
In W5 in the orange landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Lower yields in key orange-producing regions like Brazil, China, and Florida are impacting overall supply.
- Increased orange demand from Asian markets, especially China, is supporting higher exports.
- Prices in some regions, like South Africa, have risen due to stronger demand and higher-quality harvests, while others, like the US and Italy, are seeing lower prices caused by oversupply and weak domestic demand.
- Increasing global competition, especially from South Africa and Egypt, is putting pressure on prices in markets like Italy.
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Brazil's Orange Juice Industry Struggles with Declining Demand
Brazil's orange juice market is facing challenges due to a 37.7% year-on-year (YoY) decline in orange crop production for the 2024/25 marketing year (MY). This is based on Fundecitrus' updated forecast, which estimates the production at 223.14 million boxes. While this marks a 3.4% increase from the previous estimate, the reduced supply follows a dip in global demand for orange juice. In the European market, the Expana Benchmark Price (EBP) for orange concentrate has risen by 13.5% YoY, but it experienced a 4.3% decline in Q4-24, driven by lower consumption and a shift toward using other juice types, such as pineapple and apple, to adjust flavor profiles.
China
China's Orange Production Declines as Exports Rise in 2024/25 Season
China’s orange production for the 2024/25 season is projected to reach 7.62 million metric tons (mmt), slightly lower than the previous season due to persistent rainfall, high temperatures, and concerns over citrus greening disease in Jiangxi and Guangxi provinces. Despite these challenges, China’s orange exports are expected to rise to 160 thousand metric tons (mt), driven by strong demand from Asian countries and enhanced regional trade initiatives, such as the China-Laos railway. On the other hand, orange imports are forecasted to decrease by 6% YoY to 150 thousand mt, reflecting weaker consumer demand and ample domestic supply, following a 22% YoY drop in imports during the 2023/24 season.
Egypt
Egypt Expands Valencia Orange Production to Strengthen Global Market Presence
Following a successful Navel orange season, Egypt is now shifting its focus to Valencia orange production, aiming to strengthen its presence in key markets such as Poland, the Netherlands, Denmark, Russia, and Ukraine. Egyptian exporters are also expanding into East Asia while maintaining strategic partnerships in Spain to enhance quality and competitiveness. Despite rising global competition, Egypt’s citrus industry continues to maintain high standards and diversify its markets. Efforts to foster relationships in Europe, Africa, and Latin America further bolster the country’s growing role in the international orange trade.
United States
Florida’s Orange Industry Faces Historic Low Due to Climate and Disease Challenges
Florida’s orange production is expected to have a record-low harvest, with the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) forecasting a 90% decline compared to three decades ago. The industry continues to struggle with citrus greening, an incurable disease that lowers fruit yields and kills trees, compounded by extreme weather challenges that have further damaged groves. The closure of a major labor group, the exit of one of the state's largest producers from the citrus industry, and a significant loss of citrus acreage since 2012 highlights the industry's ongoing crisis. While research into genetically modified trees and protective strategies provides some hope, recovery remains uncertain. Nonetheless, committed growers and efforts to develop disease-resistant varieties demonstrate strong efforts to sustain Florida’s orange industry.
2. Weekly Pricing
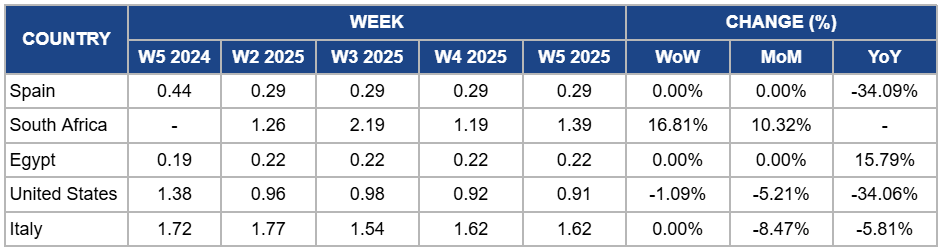
Weekly Orange Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Orange Pricing Important Exporters (W5 2024 to W5 2025)
Spain
Orange prices in Spain during W5 remained steady at USD 0.29 per kilogram (kg) since W2 with no week-on-week (WoW) and month-on-month (MoM) change due to stable demand for juice oranges as processors continued sourcing supplies amidst consistent production levels. Despite the relatively steady demand, factors such as competition from lower-cost imports, particularly from Egypt, have kept prices stable in the short term. However, YoY prices dropped by 34.09% due to ongoing pressure from these cheaper imports, which have undercut local prices, and a decline in local consumption. Additionally, farmers continue to face difficulties covering production costs, which has further weakened price support despite Spain’s significant role in the EU citrus market.
South Africa
South Africa's orange prices surged by 16.81% WoW to USD 1.39/kg in W5, with a 10.32% MoM increase due to stronger demand as fresh oranges from the new harvest entered the market. This rise is also due to improved harvest conditions in key growing regions such as Limpopo and Mpumalanga, which have resulted in higher-quality oranges. As the supply of off-season fruit decreased, the market adjusted, contributing to a price increase despite earlier declines. The overall improvement in both supply and demand dynamics has supported the higher prices seen in W5.
Egypt
In Egypt, orange prices held steady at USD 0.22/kg in W5, with no WoW and MoM change due to the successful transition from the Navel orange season to Valencia production, which has led to stable supply and consistent demand in both existing and emerging markets. Moreover, there is a 15.79% YoY increase in orange prices due to Egypt's growing market presence, particularly in Eastern Europe and East Asia. The price increase was supported by high demand despite growing competition from other global suppliers. Additionally, ongoing efforts to enhance product quality and expand export partnerships have contributed to stronger market positioning, resulting in the YoY price rise.
United States
Orange prices in the United States (US) slightly fell by 1.09% WoW to USD 0.91/kg in W5, marking a 5.21% MoM decrease and a 34.06% YoY drop due to a combination of factors, including lower demand for oranges following the end of the holiday season and increased competition from imported oranges, particularly from regions with lower production costs like Mexico.
Italy
In W5, Italy's orange prices remained steady at USD 1.62/kg, showing an 8.47% MoM decrease and a 5.81% YoY drop due to the continued oversupply of imported oranges, which has kept pressure on demand for locally produced fruit. Despite a slight reduction in competition from South Africa, ongoing production challenges and extreme weather events in key growing regions like Sicily have further limited the availability of premium-quality oranges. Additionally, consumer preference for more competitively priced imports has contributed to the YoY price decline, maintaining pressure on the domestic market.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strengthen Disease Management and Diversify Approaches for Orange Production
Orange growers in Florida should focus on enhancing disease management practices to combat citrus greening and adopt more resilient tree varieties. Implementing integrated pest management systems, supporting research on disease-resistant plants, and investing in weather-resilient infrastructure will help mitigate the challenges. Additionally, diversifying production methods and exploring new markets can provide stability as the industry navigates this crisis.
Focus on Export Growth and Strengthen Disease Management for Oranges
Orange producers in China should prioritize enhancing export strategies to capitalize on growing demand from Asian countries. To maintain a stable supply, they must focus on strengthening disease management programs, particularly targeting citrus greening, and investing in technology for improved crop protection. At the same time, cultivating relationships within regional trade initiatives can further boost export volumes.
Sources: Tridge, Freshplaza, Fundecitrus, Mintec/Expana, Producereport, Tampa Bay Times





