.jpg)
In W38 in the soybean landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- The continued absence of Chinese demand is causing US soybean prices to fall, with a 2.22% WoW drop. Creating significant economic ripple effects that threaten the country's freight and logistics sectors.
- Argentina's soybean sector is facing an internal paradox where a surge in raw bean exports to China is causing supply shortages and over 31% idle capacity for its domestic crushing industry.
- Brazil's strong export momentum saw a sharp slowdown in early Sep-25, presumably as demand from China dissipates in the short term. Meanwhile, Uruguayan prices surged over 7% WoW as it solidifies its new role as a key alternative supplier to China.
- Canadian soybean production is projected to decline by 5.7% nationwide in the 2025/26 season due to poor yields, creating a tighter domestic supply outlook. This forecast, driven by an 8.8% production drop in the key province of Ontario, is expected to provide underlying price support for Canadian producers.
1. Weekly News
Global
Global Soybean Margins Squeezed by Record Harvests and Rising Input Costs
Global soybean producers are facing a prolonged period of tightening profit margins that is expected to continue until at least mid-2027, according to a new report from RaboResearch. Farmers are facing mounting pressures from both rising operating costs and declining commodity prices. On the supply side, record-breaking harvests in key producing nations, including Brazil and the United States (US), are overwhelming the market and creating a bearish price environment. Simultaneously, input costs remain stubbornly high and are projected to climb further into the 2026 planting season. The report highlights rising fertilizer prices as a primary concern, with the global phosphate affordability index reaching its lowest point since 2010 at 0.68. While global consumption of grains and oilseeds is also at a historic high, it has been insufficient to absorb the record-breaking supply. This fundamental imbalance between massive production volumes and elevated input expenses will continue to challenge farmer profitability for the foreseeable future.
Argentina
Argentine Soy Crushers Face Pressure as Raw Bean Exports to China Surge
The ongoing trade dispute between the US and China has created a paradoxical situation for Argentina's soybean sector, where a boom in raw bean exports is simultaneously harming its world-leading crushing industry. Driven by strong Chinese demand for alternatives to US supply, Argentina's exports of unprocessed soybeans from the 2024/25 harvest have surged to a six-year high of 8.81 million metric tons (mmt). However, this has diverted supply away from domestic processors. As a result, idle capacity at the country's massive crushing facilities rose to 31% in Jul-25 and has reportedly widened since, leading to concerns about job losses and a decline in higher-value exports of soymeal and oil. The situation is compounded by increased competition from US soymeal in key markets like Southeast Asia, a byproduct of the US soybean surplus. Industry leaders have voiced concern that the trade war is ultimately detrimental to Argentina's value-added agribusiness sector, with the outlook remaining highly dependent on the outcome of US-China trade negotiations.
Brazil
Analysis Shows 97.21% of Mato Grosso's Soy Production Compliant With EUDR Standards
A comprehensive new analysis has found that over 97% of the soybean cultivation area in Mato Grosso, Brazil's largest soy-producing state, already meets the stringent requirements of the new European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). The assessment, conducted by the data intelligence firm MosaiX, is a critical development for global supply chains, as Mato Grosso accounts for nearly a third of Brazil's total soy exports. The EUDR, set to take full effect at the end of 2025, will prohibit the import of commodities grown on land deforested after December 31, 2020. Using satellite imagery and official land registry data, the study verified that 97.21% of the state's soy farmland is compliant, with no recent deforestation and full legal conformity. The remaining 2.79% was flagged as non-compliant, mostly due to post-2020 clearing. This high rate of compliance, supported by a sharp decline in the state's deforestation since 2023, provides significant reassurance to European buyers. While challenges in achieving full farm-to-port traceability remain, the findings demonstrate that major producing regions are well-positioned to adapt to the EU's rigorous environmental standards.
Brazilian Soybean Exports Slow Sharply in Early Sep-25
Brazil's soybean exports experienced a significant slowdown in the first half of Sep-25, lagging far behind the robust pace set in the same period last year. According to data from the Secretariat of Foreign Trade (SECEX), Brazil exported 2.718 mmt of soybeans between September 1 and 12. This volume is less than half of the 6.106 mmt shipped during the entire month of Sep-24, indicating a much slower start to the month's shipping program. The average daily export volume in Sep-25 was 271,800 mt, a figure down 30% from the daily average in the previous year. This deceleration contrasts sharply with a strong performance in Aug-25, when exports surged to 9.34 mmt, a 16.1% year-on-year (YoY) increase. The average export price also showed a slight decline, down 1% from last year to USD 419.1/mt. The slowdown may be linked to high inventory levels in China, Brazil's primary customer, where soybean stocks have recently been reported to be at new highs, potentially causing a temporary lull in shipment demand.
Canada
Statistics Canada Projects 5.7% Decline in National Soybean Production Amid Lower Yields
Canada's 2025 soybean production is projected to decrease by 5.7% YoY to 7.1 mmt, according to a new forecast from Statistics Canada. The national decline is primarily driven by a projected 6.9% drop in average yields to 45.7 bushels per acre, which is expected to more than offset a 1.3% increase in total harvested area. The downward trend is heavily influenced by Ontario, the country's largest soybean-producing province, where production is forecast to fall by 8.8% to 4.0 mmt due to decreases in both harvested area and yield. Production in Quebec is also expected to decline by 7.8%. In contrast, Manitoba is projected to see a 2.9% increase in production to 1.7 mmt. However, this growth is entirely the result of a 15.6% expansion in harvested area, as the province's average yield is anticipated to fall by a sharp 10.9%. The report indicates a challenging growing season for yields across Canada's key soybean regions.
United States
China's Halt on US Soybean Orders Threatens Widespread Impact on Freight Industry
The absence of new Chinese soybean orders from the US for the 2025/26 season is poised to create significant negative ripple effects that extend beyond farming to the entire US freight and logistics industry. With China shifting its purchases to South America due to high retaliatory tariffs, the anticipated decline in US export volumes threatens to reduce demand across the transportation sector, impacting rail, trucking, and port operations. The fallout is expected to be particularly severe for freight rail lines that transport soybeans from key Midwest producing states to export terminals in the Pacific Northwest. As the peak US export season begins, the lack of Chinese demand creates a logistical vacuum. In 2024, the US shipped USD 12.8 billion in soybeans to China. For the current season, zero new orders have been placed. This dramatic drop in volume is projected to put pressure on jobs across the supply chain, from rail crews and warehouse workers to port operators. The situation highlights the deep integration of the agricultural and transportation sectors and the broad economic consequences of disruptions in major international trade flows.
2. Weekly Pricing
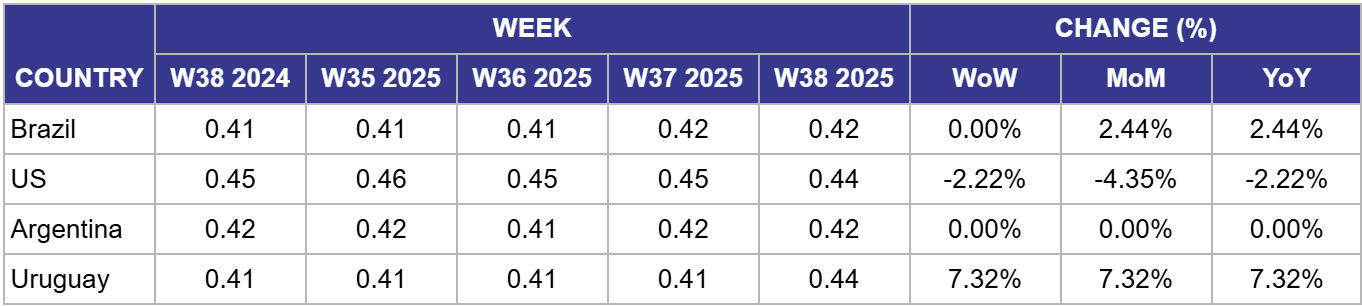
Weekly Soybean Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Soybean Pricing Important Exporters (W38 2024 to W38 2025)
Brazil
In Brazil, the price of soybeans remained stable at USD 0.42/kg in W38, experiencing no week-on-week (WoW) changes, but up by 2.44% both month-on-month (MoM) and YoY. The WoW stability reflects a market balancing mixed signals. On one hand, prices are supported by positive long-term news, such as a report showing 97% of Mato Grosso's soy is compliant with new European Union (EU) deforestation rules, which helps secure access to a key high-value market. The MoM and YoY strength is a carryover from strong demand earlier in the month. However, the market's failure to advance further WoW is due to bearish short-term export data. Reports showed that shipments in the first half of Sep-25 were significantly slower than last year's pace, with daily volumes down 30% YoY, suggesting a temporary lull in demand from major buyers like China.
United States
In the US, the price of soybeans was USD 0.44/kg in W38, showing a decline of 2.22% WoW and YoY, and a more significant drop of 4.35% MoM. The continued price decline across all timeframes reflects the intensifying pressure on the US market. The primary driver remains the complete absence of new crop sales to China, a situation now understood to be impacting the broader US freight and logistics industry, signaling a deep economic fallout. With the peak harvest season underway, the lack of its primary export outlet is creating a domestic supply glut that weighs heavily on prices. The global context of tightening farmer profitability, as highlighted in recent reports on high input costs and low commodity prices, is particularly acute in the US, where the geopolitical situation is exacerbating an already challenging market environment.
Argentina
In Argentina, the price of soybeans was USD 0.42/kg in W38, holding stable WoW, MoM, and YoY. This price stability suggests the market is digesting a complex and contradictory set of factors. While the price of raw soybeans is supported by strong export demand from China, this very trend is creating a new problem. A significant portion of the domestic crushing industry is now facing supply shortages, with idle capacity rising above 31% as unprocessed beans are prioritized for export. This internal conflict between raw exporters and domestic processors is creating uncertainty. The market appears to have reached an equilibrium, balancing the strong external demand for raw beans against the negative economic impact on its world-leading value-added soymeal and oil sector.
Uruguay
In Uruguay, the price of soybeans surged to USD 0.44/kg in W38, marking a sharp increase of 7.32% across WoW, MoM, and YoY comparisons. This significant price surge indicates that the market is now aggressively pricing Uruguay's improved standing as a supplier to China. While the news of China's supplier diversification strategy emerged in previous weeks, this sharp upward movement suggests that concrete sales or strong buyer interest are now materializing, lifting prices from their previous state of equilibrium. As a smaller producer compared to Brazil and Argentina, even moderate shifts in demand from a major buyer like China can have a disproportionately large impact on local prices. This spike reflects the country's successful capitalization on the current geopolitical shifts in the global soybean trade.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Brace for a Prolonged Downturn and Diversify Service Offerings
For US farmers and logistics providers, the severe disruption in soybean exports has become a systemic issue affecting the entire supply chain, from farm gate to port. Farmers must prepare for a prolonged period of low prices by managing costs, maximizing storage to avoid selling into harvest pressure, and focusing on domestic processors. For the freight and logistics sectors, the sharp drop in agricultural export volumes necessitates immediate diversification. Rail and trucking companies heavily reliant on the Midwest-to-Pacific Northwest grain corridor should aggressively pursue contracts in other sectors and regions to offset the lost volume. This is not a temporary dip but a significant market shift, requiring structural adjustments to business models to maintain solvency through a challenging period.
Re-evaluate Sourcing Strategies Based on New Risk and Supply Profiles
For global buyers and importers, recent developments require a reassessment of sourcing strategies. The tightening supply in North America, evidenced by a projected 5.7% drop in Canadian production, suggests buyers should secure Canadian contracts early to mitigate price risk. The internal conflict within Argentina's soy sector, where crushers are short on supply, may impact the future availability and pricing of Argentine soybeans, warranting a review of processed product contracts. Furthermore, buyers for the EU market can now source from Brazil with greater confidence, given the high EUDR compliance data from Mato Grosso. Importers should update their risk matrices to reflect these evolving supply, regulatory, and internal market dynamics in key producing nations.
Sources: Tridge, Statistics Canada, UkrAgroConsult, Farming Online, Reuters, RaboResearch




