
1. Weekly News
Global
USDA Report Projects Global Growth in Apple and Pear Production for 2023/24 Season
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) predicts a global increase in apple production by over 700 thousand tons, reaching 83.7 million tons in the 2023/24 season. This growth is driven by increased production in the United States (US) and China, which offsets production cuts in the European Union (EU) and Turkey. Exports are expected to rise by 10% to 6 million tons, largely due to increased exports from the US and Iran. China's apple production is projected to grow by 500 thousand tons to 45 million tons, with exports increasing by nearly 100 thousand tons to 870 thousand tons. Meanwhile, the EU's apple production is expected to fall by 475 thousand tons to 12.2 million tons.
Egypt
Imported Apple Prices Soar in Egypt Due to Low Demand and Reduced Supply
The price of imported apples in Egypt rose from USD 1,456.81/ton (EGP 70,000/ton) in May-24 to USD 1,873.04/ton (EGP 90,000/ton) in Jul-24. This rise is due to a combination of factors, including decreased import volumes and subdued consumer demand within the Egyptian market. As import quantities dwindled, suppliers adjusted prices upward to reflect the scarcity and maintain profitability amid the changing market dynamics.
Europe
Impact of Frost and Rain on European Apple Harvests
From April 20 to 23, 2024, frosts severely affected Polish apple orchards, while a smaller harvest is anticipated in Turkey due to heavy rain. Market projections indicate a yield of no more than 3 million tons, falling short of the expected 5 million tons. Apple juice concentrate production is estimated to decline to approximately 200 thousand metric tons (mt) in 2024/25 from 265 thousand mt in 2023/24. Turkey's apple harvest is forecasted to decrease by at least 15% year-over-year (YoY) due to the adverse effects of heavy rainfall and declining yields. Despite this, demand for Turkish apple concentrate remains robust among US buyers.
India
Lower Apple Production Expected in India Amid Weather Challenges and Changing Consumer Preferences
Apple production in India is forecasted to decrease in 2024, with some regions seeing growth compared to last year. This drop is due to weather challenges, insufficient care, and leftover fruit from last year's sales. Himachal Pradesh has performed better but is still below average. Local growers focus on varieties like Delicious for a different market. Pine Valley Agrifarms sells its apples in 18 Indian markets, where demand remains strong despite consumer preferences shifting towards non-Indian varieties.
Ukraine
Severe Frosts Devastate Ukraine's Apple Harvest in 2024
Ukraine is dealing with severe damage from frost this spring, with 200 hectares (ha) of apple orchards completely frozen. The director of Biochem Agro said that every farm was affected, and some farms lost all of their harvests. The total apple harvest is expected to decrease by 30 to 40% YoY, leading to a 20 to 40% increase in fruit prices. Moreover, early apple varieties are projected to cost USD 0.49 per kilogram (UAH 20/kg), while late varieties will range from USD 0.35 to 0.44/kg (UAH 14 to 18/kg).
2. Weekly Pricing
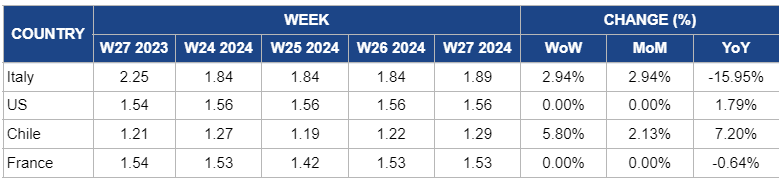
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W27 2023 to W27 2024)
Italy
In W27, apple prices saw a 2.94% week-over-week (WoW) increase and a month-on-month (MoM) increase. The WoW increase is due to stabilized domestic sales in Italy amidst export restrictions and economic challenges. Meanwhile, the 15.95% year-over-year (YoY) decrease reflects the impact of the previous year's higher price levels and market dynamics. Additionally, new varieties like Lilibet from Sanifrutta are aimed at enhancing sustainability and production efficiency in the sector.
United States
In W27, apple prices remained steady at USD 1.56/kg since W22, with a 1.79% YoY increase. This stability reflects consistent domestic demand during the US apple off-season, despite earlier fluctuations. It is supported by optimistic production forecasts and strong consumer preference for premium varieties like Envy.
Chile
The apple prices in Chile increased by 5.8% WoW to USD 1.29/kg in W27. Moreover, there is a 2.13% MoM increase. This rise is driven by a surge in local demand and adjustments in supply dynamics due to varying harvest conditions during the peak season from March to October, reflecting seasonal fluctuations and the typical volatility in the agricultural market.
France
In France, apple prices have remained steady at USD 1.53/kg in W27 since W26 after a decrease in W25. This stability comes after a 7.69% WoW increase in W26, reflecting temporary market adjustments due to renewed demand and improved supply conditions. Despite the off-season in July, consistent domestic demand has helped maintain steady prices.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Mitigating Frost Damage in Ukrainian Apple Orchards
Implement immediate measures to support affected apple orchards, including financial assistance and technical support for frost-damaged farms. Facilitate collaboration between agricultural experts and affected farmers to assess and mitigate future frost risks. Promote diversification of agricultural practices and crop insurance schemes to safeguard against unpredictable weather patterns. Strengthen resilience strategies within the agricultural industry to minimize the impact of future frost events on apple production and prices.
Strengthening Apple Production Resilience in India
To address the challenges facing apple production in India in 2024, the focus should be on implementing climate-resilient farming practices such as improved irrigation and weather forecasting technologies. Training programs should emphasize orchard management, pest control, and disease prevention to enhance care protocols. Exploring new domestic and international markets for Indian apple varieties will diversify sales channels, reducing dependence on traditional markets amidst shifting consumer preferences. Improving post-harvest handling and storage facilities is crucial to maintaining fruit quality and extending shelf life, ensuring consistent market readiness. Collaborative efforts with regional agricultural bodies can support regions like Himachal Pradesh in achieving and sustaining above-average apple production levels through targeted incentives and technical support.
Addressing Rising Apple Prices in Egypt
To combat rising apple prices in Egypt, focus on boosting local production, streamlining import processes, and encouraging market competition. Enhance domestic orchard yields through improved agricultural practices and invest in modern storage facilities to maintain supply. Additionally, negotiating better trade agreements can help stabilize import quantities and prices.
Sources: Tridge, Freshplaza, Pixabay, USDA, Guojiguoshu, Eastfruit, ProduceReport





