
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Santa Catarina's Apple Market Forecasts a Promising Harvest for 2024/25
The apple market in Santa Catarina, Brazil, is currently experiencing low supply at sorting plants, but there is a positive outlook for the 2024/25 harvest. According to the October Agricultural Bulletin from the Santa Catarina Agricultural Research and Rural Extension Company (EPAGRI) and the Santa Catarina Agricultural Observatory, wholesale apple prices increased by 4.4% month-on-month (MoM) in Sep-24, with a year-on-year (YoY) rise of 30.8%. Prices for the Gala variety rose by 1.2% MoM, reflecting a 34.9% increase YoY, while Fuji apple prices grew by 8.1% MoM, resulting in a 26.7% YoY growth. Notably, average apple prices in Brazil rose by 29.4% in the third quarter compared to 2023, despite ongoing low supply, especially in Fraiburgo, where less resilient fruit is being sold. As the final supply of the current harvest is sold, a price decrease is anticipated in Oct-24 due to an influx of imported fruit and the quality of the domestic harvest. In major producing regions like Fraiburgo and São Joaquim, the Gala and Fuji varieties are currently in the flowering phase, with a projected 55.5% increase in production for the upcoming harvest. Fuji apple yields are expected to grow by 59.6%, comprising 53.9% of total production, while Gala apples are anticipated to rise by 54.0%.
Europe
EU Apple Production Projected to Decline Significantly in 2024/25 Season
Apple production in the European Union (EU) for the 2024/25 marketing year (MY) is projected to decline to 10.1 million metric tons (mmt), marking a 10% YoY decrease and the lowest harvest since the 2017/18 season. This reduction is due to adverse weather conditions impacting primary apple-producing countries, including Poland and Germany, where harvests are expected to decrease by 20% and 16%, respectively. Similar forecasts apply to Italy, France, Romania, and the Czech Republic. The processing industry will be particularly affected, with only about 3.5 mmt allocated for processing, a decline of over 20% compared to the last five years. In contrast, production for fresh consumption is expected to experience a smaller drop of about 3%, yielding approximately 6.6 mmt, which may help stabilize consumption at around 13.6 kilograms (kg) per capita. Fresh apple exports are expected to drop by more than 10%, while imports are projected to rise by 14%, hitting an eight-year high of approximately 300 thousand metric tons (mt). Additionally, the weak apple harvest will negatively affect the trade of processed apple products, with exports anticipated to decline by over 11%.
Poland
Weather Challenges Lead to Lower Polish Apple Harvest in 2024
The 2024 Polish apple and pear harvest faced significant challenges due to adverse weather conditions, resulting in an estimated production decline of 17% YoY. The Central Statistical Office predicts that the apple harvest in 2024 will total less than 3.2 mmt, down from nearly 3.9 mmt in 2023, while the pear harvest is expected to fall to 74.1 thousand mt, a 6% YoY decrease.
Unusual weather patterns characterized the growing season, with unseasonably high temperatures in Feb-24 and Mar-24 accelerating plant growth and flowering but leading to a poor fruit set due to a lack of pollinator activity. Severe frosts in late Apr-24 and early May-24 damaged flower and fruit buds, and subsequent hail and strong winds further devastated the crops. While late May-24 to Jul-24 rainfall helped plant conditions, it also increased fungal disease pressure and resulted in uneven quality. The summer brought favorable and harsh conditions, including high daytime temperatures that caused fruit burns and poor coloration. Consequently, fruit growers believe the harvest may be even lower than official estimates, with much of the yield unsuitable for long-term storage.
Ukraine
Ukrainian Apple Prices Rise in Lviv as Demand Increases and Supplies Decline
In Ukraine, wholesale prices for popular apple varieties at the Shuvar market in Lviv have increased. However, some varieties' prices remain lower than in 2023 due to improved yields and stable supplies. Experts expect prices to rise in Dec-24 and Jan-24, driven by growing demand and heightened storage costs. Favorable weather conditions in central and western regions have increased this year's apple yield. Leading varieties like Gala, Fuji, and Golden Delicious are averaging USD 0.51/kg (UAH 21/kg), USD 0.54/kg (UAH 22.5/kg), and USD 0.57/kg (UAH 23.5/kg), respectively. This represents an increase compared to last year's prices of USD 0.35/kg (UAH 14.5/kg), USD 0.43/kg (UAH 18/kg), and USD 0.40/kg (UAH 16.5/kg). While organic apples are becoming more popular, they remain pricier. Key supplying regions include Transcarpathia, Vinnytsia, Khmelnytsky, and Chernivtsi, with southern areas expanding their apple cultivation. Experts warn that apple prices may rise significantly as supplies dwindle closer to winter.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
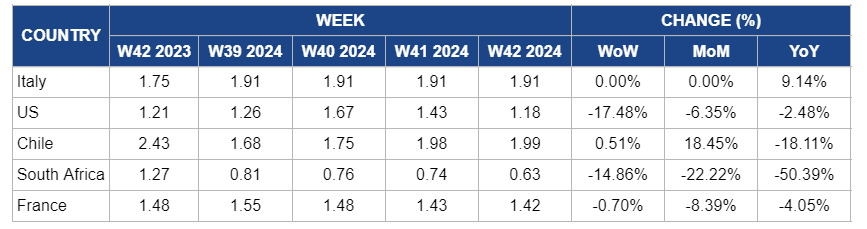
* Varieties: US and Italy (Gala), Chile, South Africa, and France (Granny Smith)
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W42 2023 to W42 2024)
* Varieties: US and Italy (Gala), Chile, South Africa, and France (Granny Smith)
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
Italy
Apple prices in Italy remained at USD 1.91/kg in W42 since W38, with a 9.14% YoY increase. This is due to continued steady domestic and international demand, particularly for premium varieties like Gala and Candine, which are well-regarded for their flavor and sustainability. Favorable weather conditions have sustained good fruit quality, and the growing interest in organic apples, which saw production increase, has further supported market stability. The rising export volumes, especially to key markets such as Germany and France, have strengthened Italy’s apple sector, contributing to the YoY price growth.
United States
In the United States (US), apple prices in W42 fell sharply by 17.48% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 1.18/kg, marking a 6.35% month-on-month (MoM) decline and a 2.48% YoY decrease. The price decline is due to increased supply as the harvest season progresses, particularly in states like Michigan, where favorable weather conditions, including cool nights and warm days, have led to an abundant apple crop. Additionally, Michigan's unique climate, moderated by the Great Lakes and fertile glacial soils, has contributed to higher production volumes. This oversupply and a temporary softening in domestic demand have led to downward pressure on prices.
Chile
In W42, apple prices in Chile rose slightly by 0.51% WoW, reaching USD 1.99/kg, marking a significant 18.45% increase MoM. The price increase is due to strong domestic demand, driven by favorable weather supporting optimal harvesting conditions and a steady local consumption rate, helping to maintain upward momentum in the market. However, apple prices declined by 18.11% YoY due to the substantial oversupply compared to the previous year, when lower yields and reduced export opportunities led to significantly higher prices. The current oversupply and moderate export demand have put downward pressure on YoY prices.
South Africa
South Africa's apple prices dropped by 14.86% WoW to USD 0.63/kg in W42. There is also a 22.22% MoM and 50.39% YoY decline due to oversupply in the market from increased production of low-chill and hot-climate apple varieties and reduced export demand. The earlier ripening of Afri Glo and Afri Star varieties, suited to warmer climates, contributed to a larger volume of apples being available earlier in the season, putting downward pressure on prices. Additionally, weaker international demand, especially from key markets, exacerbated the price drop as exporters faced increased competition from other producing countries.
France
In W42, apple prices in France saw a modest decline of 0.70% WoW, reaching USD 1.42/kg, with an 8.39% MoM and a 4.05% YoY decrease. This is due to the continued impact of oversupply in the market from accelerated harvesting, as unfavorable weather conditions led to blemished and lower-quality fruit. The persistent rain affected the quality and limited consumer demand, as buyers showed less interest in purchasing blemished apples. Despite stable production forecasts and promotional efforts such as the "Europe Never Too Green" campaign, weather-related challenges and weaker domestic consumption drove prices downward.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhance Quality Control and Diversify Markets for Brazil's Apple Producers
Producers should implement stringent quality control measures at sorting facilities to tackle low supplies and fluctuating prices in Brazil's apple market and ensure that only the best-quality fruit is marketed. Investing in advanced sorting technology and training staff on quality standards will be crucial. Additionally, producers should explore diversification strategies by targeting export markets with strong demand for quality apples or developing value-added products such as apple juice or cider. This approach will help producers better position themselves for future harvests and mitigate the impacts of price volatility across Brazil's diverse apple-producing regions.
Strengthen Quality Control and Diversification in Polish Apple Production
Polish apple producers should enhance their quality control measures to manage the impact of adverse weather on this year's harvest. Protective measures like netting to shield orchards from hail and strong winds can reduce crop damage. Additionally, diversifying crop varieties to include more resilient types can help mitigate the effects of fluctuating weather patterns. Investing in improved storage facilities will also allow for better handling of uneven-quality fruit, enabling producers to maximize market value. By focusing on these strategies, growers can stabilize production and maintain profitability despite challenging conditions.
Sources: Tridge, Agri, AgroFakt, Eastfruit, Fruitnet, Goodfruit, MXfruit, Portal Do Agronegocio, Stat.gov.pl, Sad24





