W45 2024: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
1. Weekly News
Europe
EU and UK Ban Brazilian Beef Imports Over Hormone Concerns
On November 5, 2024, the European Union (EU) and the United Kingdom (UK) announced a ban on Brazilian beef imports due to concerns about the hormone estradiol, which is prohibited in the EU because of health risks. European audits found Brazil's livestock traceability system lacking, making it unable to guarantee that meat exports were estradiol-free. Affecting nearly 7% of Brazil's beef exports, this ban poses significant economic risks for Brazil, whose agricultural sector heavily relies on these markets.
Brazil has 12 months to improve its certification protocols to meet EU standards. During this period, it must address hormone control issues and enhance its overall traceability systems. The ban also affects European consumers, who may face meat shortages and price hikes, though countries like Argentina and Australia could potentially fill the supply gap if they meet EU safety regulations. Meeting these challenges is essential for Brazil to restore consumer trust in Europe and secure its position in the global meat market.
Diverging Trends in European Cattle Herds
In its latest report, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) reveals that dairy and beef herd trends differ in Western and Central Europe. Western Europe has seen significant herd reductions, while Central Europe is stabilizing its cattle numbers, largely due to the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy (CAP). CAP’s support is land-based in Western Europe but targeted toward small cattle farms in Central Europe, fostering herd stability.
Central Europe also shows a trend of switching from dairy to beef production due to the lower investment and labor demands of beef farming. Countries like Romania anticipate steady growth in beef cow numbers through 2025, with similar developments in Croatia, Bulgaria, and Greece. This shift signals a broader trend in Central Europe toward commercializing and consolidating cattle farming, with increased efficiency and less reliance on small-scale backyard operations.
Argentina
Argentina Achieves Record Beef Exports in 2024
Argentina’s Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries reported that the country’s beef exports reached nearly 700 thousand metric tons (mt) from Jan-24 to Sep-24, generating USD 2.12 billion, the highest in 57 years. Argentina’s beef reaches 48 global markets, with 99% of shipments going to the top 10 destinations. Top export markets included the United States (US), with an increase of 46% year-on-year (YoY), followed by Chile (+21% YoY), Israel (+11% YoY), the EU (+7% YoY), and China (+4% YoY), with Mexico joining as a major importer. Of the beef exported, 16% were chilled cuts, and the rest were frozen, with chilled cut destinations expanding from 31 in 2023 to 44 countries so far in 2024.
At the China International Import Expo, the Secretary for Production Coordination emphasized Argentina’s efforts to remove trade barriers and improve export quality through electronic traceability. Argentine beef production reached 2.34 million metric tons (mmt) in the first nine months of 2024, surpassing recent averages, with 30% serving the domestic market. The secretary also promoted Argentine beef’s reputation for quality in markets like China and Japan, supporting future growth and investment opportunities.
Australia
Australia Witnesses Record Beef Exports in Oct-24
According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), Australia’s beef exports totaled 130.05 thousand mt in Oct-24. This marked a 24% increase from Oct-23 and set a new monthly record, surpassing the previous peak in Jul-24. The US emerged as the primary destination for Australian beef in Oct-24, with exports up 64% YoY to 45.34 thousand mt, the second-highest monthly shipment to the US. Most of the exported beef was frozen, although chilled beef exports surged by 88% YoY to reach 11.57 thousand mt, the highest monthly volume of chilled beef ever sent to the US.
South Korea was the second destination, with a 13% YoY import increase to 19.73 thousand mt. Indonesia was another significant destination, with shipments nearly doubled, rising 95% from Oct-23 to 11.03 thousand mt. Year-to-date (YTD), Australian beef exports have reached 1.1 mmt, the highest volume ever recorded from January to October. As projected in MLA’s latest Cattle Projections, Australia is on track to close out 2024, with export volumes potentially exceeding the record set in 2014.
Brazil
US Election Results and Its Impact on Brazil's Beef Exports to the US
According to a Brazilian agricultural consulting firm, Agrifatto, the result of the US elections could impact global trade policies, indirectly affecting Brazil’s livestock sector. The potential for protectionist measures, such as import tariffs, may make it harder for Brazil to increase its beef export quota to the US beyond the current 65 thousand mt, which faces a 26.4% surcharge. Despite this, US demand for Brazilian beef is rising due to challenges in US production, with 2025 beef output expected to be the lowest since 2015.
US beef imports are projected to reach a record high of 2.01 mmt by 2025, further boosting Brazilian exports. From Jan-24 to Sep-24, Brazilian beef shipments to the US reached a historic 117.9 thousand mt, making the US Brazil’s second-largest beef importer, accounting for 5.6% of total exports. Agrifatto stresses the importance of monitoring US beef production and imports to understand future demand for Brazilian meat.
Brazilian Beef Exports Hit Record High in Oct-24
The Brazilian Association of Meatpackers (Abrafrigo) reported that Brazil’s beef exports, including fresh and processed products, reached 319.39 thousand mt, valued at USD 1.38 billion in Oct-24. This reflects a significant 34% increase in volume and a remarkable 41% rise in value compared to Oct-23, setting a record for monthly shipment volume and revenue. The average price per ton of beef stood at USD 4,321 in Oct-24, up 5.7% from USD 4,087 in Oct-23. This price trend aligns with rising live cattle prices in the domestic market.
From Jan-24 to Oct-24, Brazil’s beef exports totaled 2.67 mmt, valued at USD 10.77 billion, a 34% YoY increase in volume and a 23% YoY rise in value. However, the average price per ton during this period was USD 4,037, down 7.9% from USD 4,382 over the same period in 2023. China continues to be the top destination for Brazilian beef, importing 1.09 mmt (+11.2% YoY), followed by the US (+88.8% YoY), the United Arab Emirates (+126.1% YoY), and Chile (+4.7% YoY).
South Korea
French Beef Returns to South Korea After 24-Year Ban Amid Market Challenges
French beef has returned to the South Korean market for the first time since a 2000 ban due to mad cow disease concerns. Following Korea's recent approval of French beef import standards, the French Embassy celebrated this milestone with an event held on November 4, 2024, importing 70 kilograms (kg) of beef for display and arranging meetings with major Korean retailers. France, the EU's largest beef producer at 1.36 mmt annually, adheres to strict farming practices, avoiding growth hormones and primarily using farm-produced feed.
However, French beef may face hurdles in the South Korean market, where imports are dominated by US and Australian beef, which represent over 90% of imported beef. Large South Korean retailers, such as E-Mart and Homeplus, remain cautious due to high import costs for French beef, which limits its price competitiveness. Currently, EU beef holds a minimal 0.1% to 0.2% share in South Korea, mainly distributed to restaurants and processors. The French industry seeks South Korean partners interested in offering premium, customized beef options.
United States
Prolonged Drought Conditions in the US Affect Cattle Herding
The US Drought Monitor reports that despite recent rain, most of Arkansas remains under drought, significantly affecting cattle producers’ hay feeding. The University of Arkansas reports that the drought has stunted the growth of fescue grass and delayed the planting of Bermuda grass, which will not be ready for grazing until late spring. With sparse forage, many pastures are overgrazed, leaving fields vulnerable to weeds and weakening root systems. While rain is expected, continued warm weather could prolong these issues, especially in northwest Arkansas and counties near Oklahoma, where drought is most severe.
The prolonged drought has also increased feed costs, but many Arkansas producers managed to harvest two hay cuttings earlier in the year. Although this supply is typically adequate, the fall drought may force earlier feeding. Extension economists noted that most cattle herds have already been downsized after years of culling, limiting further reductions. Analysts suggest conservation measures like strip grazing, which limits cattle to specific areas, and rotating animals across fields to naturally fertilize the soil and make the hay supply last longer.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
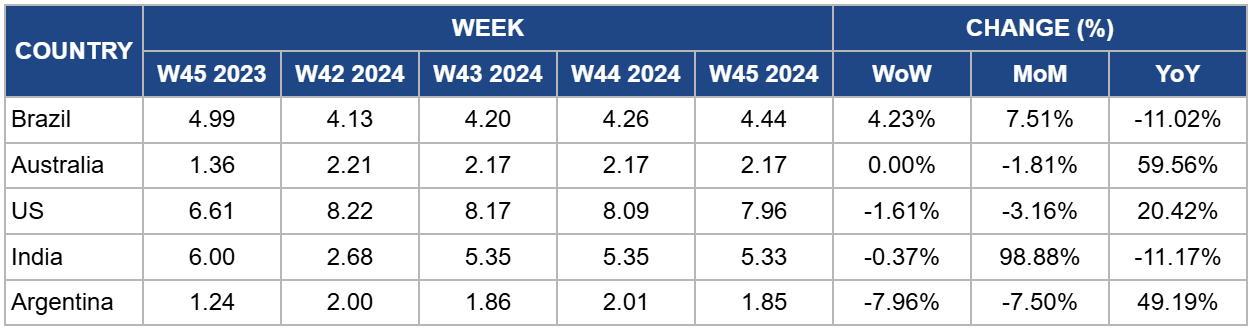
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W45 2023 to W45 2024)
Brazil
In W45, Brazil’s wholesale price for boneless rear beef rose to USD 4.44/kg, reflecting a 4.23% week-on-week (WoW) increase and marking the fifth consecutive week of price hikes. This price also represented a 7.51% month-on-month (MoM). A leading agribusiness and rural-focused television network in Brazil, Canal Rural reported that increasing demand and limited supply due to one of the season's most restricted slaughter schedules likely drove the WoW rise. However, Brazil’s low consumer purchasing power continues to constrain beef demand, pushing many consumers toward more affordable protein options like chicken, sausages, and eggs.
Australia
Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator averaged USD 2.17/kg in W45, a significant 59.56% YoY rise but a 1.81% MoM drop. According to MLA, the cattle market remained steady, with minimal changes across key indicators. Yardings rose by 2.47 thousand heads to 61.62 thousand heads, though buyer activity was somewhat subdued due to the Melbourne Cup. Despite a general dip in quality, high-quality heavy export steers and heifers were still available. The steer-to-heifer premium remains 23% to 38% above the heifer market, reflecting low demand for breeding females, which may exert downward pressure on heifer prices.
United States
In W45, lean beef (92% to 94%) in the US averaged USD 7.96/kg, reflecting a 1.61% WoW drop and marking the ninth consecutive week of price declines, the lowest level since W23. This price also represents a 3.16% MoM drop. Despite this recent decrease, prices are still up 20.42% YoY, mainly due to tight domestic supply from a shrinking cow herd. The current decline aligns with a seasonal demand dip as winter approaches, following peak consumption in the summer. Nonetheless, limited production continues to keep lean beef prices elevated overall.
India
The average price of cow beef in India reached USD 5.33/kg in W45, remaining relatively stable with a slight 0.37% WoW drop but a sharp 98.88% MoM increase. This price was also 11.17% YoY lower. This significant monthly rise underscores ongoing volatility in India’s beef market, driven by shifting domestic and international regulations alongside variable local supply. Consequently, prices have become increasingly unpredictable, shaped by evolving policies and dynamic supply chain conditions.
Argentina
In W45, Argentina's average steer beef price fell to USD 1.85/kg, a 7.96% WoW decline and a 7.50% MoM drop, reaching its lowest level since W18. Beef prices in Argentina have remained consistently low in 2024, largely due to reduced domestic demand amid the ongoing economic crisis. Data from the Chamber of Industry and Commerce of Meat and Derivatives of the Argentine Republic (CICCRA) shows that per capita beef consumption dropped by 12.3% in the first nine months of 2024, averaging 46.8 kg, an annual decrease of 6.6 kg per person. The 12-month moving average as of Sep-24 was 47.5 kg per capita, a 10.9% YoY decline.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Improve Beef Export Certification to Overcome EU and UK Ban on Brazilian Beef
To mitigate the impact of the EU and UK beef import bans, Brazil should focus on strengthening its livestock traceability and hormone control systems. Immediate steps should include upgrading the certification protocols for beef exports to meet EU regulations and enhancing traceability systems to guarantee hormone-free beef. Brazil can also invest in training for farmers and meatpacking facilities to ensure compliance with international standards. Expanding partnerships with global certification bodies can help regain trust and access to the European market within the 12-month deadline.
Leverage Argentina's Record Beef Exports for Global Market Expansion
Argentina should continue its momentum in beef exports by expanding its chilled beef offerings and entering new global markets. Strengthening electronic traceability systems and removing trade barriers will help Argentina maintain growth in markets like China and Japan. Additionally, the country should engage in strategic marketing campaigns highlighting the high quality of its beef products to attract premium buyers in the US and the EU. By prioritizing long-term relationships with key importers and strengthening logistics, Argentina can further solidify its position as a leading beef exporter.
Minimize Impact of Potential US Tariffs on Brazilian Beef Exports
Brazil should proactively monitor the political climate in the US to anticipate and mitigate the impact of potential protectionist measures. Strengthening relationships with US stakeholders, such as industry associations, could help lobby against tariffs and safeguard market access. Diversifying beef export destinations, including exploring opportunities in emerging markets like Southeast Asia, could reduce dependence on the US market. Additionally, Brazilian beef exporters should focus on promoting the quality and sustainability of their products to maintain competitive pricing and appeal to premium buyers.
Expand South Korean Market for French Beef Amidst Growing Competition
To succeed in the South Korean market, French beef producers should focus on offering premium, customized beef options that cater to the high-end restaurant and processing sectors. Collaborating with local distributors and retailers could help create awareness and build consumer demand for French beef. Additionally, strategic partnerships with South Korean chefs and foodservice providers could drive product differentiation. Pricing strategies should be adjusted to consider the high import costs, and offering tailored promotions to target niche markets could improve French beef's competitiveness.
Sources: Tridge, Agromeat, Elagro, MLA, Portal Do Agronegocio, Talkbusiness, The Cattle Site, UkrAgroConsult, Yna


