W37 2024: Strawberry Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Ethiopia
Ethiopian Farm Adopts Hydroponic Technology for Year-Round Strawberry Production
Ethiopian farm Zuqualla Horti PLC is using hydroponic technology with gutter systems in its greenhouses to grow strawberries year-round. The farm aims to optimize production cycles, cut labor costs, and enhance environmental sustainability by recycling wastewater and reducing pesticide use. In Sep-24, the farm will host open days to demonstrate its techniques and collaborate with local growers and government officials to advance Ethiopia's horticultural industry. The farm is located near Addis Ababa and benefits from a favorable climate and strong export logistics.
France
Strong Strawberry Season Anticipated in France Due to Favorable Conditions
France's 2024 strawberry season has seen higher yields due to favorable weather and low pest pressure. Around 80% of the expected 60 thousand metric tons (mt) had been harvested at the end of Jun-24. Producers in the southwest extend their season into July thanks to mild temperatures. Strong yields and positive market response have allowed French strawberries to compete well with imports. The strawberry season will continue into Oct-24 with popular varieties like Charlotte, Mara des Bois, and Cijosée.
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Greenhouse Expands to Strawberry Production
In Stepnogorsk, Kazakhstan, the Greenhouse Technologies of Kazakhstan complex is expanding to grow strawberries. Currently spanning 4.8 ha and producing 2.4 thousand tons of vegetables annually, the facility serves the capital and other regions. Supported by KazAgroFinance since its launch in 2010, the greenhouse is entering a new phase, aiming to produce up to 50 tons of strawberries annually. This expansion reflects Kazakhstan's focus on improving local food supply and boosting production and export potential.
Netherlands
High Demand for Dutch Greenhouse Strawberries
Dutch greenhouse strawberries are in high demand both domestically and internationally. With limited availability as rack crops end, the focus has shifted to Inspire strawberries, selling at prices between USD 6.68 to 8.35 per kilogram (EUR 6 to 7.50/kg). Despite the upcoming arrival of Elsanta strawberries, demand is anticipated to remain strong. While ever-bearing varieties are gaining popularity, Elsanta is still the dominant autumn variety. The cooler weather forecast is expected to improve strawberry quality. Sales typically slow in the Netherlands towards the end of the year, but demand from the United Kingdom (UK) and Ireland continues to rise during this period.
United States
Steady Strawberry Supply from California in 2024
California's strawberry supply from Watsonville/Salinas and Santa Maria remains steady, with production tapering off in Watsonville/Salinas while Santa Maria's fall crop ramps up. The Santa Maria crop is expected to reach peak volumes between mid-Sep-24 and mid-Oct-24. Overall, the strawberry supply in 2024 is slightly higher than in 2023 due to favorable weather conditions compared to 2023's floods in the Pajaro Valley. The harvest in Watsonville/Salinas is expected to finish by the end of October, with promotions continuing to support consumer demand. Mexico and Florida will supplement California's strawberry supply later in the year, continuing into 2025.
AI Enhances Strawberry Disease Detection in Florida
New research from the University of Florida (UF) shows that artificial intelligence (AI) can significantly improve leaf wetness detection, which is crucial for managing strawberry diseases like botrytis and anthracnose. Although Florida's strawberry season begins in Dec-24, scientists work year-round to develop disease management tools. The Strawberry Advisory System (SAS) UF developed uses weather data to estimate disease risk and helps farmers time fungicide applications. In a recent study, AI improved moisture detection accuracy, achieving 96% alignment with manual observations. Florida's strawberry farms, covering 5.4 thousand ha, are primarily located in Hillsborough, Polk, and Manatee counties.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Strawberry Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Strawberry Pricing Important Exporters (W37 2023 to W37 2024)
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
Mexico
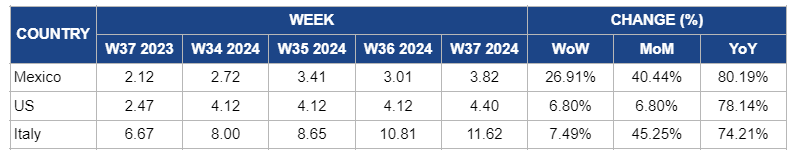
In W37, strawberry prices in Mexico increased by 26.91% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 3.82/kg, reflecting a substantial 40.44% month-on-month (MoM) rise and a 80.19% year-on-year (YoY) surge. This price increase follows a temporary 11.65% WoW drop in W36, which was due to a short-term supply boost as producers addressed earlier constraints. However, the overall market remains tight due to ongoing challenges, including persistent supply limitations and the lasting effects of extreme heat waves, drought, and unseasonal rainfall on production volumes and quality. These factors contribute to the elevated prices, as demand remains strong while supply struggles to keep up. The significant YoY increase highlights the prolonged impact of these disruptions on the market.
United States
In the US, strawberry prices in W37 reached USD 4.40/kg, reflecting a 6.80% WoW and MoM increase, and a significant 78.14% YoY surge. The WoW and MoM price rise reflects ongoing supply constraints and adverse weather conditions, including heatwaves and drought. The significant YoY increase underscores the persistent impact of these challenges on production. New AI advancements from the University of Florida are improving leaf wetness detection for better disease management. Still, the market remains under pressure until these technologies are fully implemented.
Italy
In W37, strawberry prices in Italy increased by 7.49% WoW to USD 11.62/kg. This rise also represents a 45.25% MoM and a 74.21% YoY increase. The continued price surge reflects persistent challenges in the Italian strawberry market, exacerbated by ongoing extreme heat and adverse weather conditions. These climate-related issues have further reduced supply and compromised fruit quality, maintaining upward pressure on prices. Despite efforts to stabilize production, the supply remains constrained, leading to higher prices as demand continues to outpace availability.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Adopt UV Robots and Ever-Bearing Strawberry Plants Industry-Wide
Strawberry growers across Belgium should consider adopting UV robots for managing white disease and transitioning to ever-bearing strawberry plants to boost productivity and control labor costs. These practices are gaining traction in Flanders and align with the regional trend of steady strawberry cultivation despite a decline in the number of farms. By embracing these innovations, the industry can enhance efficiency and maintain competitiveness significantly as cultivation expands and older growers retire.
Enhance Supply Chain Resilience Amidst Price Surge
Italian strawberry producers should invest in advanced weather forecasting systems to better anticipate and mitigate the impacts of extreme weather. Diversifying sourcing strategies by exploring alternative suppliers and expanding cultivation regions can reduce dependency on affected areas. Additionally, adopting heat-tolerant strawberry varieties that can withstand high temperatures and improving irrigation systems to ensure consistent water supply during droughts are crucial. These measures will help stabilize production, maintain fruit quality, and manage the ongoing price surge in the market.
Implement Long-Term Strategies to Stabilize Strawberry Prices
Strawberry producers in Mexico should focus on long-term strategies to stabilize prices amidst ongoing market challenges. This includes investing in sustainable farming practices such as using shade nets to reduce heat stress, employing efficient irrigation techniques like drip irrigation to conserve water, and integrating soil management practices to improve resilience against drought. Producers should also enhance supply chain resilience by improving storage facilities and expanding production areas to handle supply fluctuations better. These actions will help address persistent supply limitations, maintain quality, and balance the market amidst rising prices and strong demand.
Sources: Tridge, Freshfruitportal, Surexport, Freshplaza, Eastfruit, MXFruit, Hortidaily, Terredauphinoise, Kapital, VILT





