W12 2025: Tomato Weekly Update

In W12 in the tomato landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- The Netherlands led global tomato exports in 2023/24, followed by Morocco, Spain, and Türkiye. Moroccan and Spanish exports were highest in Jan-24 and Feb-24, respectively.
- Mexico and Spain saw significant price increases due to supply shortages and strong demand, while Morocco and Türkiye experienced price declines from improved weather and increased production.
- France's tomato prices surged due to rising demand, seasonal market shifts, contrasting with Türkiye’s and Morocco’s price drops driven by higher supply and logistical improvements.
1. Weekly News
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Ranks Among Russia’s Top Tomato Suppliers in 2025
Since the beginning of 2025, Azerbaijan has exported 28,700 metric tons (mt) of tomatoes to Russia, according to data from Rosselkhoznadzor. As of March 23, Azerbaijan ranks second among the top Russian tomato suppliers. Russia has imported 124,900 mt of tomatoes in 2025, with Turkmenistan leading at nearly 30 thousand mt. Azerbaijan's share in Russian tomato imports stands at 23%.
India
Tomato Prices Crash in Madhya Pradesh, Farmers Suffer Heavy Losses
Tomato farmers in Madhya Pradesh are struggling with heavy losses as wholesale prices have plunged to USD 0.023 per kilogram (kg) due to a bumper harvest. In Indore’s Devi Ahilyabai Holkar fruit and vegetable market, one of the largest markets in the state, farmers report that the current prices are too low to cover even harvesting costs. Some have been forced to discard unsold tomatoes. Many growers had expanded cultivation after high prices last year, leading to an oversupply that crashed the market. Farmer organizations, including the Sanyukta Kisan Morcha, urged the government to intervene by purchasing tomatoes at a fair price. The lack of cold storage and processing facilities in remote areas forced farmers to sell at unsustainable prices.
Netherlands
Netherlands Leads Global Tomato Exports in 2023/24
The Netherlands led tomato exports between September 1, 2023, and August 31, 2024, followed by Morocco, Spain, and Türkiye. During this period, the Netherlands exported 923,900 mt of tomatoes, valued at USD 1.93 billion, with an average price of USD 2.09/kg. Dutch exports peaked on Jul-24 (128,180 mt), followed by May-24 and Aug-24. Morocco shipped 694,450 mt, worth USD 1.12 billion, at an average price of USD 1.61/kg. Moroccan exports peaked in Jan-24 and reached their lowest levels in Jun-24 to Sep-24. Spain exported 633,330 mt of tomatoes, valued at USD 1.19 billion, at an average price of USD 1.88/kg. Spanish exports peaked in Feb-24 and hit their lowest volume in Sep-24. Türkiye exported 555,360 mt, worth USD 476.75 million, at an average price of USD 0.86/kg.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
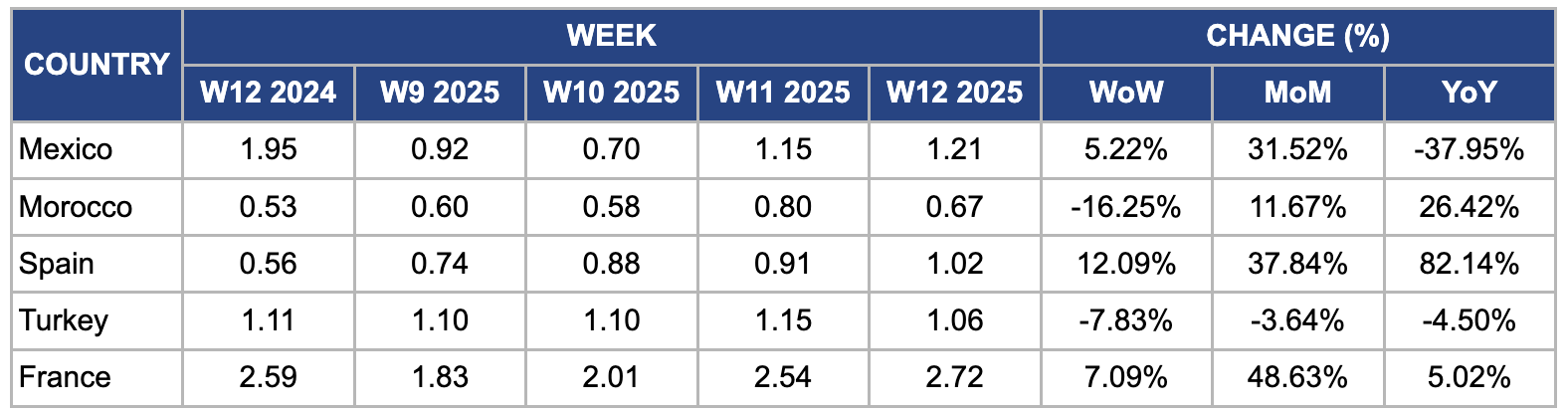
Yearly Change in Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (W12 2024 to W12 2025)
Mexico
In W12, Mexico's tomato prices surged 5.22% week-on-week (WoW) and 11.65% month-on-month (MoM) to USD 1.21/kg, driven by supply shortages and strong export demand. Unseasonably low temperatures and heavy rainfall in key producing regions such as Sinaloa and Baja California in late Feb-25 and early Mar-25 disrupted harvesting and slowed crop development, significantly reducing market availability. According to industry reports, Sinaloa’s tomato production declined by approximately 18% MoM in Feb-25, further tightening supply. Meanwhile, strong demand from the United States (US) market, where adverse weather conditions had also reduced local production, led to increased export volumes from Mexico.
Morocco
In W12, Morocco's tomato prices declined 16.25% WoW to USD 0.67/kg from USD 0.80/kg in W11 due to increased harvest volumes and improved weather conditions that boosted supply. Favorable temperatures in key production regions, particularly in Souss-Massa and Agadir, accelerated ripening and harvesting, leading to higher availability in domestic and export markets. Moreover, recent rainfall replenished soil moisture levels, enhancing plant productivity and increasing supply. At the same time, a temporary slowdown in European demand, particularly from France and Spain, reduced export volumes, leaving more tomatoes in the domestic market and pushing prices lower. The European Union (EU) market saw increased local production, reducing reliance on Moroccan imports. Furthermore, logistical improvements, including smoother transport routes and fewer disruptions at border checkpoints, facilitated faster distribution, preventing supply bottlenecks and ensuring stable market flows.
Spain
In W12, Spain's tomato prices rose 12.09% WoW, 37.84% MoM, and 82.14% year-on-year (YoY) to USD 1.02/kg, influenced by a significant reduction in production. In 2024, Spain's tomato production was approximately 3.1 mmt. However, forecasts for 2025 indicate a notable decrease to around 2.4 million metric tons (mmt), representing a reduction of 22.6% YoY. This decline is due to several factors, including decreased profitability, competition from imports, and challenges such as water scarcity and low profitability. These reductions in tomato cultivation have contributed to supply constraints, thereby driving up prices.
Türkiye
In W12, Türkiye's tomato prices decreased 7.83% WoW, 3.64% MoM, and 4.50% YoY to USD 1.06/kg. This decline is primarily due to increased domestic supply from favorable weather conditions that enhanced production in key regions like Antalya. Furthermore, logistical improvements and reduced transportation costs have facilitated more efficient distribution, leading to observed price decreases.
France
In W12, France's tomato prices surged 7.09% WoW and 48.63% MoM to USD 2.72/kg, signaling a market rebound after weak prices in Feb-25 due to sluggish demand. Market conditions shifted as demand strengthened, driven by the start of the month, school reopenings, improving weather, and a seasonal shift toward spring produce. Retail chains have begun transitioning to French-grown tomatoes, further boosting demand. Since supply cannot keep pace, producers have increased prices to capitalize on the market recovery.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversify Mexico’s Tomato Export Destinations
Mexican tomato prices have surged due to strong export demand from the US and supply constraints caused by adverse weather in Sinaloa and Baja California. To reduce dependency on the US market and stabilize price volatility, Mexico should explore alternative export destinations, including Canada, Japan, and Middle Eastern markets, where demand for high-quality fresh tomatoes is growing. Engaging in trade negotiations and leveraging existing free trade agreements, such as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), could facilitate market entry. Moreover, developing a robust cold chain logistics network will ensure that Mexican tomatoes maintain quality over long distances, making them more competitive in overseas markets. By diversifying export destinations, Mexico can mitigate risks associated with supply shortages and external demand fluctuations, ensuring more stable revenue for growers.
Strengthen Spain’s Tomato Industry Against Market Pressures
Spain's tomato production will decline in 2025 due to water scarcity, increased import competition, and reduced profitability. Spanish growers should adopt advanced irrigation technologies, such as precision drip irrigation and hydroponic farming, to maximize water efficiency and sustain production levels despite resource constraints. Furthermore, investing in high-yield and climate-resilient tomato varieties can help improve productivity while reducing input costs. Spanish farmers should also collaborate with cooperatives and industry associations to negotiate better pricing and supply chain efficiency. Expanding value-added processing, such as sun-dried and canned tomato production, can create alternative revenue streams and reduce reliance on fresh tomato sales. Strengthening these strategies will help Spain maintain its competitiveness in both domestic and export markets despite production challenges.
Expand Greenhouse Tomato Production in France
France's tomato prices surged due to tightening supply and strong domestic demand as retailers shifted towards local produce. To capitalize on this trend and ensure long-term price stability, France should expand greenhouse tomato production, particularly in regions with suitable climates like Brittany and the Loire Valley. Investing in energy-efficient greenhouse technologies, including LED lighting and automated climate control systems, will enhance productivity while reducing energy costs. Moreover, integrating vertical farming techniques can maximize space utilization, increasing yield per hectare. Government support through agricultural subsidies and research grants can encourage farmers to adopt greenhouse farming, ensuring a stable and sustainable domestic tomato supply. This approach will reduce import dependency and help maintain stable prices throughout seasonal demand fluctuations.
Sources: Tridge, Fresh Plaza, Horti Daily, Morocco World News, Outlook Business






