted only 16% of the total 595.6 thousand tons sold in 2023. The Association of Hass Avocado Producers and Exporters of Peru (ProHass) anticipates a decline in exports in 2024, forecasting a volume of 468 thousand tons.
Global Surge in Avocado Prices as Peruvian Producers Face Shortage
Due to a reduction in avocado size, Peruvian producers have experienced a 40% decrease in yields compared to the previous season. Consequently, this decline has resulted in consistently high prices in major markets such as the United States (US), Europe, and Asia, particularly for larger-sized fruit, aligning with consumer preferences.
Peruvian Avocado Industry Faces Economic Challenges Amidst Fruit Size Reduction
The significant reduction in the size of Peruvian avocados is resulting in economic losses, particularly in the Northern region, where smaller calibers (26, 28, and 30) constitute 60% to 70% of the harvest and fetch only USD 0.40 per kilogram (kg) from collectors. Avocado producers in the South are facing similar challenges but are choosing to harvest only the larger-sized avocados, leaving the smaller ones on trees. Their strategy is to wait until July or August, anticipating improved prices and increased fruit weight.
Vietnam
Vietnam's Avocado Farmers Amidst Price Drops and Crop Failures
Avocado farmers in Vietnam's Đăk Nông, Đắk Lắk , and Lâm Đồng provinces are facing crop failures, decreased fruit quality, and a drastic decline in prices, plummeting from USD 7.86/kg (VND 200,000/kg) to just over USD 0.39/kg (VND 10,000/kg). Consequently, there has been a notable decrease in avocado cultivation areas, from nearly 4.5 thousand hectares (ha) in 2020 to about 3.2 thousand ha in 2023. With the profitability of avocados dwindling, farmers are contemplating transitioning to more profitable crops like durian and coffee. However, experts in the agricultural sector caution against hasty decisions due to the substantial costs and time involved in establishing new crops. The instability in avocado farming is prompting many farmers to reconsider maintaining their avocado gardens.
2. Weekly Pricing
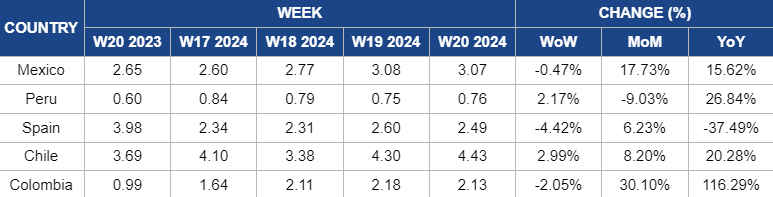
Weekly Avocado Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Avocado Pricing Important Exporters (W20 2023 to W20 2024)
Mexico
The slight 0.47% week-over-week (WoW) decrease in the price of Mexican avocados to USD 3.07/kg in W20, may be attributed to seasonal fluctuations. However, it's important to note that the overall trend for avocado prices in Mexico is upward, both monthly and yearly. The consistent increase in avocado prices is largely influenced by factors such as the threat of climate change in Mexico. Climate change poses significant risks to avocado production by disrupting weather patterns and causing extreme events like droughts, which can reduce avocado yields. With lower supply due to these challenges, the demand for avocados remains strong, leading to continuous price increases over time.
Peru
The slight increase in Peru's avocado price by 2.17% WoW, reaching USD 0.76/kg, reflects the ongoing market dynamics amid challenges in the agricultural sector. Factors such as climate change and overproduction continue to influence avocado prices, contributing to potential fluctuations in the market. Climate change, evident in hotter temperatures, erratic heavy rainfall, and soil erosion, significantly impacts farmers' productivity, damaging crops, reducing yields, and lowering avocado quality. These environmental shifts exacerbate the challenges posed by overproduction, leading to price fluctuations.
Spain
In Spain, avocado prices fluctuated in W20, decreasing by 4.42% WoW after a recent increase in W19, with the price reaching USD 2.49/kg in W20 compared to the previous price of USD 0.18/kg. Despite this decrease, there was a 6.23% increase in prices regarding MoM change. This price fluctuation is due to short-term market adjustments or variations in supply. However, despite the decline in W20, the overall trend is still upward due to severe heat waves and extreme weather conditions caused by climate change, which have negatively impacted crop yields in major avocado-producing regions such as Mexico and Spain.
Chile
The price of Chilean avocados rose by 2.99% WoW, reaching USD 4.43/kg in W20, compared to USD 4.30/kg in W19. Additionally, there is an upward trend in both monthly and yearly avocado pricing. This increase in Chilean avocado prices is attributed to the impact of drought on avocado cultivation. Avocado trees require ample water to thrive, but drought conditions are severely restricting water availability for farming in Chile. Consequently, the avocado crop area is diminishing, reducing avocado production. With a limited supply of avocados in the market, demand remains high, leading to increased prices due to the scarcity of the fruit.
Colombia
The avocado price decline observed in W20, dropping by 2.05% WoW to USD 2.13/kg from USD 2.18/kg in W19, can be attributed to the current traviesa season in Colombia. Typically running from April through August and peaking between May and June, this season is characterized by a higher volume of avocados entering the market. With increased supply during this peak period, prices tend to decrease due to the abundance of avocados available. Additionally, the projected increase in shipments for 2024, reaching a total volume of 50 million pounds (lbs) for the entire year, suggests a continued surplus of avocados, further contributing to the decline in prices as supply outpaces demand.
4. Actionable Recommendations
Supporting Vietnamese Avocado Farmers Amidst Economic Challenges
To support avocado farmers in Vietnam facing challenges such as price drops and crop failures, stakeholders should focus on providing financial and technical assistance. This includes offering subsidies for farmers to adopt sustainable farming practices and providing access to affordable credit to help them weather difficult times. Governments can also support farmers by investing in research and development of climate-resilient avocado varieties and promoting market linkages to ensure fair prices for their produce. Collaboration between government, industry, and farmers is crucial to ensure the long-term viability of avocado farming in Vietnam.
Sustainable Practices to Support Continued Growth in Brazilian Avocado Production
To sustain the growth of avocado production in Brazil, stakeholders should prioritize sustainable farming practices. This includes promoting agroecological approaches that enhance soil health and reduce reliance on chemical inputs. Investing in research and development of new avocado varieties that are more resilient to climate change can also help in maintaining production levels. Additionally, supporting small-scale farmers with access to resources, training, and market linkages can contribute to the overall growth and sustainability of the avocado industry in Brazil.
Enhancing Post-Harvest Handling for Sustainable Peruvian Avocado Exports
To maintain Peru's position as a leading exporter of avocados, stakeholders should focus on improving post-harvest handling and processing facilities. This includes investing in infrastructure and technologies that reduce post-harvest losses and improve the quality of exported avocados. Farmers should also be encouraged to adopt sustainable farming practices that enhance productivity while minimizing environmental impact. Furthermore, diversifying export markets and value-added products can help in stabilizing avocado exports and increasing revenue for Peruvian farmers.
Addressing Global Avocado Price Surges Through Efficient Supply Chains
To address the global surge in avocado prices, stakeholders should focus on improving supply chain efficiency and transparency. This includes investing in cold chain infrastructure and logistics to reduce wastage and ensure the timely delivery of avocados to markets. Governments can also play a role by implementing policies that promote fair trade practices and prevent price manipulation. Additionally, consumers can contribute by being more mindful of food waste and supporting sustainable avocado production practices.



