W46 2026: Beef

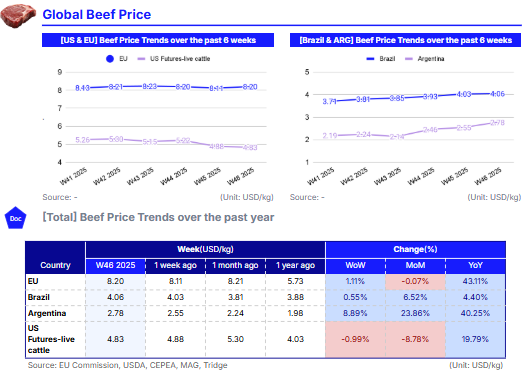
In W46, global beef markets remained tight, pushing prices higher. EU beef averaged USD 8.20/kg, up 1.11% WoW, supported by stable demand and supply constraints. Brazil and Argentina saw rises to USD 4.06/kg and USD 2.78/kg respectively, driven by strong seasonal consumption. US live cattle futures averaged USD 4.83/kg, slightly down WoW and MoM but 19.79% higher YoY, reflecting low domestic supplies. Earlier US tariffs on Brazilian beef had intensified price pressures, but the recent removal of the 40% tariff is expected to ease supply constraints and reduce retail costs. In Europe, the EU introduced a safeguard under Mercosur to protect domestic farmers, though enforcement concerns remain. Importers and processors are recommended to diversify sourcing and use forward purchasing strategies. Meanwhile, Brazilian and Argentine exporters can leverage strong domestic and international demand to optimize production and market access.
1. Weekly Price Overview
Rising Consumption and Tight Supply Drive Beef Price Movements in W46
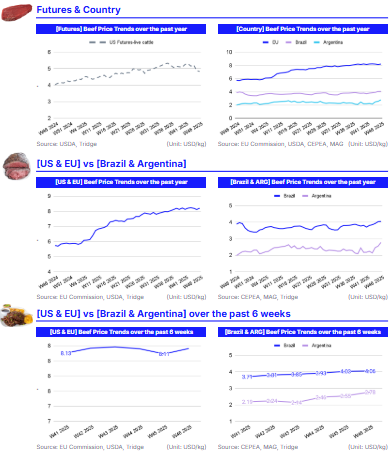
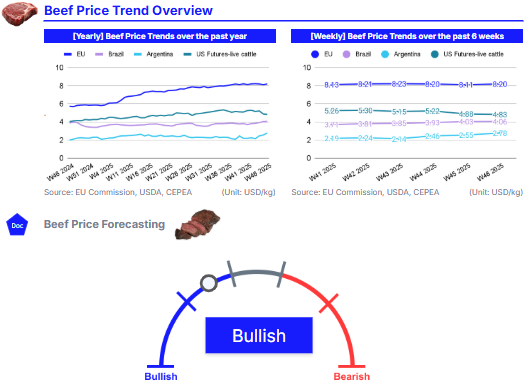
In W46, European Union (EU) beef prices averaged USD 8.20 per kilogram (kg), rising 1.11% week-on-week (WoW) and 43.11% year-on-year (YoY), but down 0.07% month-on-month (MoM). The continued elevation in prices is supported by stable domestic demand and persistent supply constraints linked to structural production challenges across the sector.
In Brazil, prices reached USD 4.06/kg, increasing 0.55% WoW, 6.52% MoM, and 4.40% YoY. The weekly gain is mainly due to stronger domestic consumption ahead of the festive season, as beef demand typically rises in the final two months of the year. Argentina recorded a significant upward trend, with beef prices rising 8.89% WoW to USD 2.78/kg, marking a 23.86% MoM and a 40.25% YoY increase. This surge reflects strengthened domestic demand in anticipation of upcoming holidays and festivals. Despite ongoing inflationary pressures expected to persist through the end of the year, consumption has continued to grow. According to the Argentine Chamber of the Meat and Meat Products Industry and Commerce (CICCRA), per capita consumption has reached 49.1 kg per year, up 3.2% compared to 2024.
Meanwhile, United States (US) live cattle futures averaged USD 4.83/kg, declining 0.99% WoW and 8.78% MoM, but still standing 19.79% higher YoY. The elevated annual level reflects historically tight cattle supplies after years of drought that reduced pasture availability and raised feeding costs. However, both live cattle and feeder cattle futures weakened under pressure from a softer cash market, contributing to the recent downward weekly and monthly movements.
2. Price Analysis
Rising Demand and Trade Measures Drive Volatility in Global Beef Markets
Global beef markets are facing tight supply and rising prices in 2025, driven by strong demand and constrained production. Robust consumption from major markets, including the US and China, combined with reduced output in New Zealand, South America, and Australia, continues to support elevated prices.
In the US, domestic cattle inventories are historically low, and tariffs on Brazilian beef earlier in 2025, ranging from 40% to 76%, further intensified price pressures by restricting imports. Initially imposed amid trade disputes, these measures contributed to higher retail beef costs and market volatility. Recent policy adjustments, including the removal of the 40% tariff on Brazilian beef on November 20 by the US government, are expected to ease supply constraints, stabilize futures markets, and reduce consumer prices, while restoring export opportunities for Brazil.
In Europe, the EU introduced a safeguard mechanism under its Mercosur trade agreement to protect domestic farmers from sudden import surges. However, some member states, notably France, have raised concerns about the enforceability of the mechanism and the adequacy of health and environmental compliance for imported beef.
3. Strategic Recommendations
Optimizing Supply and Profitability in Tight Global Beef Markets
Given the stable demand and tight supply in the EU, importers and processors should focus on establishing long-term contracts with reliable international suppliers, particularly from South America, Oceania, and Australia, to mitigate the risk of domestic production shortfalls. Diversifying sourcing portfolios will also help cushion against sudden price spikes or trade disruptions. Additionally, leveraging forward purchasing agreements and inventory buffers can allow businesses to optimize cost management while ensuring consistent product availability during periods of high domestic demand.
For producers and exporters in Brazil and Argentina, the current market environment presents an opportunity to capitalize on both seasonal and global demand trends. Strong domestic consumption ahead of the holiday season underscores the need for efficient production scheduling and supply chain management. Exporters should actively explore emerging demand in key international markets such as the US, China, and other high-protein consuming regions, aligning shipments with periods of peak global demand. With the recent removal of the 40% US tariff on Brazilian beef, there is an immediate opportunity to regain market access and improve competitiveness in the North American market. Optimizing logistics and production efficiency while maintaining quality and compliance standards will be critical to fully benefit from these policy adjustments.
In the US, importers, wholesalers, and retailers should leverage the recent tariff removal by adjusting procurement strategies to secure cost-effective supplies from Brazil while balancing domestic production. Implementing flexible inventory management systems and hedging strategies, such as futures contracts or options, can help stabilize procurement costs and protect against ongoing market volatility. Retailers may also consider dynamic pricing approaches that reflect supply conditions while maintaining consumer affordability, particularly as beef prices remain sensitive to policy changes and global supply constraints.