Lower Sugarbeet Production in China Drives up Sugar Imports in MY 2021-22

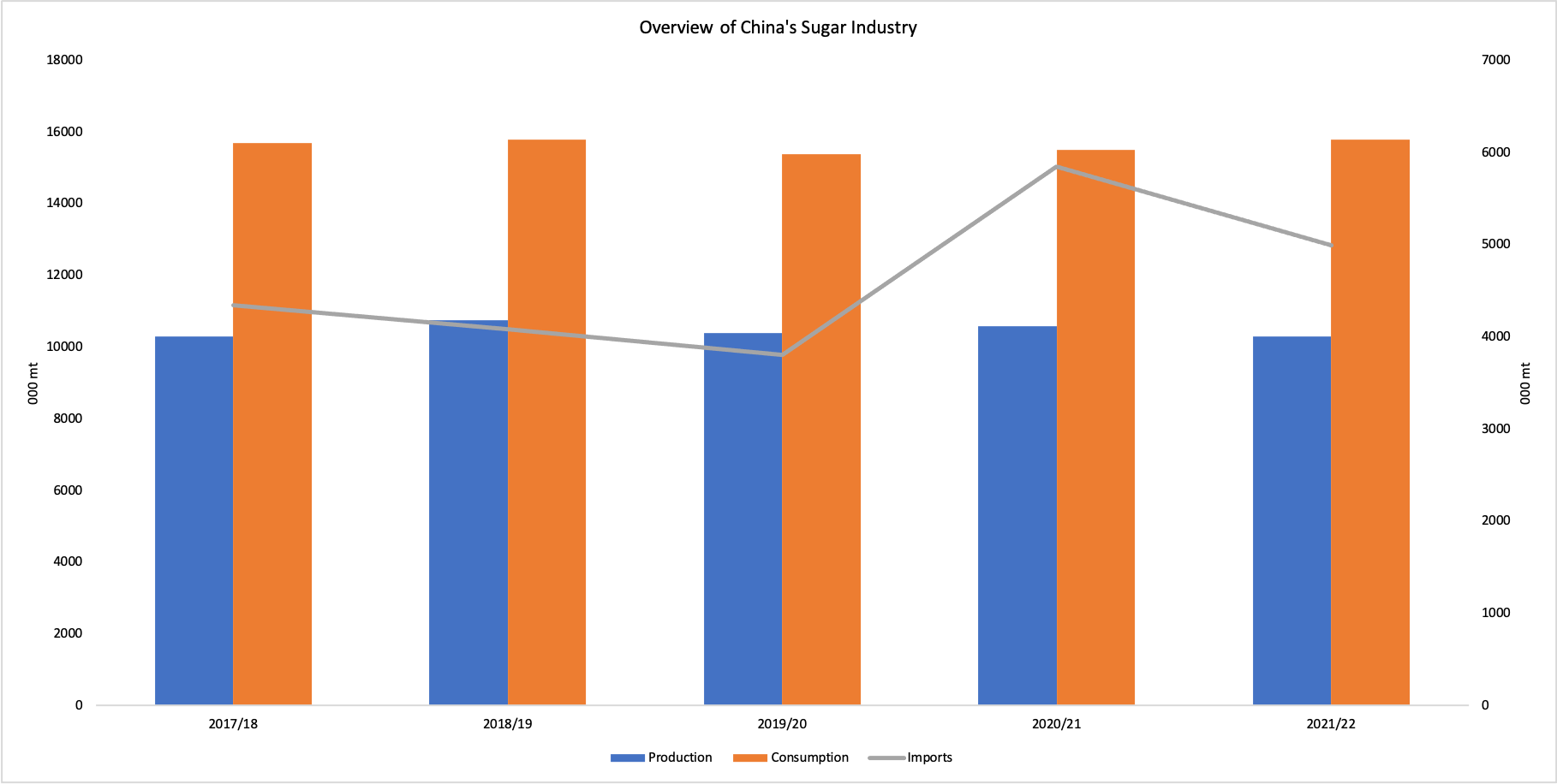
Global sugar production volumes for the Marketing Year (MY) 2021-22 is estimated to be at 181 million mt which is a little higher than the 180 million mt recorded in MY 2020-21. However, with projections that there will be a dramatic fall in sugar production in China, a detrimental impact on the global sugar market is anticipated. China is the world's third-largest sugar-producing country after Brazil and India. China is also the largest importer of sugar, importing over 5 million mt of sugar during MY 2020-21 (October 2020 - September 2021). According to the USDA’s estimates, China’s sugar production volumes are projected to be at 10.3 million mt in MY 2021-22, which is about a YoY decline of 6.3%.
China recorded a fall in sugar production due to a decline inclement weather conditions in areas devoted to sugarbeet/sugarcane production. The Guangxi region of China is a dominant sugarcane/sugarbeet and sugar-producing region that accounts for 65% of all sugar volumes produced in the country. Furthermore, severe and unexpected frosts in the Guangxi region during the main sugarbeet/sugarcane period have impacted the volume and quality of produce harvested for processing. La Niña will also likely increase the risk of frosting in the future, impacting the yield of the two sugar crops. The fall in sugar production, in particular, could be attributed to a YoY decline of 42% in the sugarbeet crop. The sugarcane crop, by contrast, only recorded a YoY decline of 1%. For the third consecutive year, China’s domestic sugar consumption is set to exceed production volumes.
China imports large volumes of sugar to meet the demand of its growing population and accommodate the population’s changing consumption patterns. It is projected that in MY 2021-22, there will be a sugar supply deficit of 5.5 million mt which will have to be met by importing sugar from other countries. Records have shown an increase in sugar imports over the past few years, brought in to meet the widening gap between production and consumption demand. Higher sugar consumption patterns in China will lead to the utilization of buffer sugar stocks maintained from the previous year’s produce. China ending sugar stocks are expected to fall to 4.19 million mt which is a YoY decline of over 13.51%.
Source: USDA
Even though China's domestic sugar self-efficiency rate is secure at 70% to 80%, which is a relatively high number. By 2030, China’s sugar production and consumption are projected to increase to 11.35 million mt and 16.44 million mt respectively. Higher sugar consumption are projected to be met by 5.52 million mt of sugar imports during the same year. In the upcoming MY, it is expected that China will continue to import sugar from other countries to meet domestic demand. Given the negative impact of recent frosts and the prolonged risk of La Niña this year's imports are set to increase steeply.





