W34 2024: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
1. Weekly News
Global
Global Beef Exports Expected to Reach Record Levels Amid Lower Prices in 2024
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) forecasts a significant increase in global beef sales, with an expected rise of approximately 750 thousand metric tons (mt) by the end of 2024, representing the most significant year-on-year (YoY) growth in the past two decades, and potentially the largest in history. This is evident in global beef export volumes registered by major countries. For example, Brazil set a new record for its highest monthly exports in Jul-24, totaling around 235 thousand mt, while Australia reached a historic high of 133 thousand mt.
On the other hand, China's beef imports were 17% higher in the first half of 2024 than in the same period in 2023. Meanwhile, the United States' (US) beef imports rose by 14% from Jan-24 to Jul-24 compared to the same period in 2023 — notably, China and the US account for 53% of global beef imports.
For the past two years, leading beef-exporting countries, such as Brazil, Uruguay, Australia, New Zealand, and Argentina, have sought to diversify their markets and reduce reliance on China. Fortunately, many of these countries have successfully identified alternative markets while maintaining overall export volumes. Emerging Asian markets, such as Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines, are becoming significant players in the global beef trade. With a combined population of over 600 million people and rising incomes, these countries purchase nearly 1 million metric tons (mmt) of beef annually.
Looking ahead, projections predict a decrease in livestock supply in some major beef-producing countries, including the US, Australia, Brazil, and Argentina. This potential "synchronization" of the livestock cycle could reduce global beef supply, potentially driving up international prices. At least until early 2025, Brazil is expected to continue liquidating livestock, benefiting from lower cattle prices compared to its competitors and an abundant supply. Brazilian exporters have also gained from the recent devaluation of the Brazilian real (BRL) and the approval of numerous new meatpacking plants for exports to China.
Despite record-high global trade volumes, global beef prices remain low. For instance, Brazilian beef's average free-on-board (FOB) price dropped from USD 6,825/mt in mid-2022 to USD 4,400/mt as of W34. On the demand side, the average cost, insurance, and freight (CIF) price China paid for frozen boneless beef has fallen from USD 7,600/mt in Jul-22 to USD 5,130/mt in W34.
The weighted average price for Mercosur countries, including Australia and the US, now stands at USD 5,800/mt, 22% lower than two years ago. Although US import prices have improved recently, the global average price, heavily influenced by Chinese purchasing patterns, is only beginning to show signs of recovery. As beef prices rise, consumers globally tend to quickly shift to more affordable alternatives, such as pork, chicken, and pond-raised fish.
China
China’s Beef Imports Expected to Rise in 2024 and 2025
China's beef imports amounted to 1.65 mmt in the Jan-24 to Jul-24 period, marking an 8% increase compared to the same period in 2023. This upward trend is expected to continue into 2025. Following a period of low prices in the first half of 2024, recent weeks have seen the prices of beef imported by China rise by USD 150/mt to USD 200/mt, translating to an average increase of 5% to 8%. Although these prices are not exceptionally high, especially given the previously low levels, the positive shift in trend could benefit Argentine beef exporters.
According to Bichos del Campo, an Argentine digital news platform that focuses on agricultural and rural sector news, this price increase is due to stock depletion by importing companies and a resurgence in consumer demand. Despite substantial supplies from major exporters like Brazil and Australia, China's growing demand has increased prices. Additionally, the recent removal of export duties on beef from cows sold to the Chinese market has improved business conditions. However, the tax relief increased cattle prices due to limited supply, indicating that the overall profitability has only seen marginal improvement.
There is optimism in the market as projections suggest that China's demand will continue to absorb large quantities of beef. The USDA forecasts that China's beef imports will likely reach 3.9 mmt in 2024, a 9% YoY increase and almost ten times more than a decade ago. By 2025, imports are expected to grow by approximately 3.95 mmt.
These fluctuations in price and volume are crucial for Argentine exporters, as over 70% of their beef exports are directed to the Chinese market. However, this share decreased to 67% in Jul-24 due to low prices, prompting Argentine exporters to explore alternative markets, including the US.
European Union
EUDR Law Pressures Global Companies to Ensure Sustainable Sourcing
The European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), aimed at curbing deforestation, will require all raw materials used in products entering the European Union (EU) to be traced back to their origin. This mandate will affect all companies operating within or conducting business with the EU whose products contain raw materials such as rubber, palm oil, cocoa, coffee, and beef. These new rules are set to take effect on December 30, 2024. The EU has set a target to reduce deforestation by 10% and decrease carbon dioxide emissions by at least 32 mmt per year.
These stringent regulations have prompted investors to reassess their portfolios due to the potential impact of the EU's efforts to combat deforestation. Companies that fail to comply with deforestation and biodiversity policies may be subjected to due diligence requirements under the EUDR. According to Jefferies Group, an American multinational independent investment bank and financial services company, companies that could be affected include DN Automotive, Hankook Tire and Technology, Kuala Lumpur Kepong Berhad, Nexen Tire, Golden-Agri Resources, Darling Ingredients, and SD Guthrie Berhad.
Several businesses and government officials, including those from Washington, have requested that the EU delay the implementation of these regulations, citing concerns about their broad scope. However, the EU has declined to alter the timeline, confirming that the new rules will be enforced starting December 30, 2024, with a six-month grace period for small businesses.
South Korea
South Korean Beef Prices Fluctuate Ahead of Chuseok Holiday
Even before the Chuseok holiday, the auction prices of Korean beef remain weak, primarily due to sluggish consumer demand amid economic challenges and an anticipated high volume of shipments. In response to the upcoming holiday demand, major livestock auction centers affiliated with the National Agricultural Cooperative Federation and private slaughterhouses have increased their slaughtering activities, even working on Saturdays, typically holidays.
Although there were signs of a price increase around August 20, 2024, the overall outlook for the Chuseok market remains pessimistic. Data from the Livestock Products Quality Evaluation Institute shows that the average auction price of Hanwoo steers across wholesale markets was USD 13.41 per kilogram (KRW 17,907/kg) as of August 22, 2024. This represents a decrease of approximately USD 1.50 (KRW 2,000) compared to the auction price of USD 14.90/kg (KRW 19,900) observed in late Aug-23 to early Sep-23, about four weeks before Chuseok.
Despite some forecasts predicting a slight price increase, the prevailing projection suggests a significant upward trend is unlikely due to the large inventory waiting to be shipped. According to the Livestock Product History Data Lab of the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA), the number of 28 to 36-month-old Korean beef bulls as of Jul-24 was 202,644, 12.4% more than the 182,922 bulls recorded during the same period last year.
Additionally, some analysts believe that the fluctuation in average auction prices between USD 12.73/kg (KRW 17,000/kg) and USD 13.48/kg (KRW 18,000/kg) is partly due to inventory depletion within the distribution industry, spurred by previous Korean beef discount events.
2. Weekly Pricing
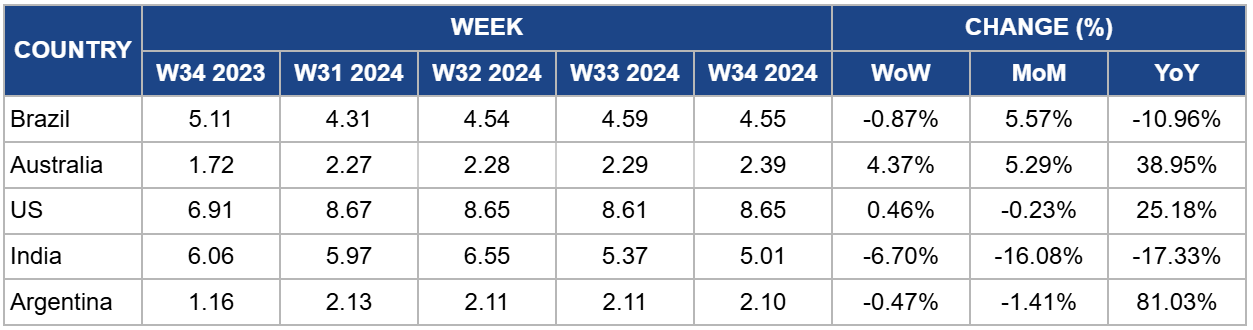
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
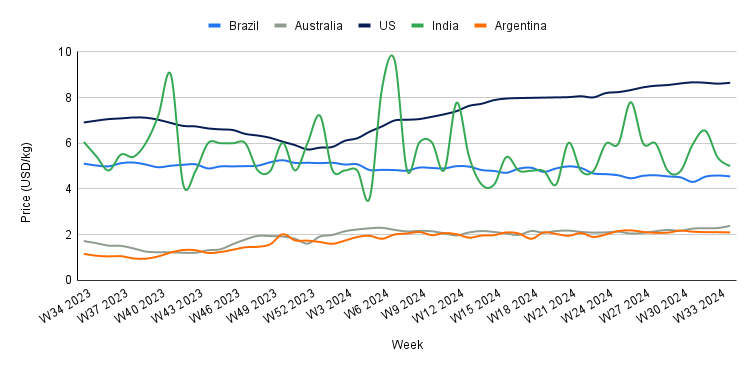
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W34 2023 to W34 2024)
Brazil
In W34, the wholesale price of boneless rear beef in Brazil averaged USD 4.55/kg, a 0.87% week-on-week (WoW) decrease and a 10.96% YoY decline. The WoW drop can be attributed to low demand and high supply in the market, as Safras and Mercado noted that the second half of Aug-24 saw reduced consumption. The YoY decrease is due to increased supply resulting from higher beef production. According to the latest USDA data, Brazil's beef production is expected to reach 11.35 mmt in 2024, marking a 3.65% increase compared to the previous year.
Australia
Australia's national young cattle indicator averaged USD 2.39/kg in W34, a 4.37% WoW rise, and a 38.95% YoY increase. The WoW increase is likely due to a drop in cattle supply at saleyards, coupled with recent rains across various states that bolstered market sentiment. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), cattle yardings decreased during the week, totaling 48.49 thousand heads. MLA also noted that a substantial portion of the supply came through online sales in New South Wales, accounting for 23% of the indicator's throughput. Additionally, the rains in New South Wales contributed to stronger restocker steer prices, particularly in Wagga Wagga.
United States
In W34, the average price of lean beef (92% to 94% lean) in the US was USD 8.65/kg, reflecting a slight 0.46% WoW improvement and a notable 25.18% YoY increase. These price hikes are primarily driven by limited beef supply in the market due to reduced domestic production. The USDA forecasts that US beef production could reach 12.14 mmt in 2024, a 1.22% YoY decline and the lowest volume since 2017. Strong beef demand, particularly during the summer, has kept prices at record highs. The USDA also projects that US beef consumption will reach 12.73 mmt in 2024, reflecting a 0.71% YoY increase.
India
The average price of cow beef in India dropped to USD 5.01/kg in W34, reflecting a 0.47% WoW decrease and a 17.33% YoY decline. These price reductions highlight the ongoing volatility in the Indian beef market, which has been especially pronounced over the past year. This instability is primarily driven by a combination of domestic and international regulations and fluctuations in supply within the Indian market.
Argentina
In W34, the average price of steer beef in Argentina was USD 2.10/kg, marking a 0.47% WoW decrease. This price reduction is attributed to weakened demand within the country, as beef consumption has reached its lowest levels amid a challenging economic environment. According to the Chamber of the Meat and Cattle Industry and Commerce (CICCRA), per capita beef consumption has dropped to its lowest point in 26 years, following a 14.1% YoY decline. This downturn is driven by a severe recession and a significant decrease in the population's purchasing power. Consequently, many consumers have shifted to more affordable options, such as poultry.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversifying Export Markets to Mitigate Reliance on a Single Destination
Given the increasing dependence on China for beef exports, countries like Brazil, Argentina, Australia, and Uruguay should continue diversifying their export markets. While China remains a significant consumer, alternative markets in Southeast Asia, such as Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines, present viable opportunities. These regions consume substantial beef annually, with a combined population of over 600 million people and rising income levels. By strengthening trade relationships and exploring market entry strategies in these countries, exporters can reduce reliance on a single market, minimizing risk and ensuring steady demand.
Capitalizing Price Recovery through Product Differentiation
The recent uptick in export beef prices to China presents an opportunity for beef-exporting countries to capitalize on market recovery. Exporters should focus on product differentiation to enhance their market appeal, emphasizing premium quality, sustainability, and traceability. These differentiators can justify higher prices and attract consumers willing to pay a premium for high-quality beef. For example, Argentine beef exporters can leverage their reputation for grass-fed, hormone-free beef to create niche markets that are less sensitive to price fluctuations and more loyal to quality standards.
Enhancing EUDR Compliance
The impending EUDR requires companies to return their raw materials to non-deforested origins. To meet these stringent requirements, beef exporters and companies involved in the supply chain should invest in transparent traceability systems. This includes implementing robust monitoring, reporting, and verification processes to ensure compliance with deforestation-free commitments. By doing so, companies can maintain access to the lucrative EU market and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers globally, enhancing their brand reputation and competitive advantage.
Increasing Marketing Efforts to Boost Consumer Demand
With sluggish consumer demand contributing to weak Korean beef prices ahead of the Chuseok holiday, there is a need for enhanced marketing and promotional activities. The National Agricultural Cooperative Federation and private stakeholders should collaborate to launch targeted campaigns emphasizing the quality and cultural significance of Hanwoo beef during this festive period. Offering special promotions or discounts, particularly on premium cuts, can incentivize purchases and help reduce inventory levels, stabilizing prices. Additionally, distributors in South Korea can explore alternative distribution channels beyond traditional wholesale markets. Direct sales to consumers through online platforms or partnerships with retail chains can provide additional avenues to move inventory, especially for premium Hanwoo beef.
Sources: Agrinet, Agromeat, Agronaplo, Canal Rural, MLA



