W44 2024: Soybean Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Global
Increased Rainfall Boosts Crop Planting and Conditions in South America and the US
Increased rainfall across South America has accelerated soybean and corn sowing, improving crop conditions and raising market pressure, with Brazil's 2024/25 soybean production forecast revised to 167 million metric tons (mmt). In Argentina, rain has replenished soil moisture for upcoming soybean planting. Meanwhile, in the United States (US), record soybean harvests driven by dry, warm weather have led to a supply surge and falling prices, with recent rains expected to improve winter wheat crop conditions.
Brazil
Brazil Soybean Planting Advanced Due to Rainfall
As of W44, Brazil planted 36% of its soybean crop, slightly behind last year's 39.1% and the 44.4% average. The planting rate advanced 18% during the week, with the state of Mato Grosso contributing half of the planting progress. Planting is more advanced in the southern regions and lagging in the central and northern areas. Recent rainfall focused on central Brazil, with drier conditions in the north and south. The forecast predicts more widespread rain in the coming days. In Mato Grosso, soybean planting reached 55.7% as of W44, compared to 70% last year and 62.3% on average. The mid-north region is the most advanced, with 74% planted, while the southeast lags at 41%.
Russia
Russia's Soybean Harvest Advanced in W44
Russian farmers have completed 88.4% of the soybean harvest as of W44, totaling 6.7 mmt with an average yield of 1.76 metric tons (mt) per hectare (ha), a drop of 0.28 mt/ha from 2023. The Southern Federal District saw the most significant yield drop, down 35%, due to drought conditions. Despite the yield reductions in the Southern and Central Federal Districts, the expansion of sown areas in the Central District has supported a high soybean harvest. The gross harvest is forecasted to reach at least 7.3 mmt, setting a record for the country.
United States
US Soybean Processing Rebounded in Sep-24, Driven by Increased Capacity and Biofuel Demand
US soybean processing rebounded in Sep-24, reaching a total of 5.6 mmt, marking a 7.2% year-on-year (YoY) increase from Sep-23. This growth is primarily driven by expanded processing capacity and the construction of new plants in recent years, as processors aim to capitalize on the rising demand for soybean oil, especially for biofuel production. The processing rate is forecasted to increase further in the coming months as the new US soybean crop enters the market, providing more supply and supporting continued growth in the sector.
US Soybean Export Sales for the Week Ending October 24
The United States Department of Agriculture's (USDA) latest weekly export sales report for the week ending October 24 showed soybean sales of 2.27 mmt from the 2024/25 harvest, falling within market expectations, which ranged between 1.6 and 2.8 mmt. China purchased 715 thousand mt, while another 446.9 thousand mt were sold to unknown destinations. Total US soybean sales for the 2024/25 commercial year have reached 26.27 mmt, up from 23.16 mmt during the same period last year. However, there is a potential slowdown in short-term demand due to longer ship certification times in China, which could lead to delays and increased risks of demurrage.
2. Weekly Pricing
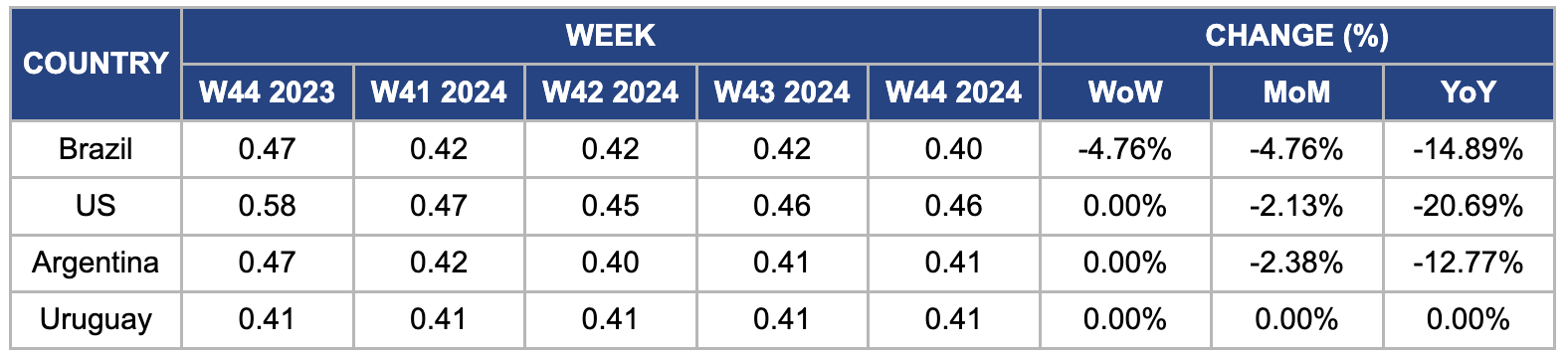
Weekly Soybean Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Soybean Pricing Important Exporters (W44 2023 to W44 2024)
Brazil
In W44, Brazilian soybean prices dropped by 4.76% week-on-week (WoW) and month-on-month (MoM), reaching USD 0.40/kg, also declining 14.89% YoY. This decline is attributed to the increase in Brazil's soybean harvest forecast to a record 166.2 mmt, up 0.7% from previous estimates, driven by a positive revision in planted area. National average productivity remained steady at 3.55 mt/ha. However, the large concentration of crops in the same development phase poses risks, with weather conditions in the coming months critical to confirming the record forecast. The soybean supply and demand balance remains unchanged, and the new cycle is expected to begin with tight stocks due to strong demand for the 2023/24 harvest.
United States
In W44, US soybean prices rose to USD 0.46/kg, reflecting a 2.13% decrease MoM and a 20.69% YoY decline. This price movement comes as the US concludes its soybean harvest with record yields. The USDA's report raised its 2024/25 US soybean production forecast to 124.9 mmt, up 4.2 mmt from the previous month's estimate. This increase was attributed to higher harvested area and yield projections, surpassing market expectations and the 2021 record of 4.46 billion bushels. The USDA also revised global ending stocks upward, further influencing the market.
Argentina
In W44, Argentina's soybean prices remained stable WoW but fell by 2.38% MoM and 12.77% YoY, reaching USD 0.41/kg. The USDA forecasted Argentina's 2024/25 soybean crop at 52 mmt, 1 mmt higher than its previous estimate. Local growers are increasingly shifting from corn to soybeans due to concerns about the corn dwarfism epidemic, low corn prices, and expectations of dry weather. Moreover, the soybean processing forecast for 2024/25 has been raised to 42 mmt, driven by expectations of higher yields and increased imports, mainly from Paraguay, as Argentina's processing sector recovers from years of drought.
Uruguay
In W44, Uruguayan soybean prices remained stable at USD 0.41/kg, supported by the strength of the Uruguayan peso against the US dollar, which helped offset currency fluctuations. Strong global soybean market trends and consistent demand from major importing countries, especially China, also contributed to the price stability. Moreover, existing inventory from previous harvests provided a buffer against potential lower yields, while the continued adoption of agricultural technology in the region bolstered yield potential, further supporting the market.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Capitalize on the Biofuel Demand
The US should continue expanding its soybean processing capacity to meet the rising demand for soybean oil, particularly from the biofuel sector. Given the recent rebound in soybean processing and the growing interest in biofuels, there is a significant opportunity to maximize the use of the 2024/25 soybean crop. By investing in new processing plants and enhancing existing facilities, US producers can increase output, ensuring more conversion of soybeans into valuable by-products like biodiesel. This will boost the domestic soybean processing industry and align the US with global sustainability trends, pushing biofuel demand. Moreover, focusing on higher-value products, such as high-protein meal and oil, can open new markets for US soybeans, increasing export opportunities.
Invest in Drought-Resilient Soybean Varieties
Russian soybean farmers must invest in drought-resistant soybean varieties, such as Pioneer 94M80 or Syngenta's NK Soybeans, specifically bred to thrive under water-stressed conditions. These varieties have improved drought tolerance, allowing for more stable yields even in dry conditions and safeguarding production in regions prone to water shortages. Additionally, incorporating advanced irrigation systems, such as drip or sprinkler irrigation, would help mitigate the impact of dry spells. Precision irrigation techniques, which optimize water use and minimize waste, can increase overall crop resilience, ensuring that Russian soybean farmers maintain competitiveness in the global market despite climatic challenges.
Optimize Planting and Harvesting Schedules to Avoid Weather Risks
Brazil should focus on improving the synchronization of soybean planting and harvesting schedules to minimize risks from adverse weather conditions. Given the uneven progress in planting across different regions and the uncertainty of future weather patterns, farmers should consider implementing a staggered planting approach. This approach, combined with improved weather forecasting tools, would allow farmers to adjust planting times based on rainfall predictions, reducing the likelihood of crop damage due to unexpected rain patterns or droughts. Furthermore, this strategy could help balance supply throughout the year, improving price stability and avoiding oversupply at harvest, which could depress prices.
Sources: Chacra Magazine, UkrAgroConsult, NoticiasAgricolas, Oilworld, FastMarkets




