
In W39 in the tomato landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Tomato prices at Brazil's Ceasa/Serra rose to USD 0.88/kg after a prior decline due to limited local winter production. Full harvests are expected in early 2026. Early Sep-25 wholesale prices fell while exports grew 28% in volume and 15% in revenue, with US tariffs limiting some markets.
- Japan approved a CRISPR/Cas9 gene-edited tomato with higher GABA content, highlighting advances in functional foods.
- In Pakistan, joint trials show pesticide use can be reduced by over 40% without affecting yields, supporting eco-friendly production and pest management.
- Kyrgyzstan’s tomato imports from Turkmenistan rose 15% YoY with higher average prices. Morocco strengthened its EU market position, exporting 568,370 mt in 2024/25 due to low production costs, favorable climate, and the Morocco-EU Association Agreement, despite falling Spanish market shares.
- The Region of Murcia highlighted tomatoes at the Fruit Attraction fair in Madrid, showcasing sustainable production, high-quality varieties, and promoting export opportunities through institutional support and innovative presentations.
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Tomato Prices Rise in Caxias do Sul as Regional Supply Awaits 2026 Harvest
Tomato prices at the Central Supply Center of Serra (Ceasa/Serra) in Caxias do Sul, Brazil, rose from USD 0.77 to 0.88 per kilogram (BRL 4.10/kg to 4.71/kg) after a period of decline, according to the Technical Assistance and Rural Extension Company of Rio Grande do Sul and the Southern Association for Rural Credit and Assistance (Emater/RS-Ascar). The increase reflects reliance on supplies from other regions, as local production was limited during winter despite greenhouse use. Planting has begun in lower-lying areas to advance the harvest. However, the bulk of the regional output is expected to be transplanted in Oct-25 and Nov-25, with harvesting projected for early 2026.
Brazilian Wholesale Tomato Prices Continue Sep-25 Decline Alongside Broader Vegetable Market Trends
Wholesale tomato prices in Brazil declined in early Sep-25, continuing a downward trend from Aug-25, with the weighted average price in Aug-25 falling 19.86% month-on-month (MoM), despite slightly lower supply, according to the National Supply Company's (CONAB) 9th Prohort Bulletin. The decrease reflects broader price reductions across several vegetables, while some high-quality products, such as carrots and watermelons, saw price increases due to limited supply. In the export sector, fruit and vegetable shipments increased by 28% in volume and 15% in revenue in the first eight months of 2025, although United States (US) tariffs constrained certain markets.
Japan
Japan Approves Gene-Edited Tomato with Enhanced GABA Content for Food Use
Japan’s Consumer Affairs Agency (CAA) has approved a gene-edited tomato for food use. The tomato was developed using CRISPR/Cas9, a precise gene-editing technology that allows targeted modification of DNA to alter specific traits. This modification enhances the activity of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD), thereby increasing GABA content in the fruit. This follows safety reviews of one genetically modified corn (MON95275) and one genetically modified cellulase (JPAN011). The gene-edited tomato represents a new addition to Japan’s list of approved gene-edited products, highlighting advances in functional food development.
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Boosts Tomato Imports from Turkmenistan by 15% YoY in Early 2025
Between Jan-25 and Jul-25, Kyrgyzstan imported 15,400 metric tons (mt) of tomatoes from Turkmenistan, a 15% year-on-year (YoY) increase from 2024, with a total value of USD 10 million. The average import price rose to USD 675/mt, an increase from USD 588/mt in the same period last year, reflecting higher costs alongside increased volumes.
Morocco
Morocco Emerges as Key Supplier in European Tomato Market
Morocco has strengthened its position in the European tomato market, exporting 568,370 mt to the European Union (EU) in 2024/25, representing 19.63% of total imports and generating USD 1.22 billion (EUR 1.04 billion). Its competitiveness stems from lower production costs, a favorable climate, and a cost-effective workforce, allowing extended production cycles without energy-intensive greenhouses. Supported by the Morocco-EU Association Agreement, Moroccan exports have gained market trust, positioning the country as a key supplier and a strategic partner in Europe’s tomato supply chain, amid declining shares from Spain and steady volumes from the Netherlands.
Pakistan
Pakistan–China Study Shows Eco-Friendly Pest Management Can Cut Tomato Pesticide Use by 40%
A joint Pakistan–China study demonstrated that Pakistani tomato farmers can reduce pesticide use by over 40% without affecting yields. Field trials in Sargodha, conducted by the University of Agriculture Faisalabad (UAF) and Yunnan University (YNU), tested an eco-friendly pest management system targeting invasive pests such as Tuta absoluta, an invasive moth species, commonly known as the tomato leafminer, that causes severe damage to tomato crops by feeding on leaves, stems, and fruits. The approach aims to improve tomato productivity across Pakistan’s 150,000-hectare (ha) tomato-growing area while mitigating environmental and health risks associated with excessive chemical spraying.
Spain
Murcia Highlights Tomatoes and Agricultural Innovation at Fruit Attraction Fair in Madrid
At the Fruit Attraction fair in Madrid, taking place from September 30 to October 2, 123 companies from the Region of Murcia will showcase their produce, with a special focus on tomatoes. Murcia’s 64 square meters (m²) institutional stand will feature an expanded vertical garden, a presentation and meeting area, and a kitchen for cooking demonstrations highlighting tomatoes. The region aims to promote exports, open new markets, and demonstrate its agricultural potential, supported by the participation of producers, exporters, and the Murcian Institute for Agricultural and Environmental Research and Development (IMIDA), which will present innovations in sustainable, high-quality food production.
Extremadura Tomato Producers Face USD 89 Million Losses Due to Adverse Weather and Low Industrial Prices
Tomato producers in Extremadura are facing estimated losses of USD 89.18 million (EUR 76 million) this season, according to the Union of Small Farmers and Ranchers – Union of Cooperatives of Extremadura (UPA-UCE). Adverse weather, including delayed spring rains and August heat waves, reduced yields by 20%, while industrial buyers imposed prices below production costs. Average production reached 82 mt/ha compared to the contracted 93 mt, threatening the viability of the region’s tomato sector and prompting concerns over the sustainability of future campaigns.
2. Weekly Pricing
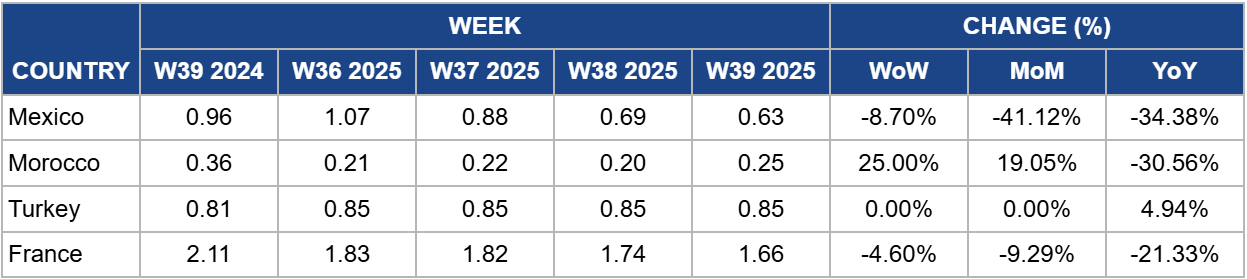
Weekly Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (W39 2024 to W39 2025)
.png)
Mexico
Mexico’s tomato prices fell 8.70% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 0.63/kg in W39, marking a 34.38% decline YoY from USD 0.96/kg. The drop reflects weakened demand in key export markets, especially the US, after the mid-July termination of the Tomato Suspension Agreement and the imposition of a 17.09% duty on Mexican imports. Exporters have adjusted volumes and pricing strategies, while the government’s minimum export price policy, establishing floors of USD 0.95/kg for round tomatoes, USD 0.88/kg for Roma, and USD 1.70/kg for specialty tomatoes, helped stabilize prices. Continued harvesting of pre-policy crops, coupled with higher yields from Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) and seasonal production peaks, created a temporary oversupply, contributing to the price decline. If current supply trends persist and export restrictions remain, prices may stay subdued in the near term, though minimum export prices could limit further losses.
Morocco
In W39, Morocco’s tomato prices rose 25% WoW to USD 0.25/kg, though they remain 30.56% below last year’s USD 0.36/kg. The price decline reflects abundant domestic supply and record 2024/25 exports of 745,000 mt, a rise of 8.3% YoY, which ensured steady availability in European markets. Despite a minor contamination alert in early Sep-25, shipments continued, maintaining strong flows. High production volumes, competitive pricing, and lower-cost imports continue to exert downward pressure on wholesale prices, limiting near-term gains and keeping Morocco highly competitive against higher-cost European producers.
Türkiye
Türkiye’s tomato prices held steady at USD 0.85/kg in W39, unchanged WoW and MoM, but a rise of 4.94% YoY from USD 0.81/kg. Price stability is supported by consistent domestic demand, abundant late-summer harvests, and favorable weather, while low-capacity factory processing and regional harvest timing moderate fluctuations. The modest YoY increase reflects inflationary pressures, including higher labor, energy, and packaging costs. This stability suggests that near-term prices are likely to remain steady, with limited upside unless export demand strengthens or supply constraints emerge.
France
In W39, France’s tomato prices fell 9.29% WoW to USD 1.66/kg, a decline of 21.33% YoY from USD 2.11/kg. The decline reflects weaker domestic consumption due to cooler weather, increased imports of lower-priced Moroccan tomatoes, and rising domestic supply. Accumulating stockpiles and competition from international suppliers continue to pressure prices, while quality remains generally good despite a higher proportion of green fruits being delivered. If imports and subdued consumption persist, French tomato prices are likely to remain under pressure in the near term.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhance Winter Production and Early Harvest Planning
Brazilian tomato producers, particularly in Serra and Caxias do Sul, should accelerate the development of lower-lying and greenhouse areas to advance planting and harvesting. Implementing staggered transplant schedules and leveraging CEA can help mitigate winter supply shortages, stabilize wholesale prices, and reduce reliance on interregional imports. Coordination with local extension services, such as Emater/RS-Ascar, can optimize timing and yield outcomes.
Promote Sustainable Pest Management in Key Producing Regions
Authorities and agricultural associations should encourage the adoption of eco-friendly pest control practices, similar to Pakistan–China trial systems, to reduce pesticide use by over 40% while maintaining yields. Integrating biological control methods against invasive pests like Tuta absoluta, combined with training and support programs for farmers, can enhance productivity, lower input costs, and improve the environmental sustainability and marketability of tomatoes in domestic and export markets.
Leverage International Market Opportunities and Product Differentiation
Exporters should capitalize on functional and high-quality tomato innovations, such as gene-edited or high-GABA varieties, to access premium markets like Japan. Simultaneously, producers in competitive regions (e.g., Morocco, Murcia, France) should differentiate through quality certifications, traceability, and marketing campaigns highlighting sustainability, specialty varieties, and seasonality. Targeting emerging markets in Europe, West Africa, and Asia while monitoring tariff and regulatory changes will help maintain stable revenue and mitigate price volatility.
Sources: Tridge, Agrolink, Agro Diario, Foodmate, Fresh Plaza, HortiDaily, Morocco World News, Unión de Pequeños Agricultores y Ganaderos (UPA)






