
1. Weekly News
Argentina
Banana Production in Argentina's Formosa Province Declines Amidst Crisis
Banana production in Argentina's Formosa province, once the country's primary hub, has sharply declined from 12 thousand hectares (ha) in the 1960s to 1980s to just 500 ha today. Small-scale farmers are facing a "terminal crisis" due to a lack of support from both provincial and national governments. This neglect has led many to abandon or destroy their plantations, worsening poverty and rural disintegration. While Argentina's banana production in the Northeastern Argentine (NEA) region once met 10 to 15% of local demand, it continues to decline, with more significant banana ventures emerging in the northwest. Producers call for urgent action to revive the industry and ensure its sustainability.
Ecuador
Ecuador's Banana Industry Shows Resilience in Overcoming Challenges
Centered on the Cavendish variety, Ecuador's banana industry remains a key pillar of its agricultural economy. It supplies markets in the United States (US), Europe, the Middle East, and the Southern Cone. Despite high operational costs and threats from Fusarium Tropical Race 4 (TR4) and the Moko bacterium, growers have implemented strict biosecurity measures to ensure quality. Exporters ship 10 to 20 thousand boxes weekly, with plans to double volumes. While climate change and market fluctuations pose challenges, investments in sustainability and diversification into products like pineapple and pitaya offer promising growth opportunities, solidifying Ecuador's global reputation for quality produce.
Philippines
Strong Investments Boost Davao Region’s Banana Exports
Supported by the Department of Trade and Industry - Region 11 (DTI), the Davao Region in the Philippines experienced strong growth in its banana industry in 2024, driven by USD 2.7 million in Cavendish banana exports and USD 1.53 million in banana chip exports. These investments created 1 thousand jobs and achieved USD 826.2 thousand in export sales alongside USD 738 thousand in domestic sales. In 2023, bananas accounted for USD 1.19 billion, or 48.18% of the region’s total exports. While more extensive plantations use advanced technologies to address Fusarium wilt, smaller farms face challenges combating the disease.
South Africa
Post-Election Unrest Disrupts Mozambique's Banana Exports to South Africa
Mozambique's banana exports to South Africa have been severely disrupted due to border closures following post-election violence and resulting strikes and protests. These disruptions have caused banana prices in South Africa to triple, as Mozambique typically supplies two-thirds of the country's bananas. With consignments turned back, farms have struggled to manage overflowing storage capacities. Although the border has reopened for traffic, cargo, including bananas, remains stalled, leading to significant economic losses estimated at USD 547.1 million (ZAR 10 million) daily. This situation highlights the importance of stable trade routes for the agricultural markets of both nations.
Vietnam
Vietnam's Expanding Banana Industry Faces Risks from Market Dependence
Vietnam's banana cultivation has surged to around 154.2 thousand ha, driven by strong exports to China in recent years. Dong Nai province leads production, accounting for over 70% of the Southeast region's acreage with 16.7 thousand ha. In 2024, Dong Nai's banana production soared to nearly 343.5 thousand tons, a 67% year-on-year (YoY) increase. While China remains the dominant export market, smaller shipments go to Korea, Japan, and Europe. However, experts warn that heavy reliance on China exposes the industry to risks, as past market fluctuations have caused price crashes and unsold harvests. To stabilize, experts recommend diversifying export markets and strengthening connections between growers and exporters.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Banana Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
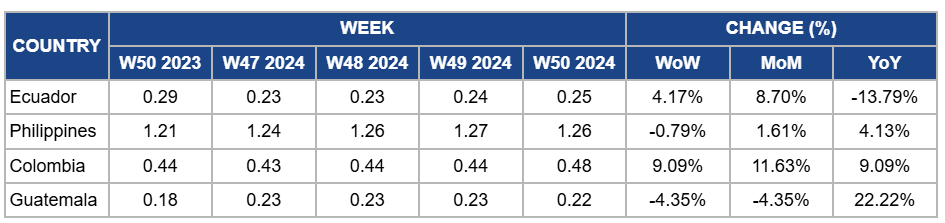
Yearly Change in Banana Pricing Important Exporters (W50 2023 to W50 2024)
Ecuador
Ecuador's banana prices increased by 4.17% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 0.25 per kilogram (kg) in W50, reflecting an 8.70% month-on-month (MoM) increase. The price increase is due to improved export flow as logistical issues, such as port congestion, and steady demand from primary markets like the US, the Middle East, and Russia began to ease. However, there is a 13.79% YoY decrease due to ongoing competitive pressure from other banana-exporting countries, resulting in lower overall prices than last year. Despite these challenges, the anticipated Ecuador-China Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in 2025 can potentially boost long-term export prospects.
Philippines
In W50, banana prices declined slightly by 0.79% WoW to USD 1.26/kg due to a slight reduction in export demand from key markets and increasing availability as supply stabilized following previous weather disruptions. However, there is a rise of 1.61% MoM and a 4.13% YoY increase due to limited production efficiency resulting from challenges faced by smaller farms in combating diseases like Fusarium wilt. These challenges have created a tighter supply despite stable demand, particularly from key export markets. Furthermore, more extensive plantations using advanced technologies have maintained higher production levels, supporting the upward price trend compared to the previous month and the same period last year.
Colombia
Banana prices in Colombia increased by 9.09% WoW to USD 0.48/kg in W50, with an 11.63% MoM increase and a 9.09% YoY rise due to sustained export demand from major markets like the US and Europe, driven by seasonal holiday consumption. Favorable weather conditions supported stable production, while improved yields from recent rains bolstered supply volumes. Effectively managing TR4 impacts also contributed to maintaining production quality. These factors and increased export activity during the holiday season underpinned the price increases.
Guatemala
Guatemala's banana prices dropped by 4.35% WoW and MoM to USD 0.22/kg in W50 due to a continued easing in export demand following the conclusion of the peak season, leading to higher supply levels relative to market needs. A slight oversupply in some key export destinations also contributed to the price decline. However, prices increased by 22.22% YoY due to improved export dynamics compared to last year, when adverse weather and logistical challenges limited production and shipment volumes, keeping prices lower.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strengthen Disease Management for Small-Scale Banana Farms
Banana growers in the Davao Region should prioritize adopting cost-effective methods to combat Fusarium wilt, including improved crop rotation practices, resistant banana varieties, and soil health management. More extensive plantations can provide training and share technological advancements with smaller farms to strengthen disease management across the sector. Collaborating within the industry will ensure more resilient production systems, benefiting the entire banana supply chain and sustaining the region’s growth in export and domestic markets.
Enhance Sustainability and Product Diversification
Ecuadorian banana growers and exporters should focus on further investing in sustainable practices, such as reducing water usage and improving waste management, to strengthen their market position amid operational challenges. Additionally, they should actively diversify product offerings by expanding cultivation of high-demand fruits like pineapple and pitaya, leveraging existing export networks to tap into new markets and increase profitability.
Revitalize Local Banana Cultivation with Sustainable Practices
Farmers in Formosa province should collaborate to form cooperatives that pool resources for modernizing farming techniques. By implementing efficient irrigation systems, growers can optimize water usage and ensure consistent crop hydration even in challenging climates. Adopting disease-resistant banana varieties will help reduce losses caused by Fusarium wilt and other diseases, improving overall yield. Strengthening ties with local distributors to promote regionally-grown bananas can further support sustainable market access and community growth.
Sources: Tridge, Baodongnai, Bichos de campo, Business in Cameroon, Freshplaza, Mindanao Times, Mxfruit





