
1. Weekly News
Canary Islands
Canary Islands Advances Draft Decree to Regulate Banana Production under POSEI
The Canary Islands government is moving forward with a draft decree to regulate the allocation and reservation of reference quantities for banana producers under the Specific Options Program for Remote and Insular Regions (POSEI) program. The decree is expected to be finalized by late Feb-25 or early Mar-25, incorporating feedback from the public participation process completed in Dec-24. The regulations align with previous legislation, accounting for plantations established by Aug-24 for the following reference quantity revision. It also includes an exception for newly incorporated young producers, reflecting broad support in the Canary Islands Parliament. This initiative aims to strengthen the stability and growth of the region’s banana production industry.
Ecuador
Ecuador Boosts Banana Exports to the US and South Korea Despite Decline in Russian Shipments
Ecuadorian banana exports reached 306.64 million boxes by Oct-24, slightly surpassing the 305.73 million boxes exported in the same period in 2023. The European Union (EU) remained the top market, accounting for 29.59% of exports (90.72 million boxes), followed by Russia at 17.78% (54.53 million boxes). However, exports to Russia declined by 16.35% due to higher banana prices and rising freight costs. Despite this drop in Russian exports, Ecuador boosted exports to the United States (US) and South Korea with a remarkable 245% surge driven by tariff exemptions. This focus shift demonstrates Ecuador's ability to adapt and sustain intense export levels despite market challenges.
France
Bananas Lead French Fruit Market with 6% Consumption Growth Despite Global Trade Challenges
Bananas are the most popular fruit in France, making up 18% of the market. Their affordability, convenience, and nutritional benefits contribute to their high consumption. From 2020 to 2024, consumption grew by 6%, with average prices at USD 1.95 per kilogram (EUR 1.86/kg), despite the global decline in the banana trade, which fell below 20 million metric tons (mmt) in 2022. The industry faces climatic, logistical, and economic challenges despite this growth. Stakeholders emphasize shared responsibility to sustain banana availability and navigate evolving market demands.
Malawi
Malawi Revives Banana Cultivation to Reduce Imports and Boost Agriculture
Malawi is focusing on reviving banana cultivation to enhance local production and reduce dependency on costly imports, which amount to 20 thousand metric tons (mt) annually at USD 12 million. Supported by a USD 110 thousand investment from the National Bank of Malawi (NBM) and the Centre for Agriculture Transformation’s (CAT) expertise, the initiative introduces resilient banana varieties and modern farming techniques to combat challenges like the Banana Bunchy Top Virus. The project aligns with Malawi's 2063 blueprint to modernize agriculture and strengthen economic independence through increased local production and exports by empowering smallholder farmers through training, demonstration plots, and irrigation upgrades.
Russia
Russia Plans Greenhouse Banana Cultivation to Boost Local Production and Enhance Food Security
Relying heavily on Ecuador for its annual banana imports of around 1.4 million tons, Russia is exploring greenhouse banana cultivation to improve food security. Although imported bananas remain cheaper, their price has risen from USD 0.78 to 1.36/kg (RUB 80 to 140/kg) over the past two years due to currency fluctuations and import restrictions. Inspired by Kazakhstan's success with greenhouse bananas, Russia aims to establish its first large-scale banana-growing complex in Stavropol Krai by 2025, spanning 46 hectares (ha). While the viability of this project depends on technology and investment, it reflects Russia's goal to reduce reliance on imports and boost local production.
2. Weekly Pricing
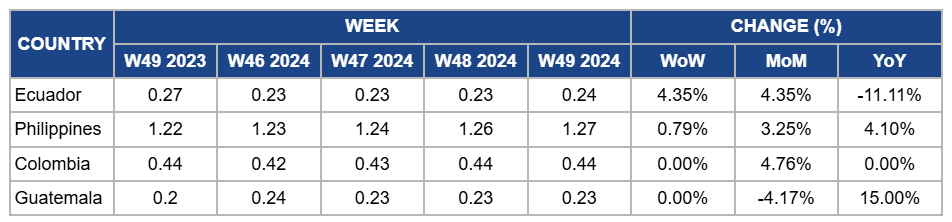
Weekly Banana Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Banana Pricing Important Exporters (W49 2023 to W49 2024)
Ecuador
Ecuador's banana prices increased by 4.35% week-on-week (WoW) and month-on-month (MoM) in W49 due to improved export flow as logistical issues, such as port congestion, began to ease. Steady demand from key markets, including the US, the Middle East, and Russia, also helped support the price increase. However, there is an 11.11% year-on-year (YoY) drop due to the ongoing competitive pressure from other banana-exporting countries, resulting in lower overall prices than last year. The market continues to face challenges, but the expected Ecuador-China Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in 2025 could help boost long-term export prospects.
Philippines
Banana prices in the Philippines increased slightly by 0.79% WoW to USD 1.27/kg in W49, with a 3.25% MoM increase and 4.10% YoY due to continued strong export demand from key markets such as Japan and South Korea. Improved logistics following earlier weather disruptions and enhanced production efficiency, including adopting disease-resistant varieties, contributed to price stability. The combination of these factors and a steady recovery in supply after the typhoon have supported the upward price trend compared to the previous month and the same period last year.
Colombia
In Colombia, banana prices remained steady at USD 0.44/kg in W49, with no YoY change and a 4.76% MoM increase. This is due to sustained high export demand from key markets like the US and Europe, along with favorable weather conditions supporting stable production. Additionally, effective management of Fusarium Tropical Race 4 (TR4) impacts helped maintain supply levels, while seasonal adjustments in supply and improved yields from recent rains eased earlier market tightness. These factors, combined with the ongoing demand, contributed to the stability and price increase compared to the previous month.
Guatemala
Guatemala's banana prices held steady at USD 0.23/kg in W49, with a 4.17% MoM decline due to a slight easing in export demand after the peak season, leading to a more balanced supply and demand dynamic. However, YoY prices dropped significantly by 15% due to a higher base of comparison from the previous year, when market conditions were particularly favorable, and demand was exceptionally strong, pushing prices higher.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Empower Smallholder Farmers for Sustainable Banana Revival
Smallholder farmers in Malawi should adopt resilient banana varieties and modern farming techniques promoted by the Centre for Agriculture Transformation (CAT). By engaging in training programs, utilizing demonstration plots, and upgrading irrigation systems, farmers can effectively combat diseases like Banana Bunchy Top Virus and enhance productivity.
Establish Greenhouse Banana Farms to Reduce Import Dependency
Agribusiness investors and technology providers in Russia should collaborate to establish greenhouse banana cultivation complexes, such as the planned facility in Stavropol Krai. By leveraging advanced greenhouse technologies and expertise from successful models like Kazakhstan, stakeholders can reduce reliance on Ecuadorian imports, stabilize supply, and address rising banana prices caused by currency fluctuations and import restrictions. This approach ensures a sustainable and secure local banana supply while supporting Russia's food security goals.
Collaborate to Ensure Banana Supply Stability
French retailers and banana suppliers should strengthen collaboration by establishing clear communication channels, sharing market data, and effectively aligning demand forecasts to address supply chain challenges. Adopting sustainable sourcing practices involves working with producers to implement environmentally friendly farming techniques, such as reducing chemical usage and preserving biodiversity, ensuring long-term banana production viability. Optimizing logistics includes streamlining transportation networks, adopting cold chain technology to reduce spoilage, and utilizing digital tools for real-time supply chain tracking to enhance efficiency and minimize costs. These measures can sustain steady banana availability in France's growing market while addressing global trade pressures.
Sources: Tridge, Agraria, Elapuron, Freshplaza, MXfruit, RG, The Pinnacle Gazette





