
1. Weekly News
Global
Global Orange Industry Faces Crisis from HLB Disease
The global orange industry is facing an unprecedented crisis due to the spread of Huanglongbing (HLB) disease, or citrus greening disease, transmitted by psyllids. This disease has devastated citrus plantations for decades, forcing the uprooting of 56 million trees and significantly reducing production in regions like Florida, the United States (US), and Brazil. The disease is advancing in Europe, and cases have been reported in Portugal, Spain, and Cyprus. The economic toll has been severe, and orange juice prices have tripled since 2022. Researchers have not yet found a fully effective treatment despite extensive efforts. Efforts to combat the disease are underway, with international initiatives mobilizing in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. However, the rapid spread of HLB raises the alarming prospect of orange juice becoming a luxury product or disappearing entirely.
Brazil
Brazil's Orange Production Faces Historic Decline Due to Drought and Disease
Extreme drought and widespread citrus greening disease are expected to drive Brazil's orange production to its lowest level in over 30 years. Extreme drought in the country has severely impacted water levels across the Amazon basin, affecting soil moisture and disrupting river navigation. In addition, extreme heat and a 30% reduction in yields due to citrus greening have led to a 24% drop in the 2024/25 orange crop. This decline caused a significant rise in orange prices and led to a 50% increase in global orange juice prices. Brazil, the world's largest exporter of orange juice, is facing a substantial decrease in its supply, causing global market instability and prompting some countries to seek alternative suppliers.
Egypt
Slow Start for Egypt's Navel Orange Season Due to Increased Global Competition
Egypt's navel orange season started on December 1, 2024, but demand has been slow across primary markets. Competition from Chinese oranges in the Far East, Spanish produce in Europe, and ongoing harvests in Turkey and Greece have dampened interest in Egyptian exports. This market saturation has made it difficult for suppliers to secure traditional buyers, sparking concerns about a potential price decline as the season advances.
Egyptian Orange Prices Dropped in Brazil Amid Increased Competition
Egyptian navel orange producers began offering the prices in W45, with Class 1 oranges initially offered at USD 13 to 15 per 15-kilogram (kg) box (CIF-Santos). By W47, prices declined to USD 11 to 11.75 15-kg box for shipments departing on December 7, 2024. The reductions are due to heightened competition among suppliers targeting the Brazilian market, intensifying price pressures.
France
Moroccan, Spanish, Italian, and Portuguese Oranges Dominate French Market Amid Price Fluctuations
France’s orange market is experiencing strong demand, with Morocco continuing to be a primary supplier alongside major European producers like Spain, Italy, and Portugal. Spanish regions such as Seville, Malaga, and Valencia supply varieties like Naveline and Salustiana. Meanwhile, Italy offers premium Naveline Feuille and Washington navel oranges, and Portugal provides Newhall and IGP Citrinos do Algarve. However, Spain’s orange production faced challenges due to floods in Valencia, reducing volumes, though harvests in Seville and Malaga have mitigated the impact. Despite high prices ranging from USD 1.06 to 1.59/kg (EUR 1 to 1.50/kg), experts anticipate stabilizing prices as the season progresses and supply volumes increase. While bad weather and logistical issues have caused some disruption, the quality of oranges remains a priority to meet the expectations of French consumers.
Spain
Catalonia’s Citrus Crops Hit Hard by Recent Storm
The recent passage of DANA, or high-altitude isolated depression, caused significant damage to crops in Catalonia, particularly in the Baix Ebre and Montsià regions of Tarragona. The Federation of Agricultural Cooperatives of Catalonia (FCAC) warns that citrus crops, including clementines and certain orange varieties, could see losses of up to 40%, with some areas experiencing a 70% reduction in harvests. Heavy rains in late October led to fruit drop, rotting, and flooding, while prolonged humidity and high temperatures fostered the growth of fungi, damaging fruit quality.
2. Weekly Pricing
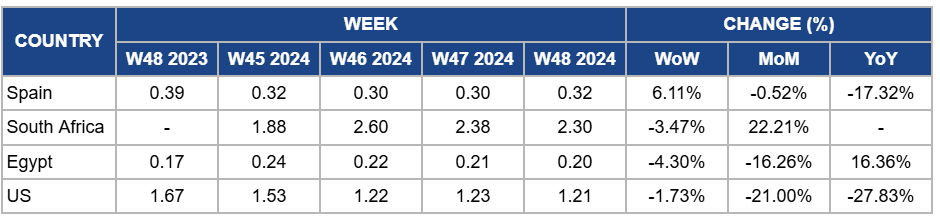
Weekly Orange Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Orange Pricing Important Exporters (W48 2023 to W48 2024)
Spain
Spain's orange prices increased by 6.11% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 0.32/kg in W48 due to reduced supply following the severe crop damage caused by DANA in Catalonia, particularly in Tarragona's Baix Ebre and Montsià regions. However, prices dropped by 0.52% month-on-month (MoM), with a more significant drop of 17.32% year-on-year (YoY) due to ongoing market challenges, including competition from other orange-producing regions and the lingering effects of earlier oversupply from the peak harvest season. Despite the recent supply disruptions, these factors have pressured overall price levels.
South Africa
Orange prices in South Africa dropped slightly by 3.47% WoW to USD 2.30/kg in W48 due to the continued stabilization of market supply as harvesting activities progressed in primary citrus-producing regions. The improved supply chain dynamics helped ease some pressure from earlier weather-related disruptions, keeping prices under downward pressure. However, prices increased by 22.21% YoY due to reduced production volumes earlier in the year, driven by adverse weather conditions and high input costs, which limited supply compared to the previous year. Additionally, improved export opportunities and a weaker local currency have supported higher YoY prices.
Egypt
In Egypt, orange prices fell by 4.30% WoW to USD 0.20/kg in W48, with a 16.26% MoM decline. The price drop is due to the anticipation of the upcoming harvest season, which is expected to significantly increase supply, encouraging producers to clear out the remaining supply from the previous season at lower prices. Strategic price adjustments ahead of the export season have further contributed to the downward trend. However, prices have increased by 16.36% YoY due to strong international demand, particularly from key export markets, and tighter supply conditions compared to the previous year. Limited carryover supply and ongoing global citrus shortages supported market interest in Egyptian oranges.
United States
Orange prices in the US dropped by 1.73% WoW to USD 1.21/kg in W48, with a 21% MoM decline and a more significant drop of 27.83% YoY due to improved local supply following the resolution of earlier weather-related disruptions in Northern California, which allowed for increased harvesting and distribution. Additionally, higher import volumes from other citrus-producing regions have contributed to easing local market pressures. The YoY decline reflects weaker consumer demand than last year and the production recovery in primary regions like Florida, which had previously faced severe challenges due to citrus diseases and unfavorable weather.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strengthen Crop Protection and Climate Resilience
Orange farmers should prioritize investing in climate-resilient agricultural practices to mitigate the impact of storms. This includes adopting advanced pest and fungal control methods, enhancing drainage systems to prevent flooding, and planting more resilient crop varieties. Investing in early-warning systems and monitoring tools will allow for better preparedness for extreme weather events. By implementing these strategies, producers can reduce future crop losses and maintain more stable yields despite adverse weather conditions.
Optimize Pricing Strategy and Manage Inventory for Export Efficiency
Egyptian orange producers should closely monitor market trends and adjust pricing strategies to align with supply forecasts, ensuring competitive pricing as the new harvest season approaches. They should prioritize efficient inventory management to clear out the remaining supply at optimized prices before the new crop is available. Additionally, they should plan for the upcoming export season by securing export contracts in advance, ensuring strong international demand and stable pricing. Producers can maximize profitability during the transitional period by balancing inventory control and proactive export planning.
Sources: Tridge, Agricolae, Agrimaroc, Freshplaza, Eastfruit, MX Fruit, Portal Del Campo, Simfruit, Valencia Fruits





