
In W16 in the banana landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Rising costs and production challenges are straining banana industries in Peru and the Philippines, where growers face high logistics and input expenses, water shortages, and disease outbreaks, leading to lower yields and declining competitiveness in global markets.
- Export diversification and compliance improvements are becoming more important, as seen in Ecuador’s push for international compliance standards and Colombia’s focus on sustainable practices to secure premium access to the EU market.
- Geopolitical and trade policy shifts are creating uncertainty in major banana markets, with the US introducing a 10% tariff affecting key exporters such as Colombia, Peru, and Ecuador, potentially increasing prices and disrupting established trade flows.
- Recovery and investment efforts are helping Cameroon rebuild its banana industry post-crisis, supported by government aid, debt restructuring, and reopening of plantations, signaling long-term potential despite earlier disruptions.
1. Weekly News
Ecuador
Ecuador Enhances Compliance Standards in Banana Export Industry
Ecuador is strengthening its banana export industry through new partnerships between the Association of Banana Exporters of Ecuador (AEBE) and two international firms, Coface and Verificante. This collaboration introduces a structured system to assess the compliance of current and future exporters, focusing on key areas such as financial health, operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, product quality, and commercial performance. Coface, known for credit insurance and risk analysis, and Verificante, an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based identity verification platform, will help ensure Ecuador’s banana exports meet global trade standards. The initiative aims to improve transparency, build international trust, and strengthen oversight in one of Ecuador’s most important export industries.
Cameroon
Cameroon’s Banana Exports Reach Seven-Year High Amid Recovery
Cameroon exported 10.4 thousand tons of bananas in the first quarter of 2025 (Q1-25) through the Cameroon Development Corporation (CDC), marking its strongest quarterly performance since 2018. The company halted banana exports in late 2018 due to the Anglophone crisis, a prolonged conflict that began in 2016 between the Cameroonian government and separatist groups in the English-speaking regions of the country. The crisis led to widespread violence, protests, and the disruption of daily life, including the closure of several plantations and the suspension of economic activities in these regions. The conflict severely affected the CDC’s operations, forcing the company to cease banana exports. Since resuming in mid-2020, the CDC has steadily rebuilt its banana exports, supported by improved security, government assistance, and the reopening of previously abandoned farms. A debt restructuring deal covering over USD 98 million in liabilities also supported the company’s recovery, helping stabilize operations and secure worker payments. This progress marks a key milestone in reviving Cameroon’s banana industry.
Colombia
Colombia Targets EU Market for Sustainable Banana Exports
Colombia, the world’s fifth-largest banana producer, is working to strengthen its position in the European Union (EU), which already receives around 70% of its banana exports. In 2024, Colombia exported over USD 1 billion worth of bananas, equal to 109 million 20-kilogram (kg) boxes. The European market offers premium prices due to Colombia’s adherence to sustainability practices and living wage standards, making it financially attractive for growers. While the United States (US) and the United Kingdom (UK) each account for about 15% of Colombia’s banana exports, industry leaders have downplayed concerns over possible US tariffs, although analysts warn that such measures could still affect demand and overall sales.
Peru
Peruvian Banana Exports Decline Due to Water Shortages and Rising Costs
Peru’s banana exports fell sharply in Q1-25, totaling 39.6 thousand metric tons (mt) worth USD 34 million, a 12% year-on-year (YoY) drop in volume and a 9% YoY decline in value. While the average price per kg edged up to USD 0.87/kg, it wasn’t enough to offset the impact of severe water shortages in Piura that reduced banana cultivation in the Chira Valley. The industry also faces rising production and logistics costs, a fragmented network of small producers in northern Peru, and stronger global competition. Adding to the uncertainty is a proposed 10% US import tariff, suspended for 90 days, threatening trade with the US, Peru’s second-largest banana market after the EU. In 2024, the US imported 8.1 thousand mt of Peruvian bananas valued at nearly USD 8 million. Banana exports from Peru are expected to decline by 2% to 7% over the remainder of 2025.
Philippines
Philippine Banana Sector Faces Steep Decline Due to Rising Costs and Disease
The Philippines' banana industry, especially in the Davao Region, is facing a significant decline in Cavendish banana production. Production is expected to fall by 10 to 15% due to high logistics costs and the ongoing spread of Fusarium wilt. Small-scale growers in areas like Davao del Norte and Davao del Sur are particularly affected, leaving many farms idle. With production costs approaching USD 18 thousand per hectare (ha) and profit margins shrinking, limited access to credit has made it even harder for farmers to stay afloat. Despite strong demand from the US, Philippine exporters struggle to compete with countries like Ecuador, held back by inadequate infrastructure and the banana’s short 40-day shelf life. Rising input costs, herbicide, and fertilizer prices have more than doubled in the last five years, adding to the strain. As the country continues to lose market share in Japan and China, industry stakeholders are calling on the government to step in with support measures. These include improved credit access, disease-resistant crop research, and a comprehensive revitalization roadmap to guide long-term recovery.
United States
US Banana Prices Expected to Rise Following New Tariff Policy
The US is facing a potential USD 250 million annual increase in banana costs following the introduction of a 10% reciprocal tariff by the Trump Administration on April 5, 2025. The tariff aims to address trade imbalances and support domestic production. However, it impacts bananas, a crop that cannot be commercially grown in the US due to unsuitable climate conditions. In 2024, the US imported over USD 2.5 billion worth of fresh bananas, primarily from Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Guatemala, and Honduras, supplying more than 90% of the market. However, US trade data shows a USD 4.7 billion trade surplus with these countries, raising questions about the tariff’s effectiveness in achieving its intended goals. With no boost to local production expected, American consumers will face higher prices for organic and conventional bananas, while the overall trade balance remains largely unaffected.
2. Weekly Pricing
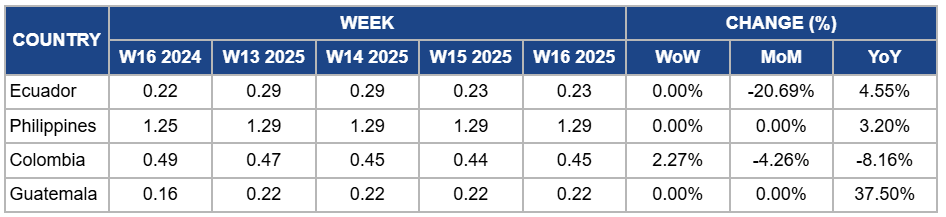
Weekly Banana Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Banana Pricing Important Exporters (W16 2024 to W16 2025)
Ecuador
Ecuador's banana prices remained steady at USD 0.23/kg in W16, with no week-on-week (WoW) change due to stable demand from key export markets and a consistent supply from major producing regions. However, banana prices dropped by 20.69% month-on-month (MoM) due to an oversupply in the market following the peak harvest season months of December to March, and logistical delays that impacted timely shipments. The seasonal glut and some fluctuations in export demand, particularly from Europe, contributed to the decline, despite ongoing efforts by the AEBE to enhance export efficiency through new international partnerships. On a YoY basis, banana prices have increased by 4.55%, reflecting stronger market conditions compared to the same period last year.
Philippines
In the Philippines, banana prices remained steady at USD 1.29/kg with no WoW and MoM change due to consistent local supply despite challenges in production. However, prices slightly increased by 3.20% YoY due to reduced availability caused by the expected decline in Cavendish banana production, primarily impacted by high logistics costs and the spread of Fusarium wilt. Despite the continued demand from the US, the Philippines’ struggle to compete with lower-cost producers like Ecuador, combined with rising input costs, has led to slight price increases as the industry deals with shrinking profit margins and limited access to credit for small-scale farmers.
Colombia
Banana prices in Colombia increased by 2.27% WoW to USD 0.45/kg in W16 due to strong demand from the EU countries, driven by Colombia’s adherence to sustainability practices and premium pricing. However, prices dropped slightly by 4.26% MoM and 8.16% YoY due to heightened competition from other banana-exporting countries, such as Ecuador, and shifting market dynamics, with the peak harvest season winding down, leading to a natural seasonal decrease in supply.
Guatemala
In W16, Guatemala banana prices remained stable at USD 0.22/kg, with no WoW or MoM change. This stability is due to ongoing supply challenges that have kept market prices high and steady. Producers continue to face the aftereffects of heavy rainfall and flooding earlier in the year, which disrupted harvest cycles and reduced overall yields. However, there is a 37.50% YoY price surge due to lower local production, continued logistical challenges, and strong import demand from primary markets in North America and Europe. Buyers in these regions seek to secure supply amidst tightening global availability, contributing to the significant price increase compared to the same period last year.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Adopt Disease-Resistant Varieties and Improve On-Farm Practices
Banana growers and exporters in the Davao Region should prioritize the adoption of Fusarium wilt-resistant Cavendish varieties and improve farm sanitation practices to control disease spread. Although Fusarium wilt, particularly caused by Fusarium oxysporum Tropical Race 4 (TR4), is difficult to eradicate once present, these measures can help manage the disease. For example, growers can rotate crops in heavily infected fields, sterilize tools between uses to prevent cross-contamination, and create physical barriers to limit soil movement, reducing the risk of spreading the pathogen. Exporters should support small-scale producers by facilitating access to quality planting material, such as Fusarium-resistant varieties, and offering technical training on disease management practices. This dual approach can help sustain production, reduce losses, and strengthen the Philippines’ competitive position in key export markets like Japan and China.
Enhance Supply Chain Efficiency and Strengthen US Market Position
Peruvian banana exporters should focus on improving supply chain efficiency by consolidating production from smaller farms in the Chira Valley to reduce logistical costs and better meet export demand. By implementing a centralized distribution model, exporters can streamline shipments and mitigate the impact of the proposed US tariff. Additionally, exporters should prioritize strengthening relationships with US retailers through value-added products or promotions to differentiate themselves from global competitors. This will help secure market share and offset the adverse effects of logistical challenges and price fluctuations.
Sources: Tridge, AEBE, Bluebookservices, Business in Cameroon, Freshfruit, Freshplaza, Fruitnet, Reuters, SunStar






