
1. Weekly News
Colombia
Colombia's Banana Industry Overcomes Challenges to Strengthen Global Presence
Colombia's banana industry has encountered challenges, including rising production costs, climate change, and pest issues, but producers have worked hard to strengthen their global presence. Investments in quality, innovation, and sustainable practices have led to steady increases in export volumes to key markets like the United States (US) and Europe. Despite these obstacles, the industry remains resilient, adapting to fluctuating international prices and continuing efforts to boost competitiveness, securing Colombia's position as a prominent player in the global banana market.
Ecuador
Ecuador's Banana Exports Show Steady Growth Despite Global Challenges
Ecuador's banana exports have risen for the third consecutive month, reaching 330.90 million boxes by Nov-24, a 1.39% year-on-year (YoY) increase. The European Union (EU) remains the top market, with exports growing by 3.20%, driven by strong demand from Malta, France, Italy, and Germany. Significant growth was also seen in the US, with an increase of 27.24%, and Eastern Europe, with an increase of 30.57%. Exports to Asia rose by 0.99 million boxes, while shipments to Russia decreased compared to the previous year. Despite logistical hurdles like route congestion, container shortages, and competition from Chile in the US market, Ecuador's banana industry has shown resilience by diversifying its export destinations, offsetting reduced demand in Russia and the Middle East with steady export performance.
Ethiopia
South Ethiopia Expands Banana Production for Middle Eastern Markets
South Ethiopia Regional State is working to expand its banana exports to the Middle East, leveraging its favorable climate and strong agricultural initiatives. The region focuses on increasing production by providing farmers with improved seedlings and efficient farming techniques to enhance yields. This effort targets nearby markets in Sudan, Somalia, and Djibouti while exploring new opportunities in the Middle East. The initiative aims to drive economic growth, create jobs, and improve food security, further solidifying the region’s role in the global banana market.
India
India Expands Banana Exports with Sea Transport Initiative
India is working to increase banana exports by developing sea transport protocols to supplement its reliance on air freight. The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) is collaborating with stakeholders to enhance exports of bananas, mangoes, and pomegranates through maritime routes, aiming to improve volume and cost-efficiency. This initiative supports the government’s strategy to upgrade infrastructure, support farmers, and improve market access, keeping India’s bananas globally competitive.
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Ventures into Banana Cultivation with Ambitious Agricultural Project
GenGroup Qazaqstan, a leading agricultural company in Kazakhstan, is expanding its operations in the Turkestan region. Located in Kasymbek Datka village, the company’s 5-hectare (ha) farm plans to introduce banana cultivation, alongside its successful mango production, through an ambitious greenhouse project. Backed by an investment exceeding 10 billion tenge (around EUR 18.3 million), the initiative aims to triple its area and drive agricultural innovation, representing a major milestone for Kazakhstan's growing agricultural sector.
Philippines
Philippines Secures Tariff-Free Access for Bananas in South Korea Under FTA
The Korea-Philippines Free Trade Agreement (FTA) will phase out the 30% tariff on Philippine bananas over five years, gradually reducing it by 6% annually. This is expected to boost banana exports to South Korea. South Korea has introduced Agricultural Safeguard (ASG) measures to address potential import surges, allowing up to 30% tariffs if import volumes exceed limits within the first ten years. The agreement deepens trade ties while balancing protections for sensitive agricultural sectors.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Banana Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
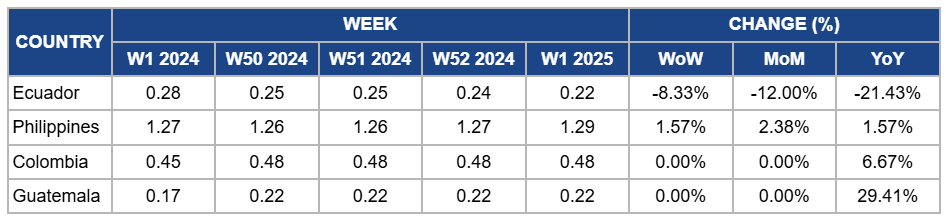
Yearly Change in Banana Pricing Important Exporters (W1 2024 to W1 2025)
Ecuador
Banana prices in Ecuador dropped by 8.33% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 0.22 per kilogram (kg) in W1, reflecting a 12% month-on-month (MoM) decline and a 21.43% YoY decrease. The price drops are due to increased local supply, which remains higher than the previous year as the effects of last season's drought and disease outbreaks continue to subside. This oversupply, combined with intensified competition from other banana-exporting countries offering more competitive pricing, has put downward pressure on prices. Additionally, despite Ecuador's efforts to boost exports to primary markets in Europe, the US, and Asia, logistical challenges and global market conditions have further constrained price recovery, contributing to the significant YoY decline.
Philippines
In W1, banana prices in the Philippines climbed slightly by 1.57% WoW to USD 1.29/kg, with a 2.38% MoM increase and a 1.57% YoY rise. The price growth is due to a slight tightening of supply following a stable production period. Despite improved weather conditions allowing for better yields, the previous disruptions from diseases and adverse weather earlier in the year caused enough market volatility to maintain higher price levels. Demand, especially in export markets, increased prices as these challenges eased. The supply-demand balance in W1 resulted in a modest price uptick despite better overall production.
Colombia
Colombia's banana prices remained steady at USD 0.48/kg in W1, with no WoW and MoM change due to a stable supply and demand dynamic. Favorable weather conditions and steady production have contributed to this price stability. However, YoY prices rose by 6.67% due to sustained export demand, particularly from key markets like the US and Europe, where seasonal holiday consumption led to higher demand. The industry's resilience in overcoming rising production costs, climate change, and pest issues has also supported its position in the global banana market, contributing to the upward price trend compared to last year.
Guatemala
In Guatemala, banana prices held steady at USD 0.22/kg in W1, with no WoW and MoM change due to stable market conditions during the low production season in January, which balanced supply and demand. However, YoY prices increased significantly by 29.41% due to reduced production levels compared to last year, influenced by scattered showers and rainy weather early in the month. These weather conditions have slightly constrained harvesting and logistical operations, contributing to tighter supply and supporting higher YoY price levels.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Maximize Opportunities from the Korea-Philippines FTA for Banana Exports
Philippine banana exporters should strategically plan to maximize the benefits of the Korea-Philippines FTA by expanding their market presence in South Korea. They can achieve this by collaborating with local distributors and retailers in South Korea to establish a consistent supply chain and develop marketing strategies tailored to Korean consumers. Exporters should also closely monitor ASG thresholds and adjust shipping volumes accordingly to avoid triggering higher tariffs. Diversifying product offerings, such as premium or organic bananas, could further enhance their competitive edge in the Korean market.
Strengthen Export Logistics and Market Diversification
Banana exporters in Ecuador, Colombia, and the Philippinesbanana exporters should enhance their export strategies by addressing logistical challenges such as route congestion and container shortages through better coordination with shipping partners and investment in efficient transport systems. Additionally, exporters should capitalize on growing demand in key markets like the EU, US, and Asia by strengthening distribution networks and promotional campaigns tailored to consumer preferences in these regions. Diversifying exports to untapped or less competitive markets can also mitigate risks associated with reduced demand in Russia and the Middle East.
Optimize Harvesting and Logistics to Overcome Weather Challenges
Guatemalan banana producers and exporters should improve weather-adaptive harvesting strategies, such as scheduling harvests during dry windows and using protective coverings for crops during scattered showers. Additionally, they should enhance logistical operations by coordinating with transportation partners to minimize disruptions caused by rainy weather. These measures can ensure consistent supply and maintain stable market conditions during challenging weather periods.
Sources: Tridge, Agraria, Business Standard, Eluniverso.com Kz.kursiv.media, Nongmin, 2Merkato






