W28 2024: Orange Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Brazil
Orange Shortage in Brazil Leads to Surge in Prices in Jul-24
In Jul-24, the orange market is facing a shortage due to a reduced Brazilian harvest for the 2024/25 season. Orange prices surged by 33% in Jun-24, and the crushing industry's spread in juice sales remained high. Meanwhile, orange exports dropped to 72 thousand tons on May-24 compared to the previous year. Still, the average price hit a new record, exceeding USD 3 thousand per ton of frozen concentrated orange juice (FCOJ) equivalent, boosting the sector's revenue by 22.3%. The Brazilian orange harvest is expected to yield 232 million boxes, a 24.4% year-over-year (YoY) decrease. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) estimates Brazilian production to be 375 million boxes, with juice production at 1.06 million tons of FCOJ and exports at 1 million tons. Meanwhile, the USDA revised Florida's orange production estimate to 17.8 million boxes and projected the total United States’ (US) orange production at 64.96 million boxes.
Colombia
Colombia's Initiatives in Citrus Pest Management and Disease Prevention
The Colombian Agricultural Institute (ICA) in Caquetá, in collaboration with Versalles Nursery in Pitalito, Huila, organized a talk to raise awareness about integrated pest management and diseases such as Huanglongbing (HLB) in citrus. The event highlighted the importance of registering holder obligations to prevent pest entry. Versalles Nursery presented on cultivar identification and organoleptic characteristics for Caquetá citrus. ICA oversees 18 registered nurseries in the department, three of which are citrus-specific. The institute focuses on preventing pests like black aphids, leaf miners, and Diaphorina citri. ICA reminded producers to rigorously manage propagation materials to ensure plant health and minimize pest spread. Resolution 12816 of 2019 aims to prevent the spread of Diaphorina citri, a carrier of HLB.
Morocco
Moroccan Orange Exports are Expected to Increase Slightly For the 2023/24 Season Despite Adverse Weather Conditions
Morocco expects a slight increase in fresh orange exports to 40 thousand metric tons (mt) in the 2023/24 season but faces strong competition from Egypt in primary markets like the European Union (EU), Canada, the US, and Russia. Meanwhile, orange juice exports will decrease from 2.8 thousand mt to 2.5 thousand mt in 2024. Export forecasts for lemons and limes have been scaled down to 4 thousand mt as Moroccan exporters prioritize local markets. However, the citrus industry in Morocco confronts challenges such as high temperatures, drought, and adverse climatic conditions, as noted in the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS) report. These factors may impact both exports and local production in the foreseeable future.
Spain
Spain's Citrus Export Success Amidst Adverse Conditions
Spain's citrus exports achieved a positive trade balance of USD 2.7 million (EUR 2.5 million) in the 2023/24 campaign, with a coverage rate of 1,740%, despite declining production due to adverse weather conditions. Spain remains the world's leading marketer of fresh citrus, accounting for 25% of total global exports. The campaign has faced drought, extreme weather, and irrigation supply limitations, resulting in the lowest expected harvest of 5.73 billion mt. Oranges have been hit the hardest, with production dropping to 2.65 million metric tons (mmt), a 10.6% YoY decrease and 24.2% below the average of the past five campaigns. Meanwhile, small citrus fruits are also expected to see a 15% YoY reduction in production. Andalusia has been the most affected, experiencing a 20% YoY reduction in overall production compared to the average of the last five campaigns. The Valencian Community, the country's leading citrus producer, will see a 17% YoY decrease in total production. In comparison, the Region of Murcia will buck the trend with a 6% YoY increase in overall production.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Orange Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Orange Pricing Important Exporters (W28 2023 to W28 2024)
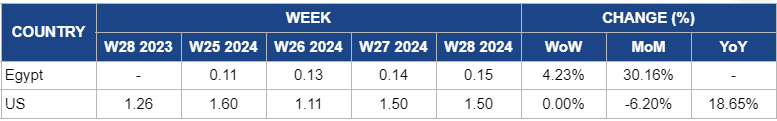
Egypt
In W28, Egyptian orange prices increased by 4.23% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 0.15 per kilogram (kg), with a notable 30.16% month-on-month (MoM) rise. This price surge is driven by heightened demand and ongoing supply constraints despite recent improvements in harvesting practices. The reduced export volume to Southeast Asian countries in the 2023/24 season, which amounted to only 42 thousand tons, reflects broader market challenges. Additionally, the Red Sea blockade by Yemeni Houthis has disrupted supply chains, temporarily closing the Asian market. This disruption has intensified the pressure on prices, even as record harvests are anticipated.
United States
In the US, orange prices have remained steady at USD 1.5/kg since W27, showing a 6.2% MoM decrease. This stability is due to the USDA's revised crop report, which predicts a slight increase in Florida's Valencia orange production for the 2023/24 season, now estimated at 18 million boxes. Despite the current price stability, the drop is due to the forecast of increased supply as market participants adjust to the expected rise in availability.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Addressing the Brazilian Orange Shortage
In collaboration with exporters and regulatory bodies, Brazilian orange growers should implement strategic measures to mitigate the impact of the reduced 2024/25 harvest. These measures include enhancing orchard management practices through precision agriculture, integrated pest management, and soil health improvement; optimizing resource allocation with efficient irrigation systems and mechanized labor; and exploring alternative markets by diversifying export destinations and developing value-added products. Strengthening supply chain partnerships through collaboration and regular market analysis and adopting diversification strategies like crop diversification and agroforestry will further stabilize supply chains and maintain quality standards.
Strengthening Spain's Citrus Industry Resilience Amidst Production Challenges
Spanish citrus growers and exporters should focus on enhancing irrigation infrastructure and adopting resilient agricultural practices, such as implementing drip irrigation systems and soil moisture sensors, to mitigate the impact of adverse weather conditions on citrus production. They should collaborate with regional governments and research institutions to innovate sustainable farming techniques and drought-resistant citrus varieties. They should also diversify export markets and leverage Spain's global position in fresh citrus to maintain trade balance and capitalize on emerging market opportunities.
Enhance Morocco's Citrus Export Competitiveness
Moroccan citrus exporters should invest in advanced irrigation technologies, such as drip irrigation systems and soil moisture sensors, to optimize water usage and improve resilience against drought. They should also adopt climate-resilient agricultural practices, including using drought-resistant citrus varieties and mulching to retain soil moisture. Collaborating with international trade partners can help secure better market positions in the European Union, Canada, the US, and Russia. Additionally, they should focus on enhancing the quality of orange juice to mitigate the expected decrease in exports.
Sources: Tridge, Freshplaza, Campocyl, MXfruit, Portal Do Agronegocio, Agrimaroc, Prnewswire, EastFruit, USDA, FreshFruitPortal





