
In W5 in the banana landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Increased competition, trade barriers, and shifting import preferences are affecting banana exports, with Brazil, Mexico, and the Philippines facing hurdles in key markets.
- Weather conditions are influencing banana supply, with Ecuador recovering from earlier disruptions, while Cyprus struggles with water shortages that threaten production.
- Growers in Ecuador and the Philippines are negotiating sustainability costs and tariff adjustments with key markets, which could impact long-term pricing and trade relationships.
- Tanzania is ramping up efforts to combat BBTV, while the Philippines continues to face challenges from FocTR4, affecting overall production and market stability.
- Consumer demand remains strong in established markets like France, but exporters must navigate evolving quality standards and tariff structures to maintain market share.
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Brazil's Banana Exports Decline as Regional Competition Intensifies
Brazil's banana exports totaled 49 thousand tons in 2024, marking a 13% year-on-year (YoY) decline. The decrease was primarily due to a controlled domestic supply of dwarf bananas and heightened competition from Bolivia and Paraguay within the Mercosur market. Uruguay remained the leading destination, accounting for 50% of Brazil's banana exports, followed by Argentina at 40% and the Netherlands at 5%. In Dec-24, exports fell 53% month-on-month (MoM) from Nov-24 to 2.95 thousand tons due to seasonal supply reductions. However, they remained 79% YoY higher, driven by temporary supply increases from warm weather conditions.
Cyprus
Water Shortages Threaten Banana Production in Cyprus
Banana growers in Cyprus' Paphos district are facing severe irrigation challenges after the Mavrokolympos reservoir was drained, compounded by the driest January since 1997. The water shortage has significantly impacted banana cultivation, with farmers warning of potential losses if conditions persist. During a recent meeting of 250 stakeholders, growers urged the government for financial support to sustain production. Meanwhile, the Asprokremmos reservoir remains at 28.5% capacity, and additional strain from a damaged desalination plant has intensified concerns. In response, local officials have called for state intervention and proposed new dam projects to address long-term water scarcity.
Ecuador
Ecuador’s Banana Supply Stabilizes as Weather Conditions Improve
Ecuador, one of the world's leading banana exporters, saw high spot prices at the start of the year, which have since moderated as supply recovered. Late 2023 production and exports were impacted by warm, dry weather, but recent rainfall has improved growing conditions. Ecuador remains a key supplier to Russia and Eastern markets, operating on a spot pricing system as contract prices remain high. Meanwhile, Latin American growers are urging European Union (EU) retailers to share the costs of social and environmental sustainability requirements. Despite recent electricity shortages, banana production remains stable, supported by diesel-powered irrigation and backup power at packing stations and ports.
France
Bananas Remain the Top-Selling Fruit in France
Bananas were the most purchased fruit in France during the fourth quarter in 2024 (Q4-24), with sales reaching 109.2 thousand tons, a nearly 7% YoY increase. This growth underscores the fruit’s steady popularity among French consumers. Apples followed with 98.8 thousand tons sold, while mandarins ranked third at 52.1 thousand tons. The report highlights the strong and consistent demand for bananas in the French market, reinforcing their position as a staple choice for consumers.
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Sees Sharp Rise in Banana Exports to Uzbekistan
According to the National Statistics Committee, Kyrgyzstan significantly increased its banana exports to Uzbekistan in 2024. Between Jan-24 and Nov-24, Kyrgyzstan shipped 169 tons worth USD 80.3 thousand. This is a 4.2-fold increase from the 39.4 tons, valued at USD 19.7 thousand, shipped during the same period in 2023. The average export price to Uzbekistan stood at USD 481/ton. Meanwhile, Ecuador remained Kyrgyzstan’s primary banana supplier, providing 29 thousand tons worth USD 20 million at an average import price of USD 717/ton.
Mexico
Potential Tariffs Could Impact Mexico's Banana Exports to the US
Mexican banana growers and exporters are closely monitoring the potential 25% tariffs on goods entering the United States (US), which could put them at a disadvantage against competitors from Guatemala, Costa Rica, and Ecuador. While Mexican bananas are prized for their freshness, larger size, and higher sugar content, prolonged tariffs could prompt US buyers to shift sourcing elsewhere. Meanwhile, seasonal supply shortages have kept prices high on the spot market, though demand remains strong. Industry experts anticipate stable banana prices in 2025, reinforcing the fruit’s appeal to consumers.
Philippines
Philippines Seeks Trade Agreement Review to Boost Banana Exports to Japan
Japan aims to strengthen trade ties with the Philippines by increasing imports of Philippine bananas, but market share has declined from 90% in 2012 to 75% in 2024 due to Japan’s strict quality standards and pest concerns. In response, the Philippines is advocating for a review of the Japan-Philippines Economic Partnership Agreement (JPEPA) to regain its position, pushing for zero tariffs similar to those Japan plans to grant Vietnam and other suppliers by 2028. While the Philippines prefers bilateral negotiations, Japan suggests addressing the issue within the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), raising concerns about potential broader trade concessions.
Tanzania
Tanzania Strengthens Efforts to Combat BBTV
Experts in Tanzania’s banana industry are developing a strategy to combat the banana bunchy top virus (BBTV). The virus has severely affected primary banana-growing regions, including the northeastern region, southern highlands, Lake Victoria zone, and the western zone. A recent meeting in Moshi, Kilimanjaro Region, brought together representatives from the Tanzania Plant Health and Pesticides Authority (TPHPA), the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (UN FAO), and other stakeholders to coordinate efforts in controlling the disease. The strategy includes restricting infected seed transportation, raising farmer awareness, and implementing measures such as plant removal and herbicide use. FAO, in collaboration with the EU, remains committed to eradicating BBTV and ensuring the long-term sustainability of Tanzania’s banana industry.
2. Weekly Pricing
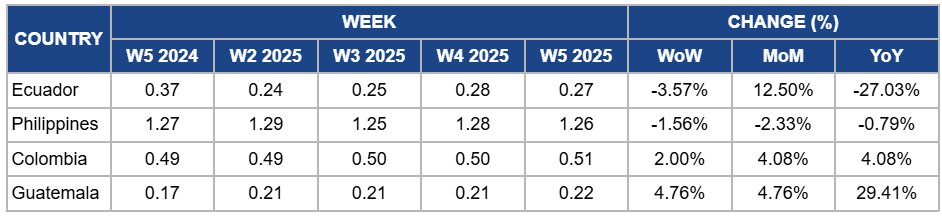
Weekly Banana Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Banana Pricing Important Exporters (W5 2024 to W5 2025)
Ecuador
Banana prices in Ecuador dropped by 3.57% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 0.27 per kilogram (kg) in W5, with a 27.03% YoY decline due to improved supply recovery following earlier weather disruptions, stabilizing production levels, and softer demand in key markets. The push for lower pricing in Eastern markets and ongoing negotiations with EU retailers over sustainability costs have also contributed to the YoY price drop. However, MoM prices increased by 12.50% due to strong spot market activity, sustained demand from Russia and other Eastern markets, and the impact of previous production constraints, which kept supply tighter at the start of the year.
Philippines
In W5, banana prices in the Philippines dropped slightly by 1.56% WoW to USD 1.26/kg, marking a 2.33% MoM drop and a 0.79% YoY decrease. The price drop is due to easing export demand from key Asian markets, particularly Japan, where stricter quality standards and ongoing pest concerns have limited shipments. Additionally, Japan’s preference for addressing tariff revisions within the RCEP framework has created uncertainty for Philippine exporters, affecting trade dynamics. Meanwhile, improving weather conditions have supported production recovery in some regions, increasing supply availability and slightly lowering prices. However, ongoing challenges from Fusarium TR4 (FocTr4) in Mindanao continue to limit overall production growth, preventing a more significant price decline.
Colombia
Colombia's banana prices rose slightly by 2% WoW to USD 0.51/kg in W5, with a 4.08% MoM and YoY increase. The price increase is due to sustained export demand from key markets such as the US and Europe, where seasonal consumption remains strong. Additionally, stable production supported by favorable weather conditions has ensured consistent supply, preventing major price fluctuations. Reduced competition from other exporting countries has also contributed to steady demand, while ongoing efforts to improve logistical efficiency have helped maintain reliable export flows. The YoY increase reflects overall market stability and continued strong performance compared to the same period in 2024.
Guatemala
Banana prices in Guatemala rose slightly by 4.76% WoW and MoM to USD 0.22/kg, with a 29.41% YoY increase due to steady export demand from primary markets and stable supply conditions. The price increase reflects seasonal adjustments and stronger purchasing activity from importers, particularly in North America and Europe, where demand remains consistent. Additionally, improved logistical efficiency and stable growing conditions have supported production, preventing sharp fluctuations. The YoY increase is due to higher input costs and ongoing efforts to enhance quality standards, which have contributed to overall price stability and gradual upward trends in the market.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversify Export Strategies to Mitigate Tariff Risks
Mexican banana exporters should diversify their market strategies to reduce dependence on the US and mitigate potential tariff impacts. Strengthening trade relationships with alternative markets, optimizing logistics to maintain competitive pricing, and enhancing branding efforts can help sustain demand. Additionally, growers should focus on production efficiency and cost management to remain competitive against suppliers from Guatemala, Costa Rica, and Ecuador.
Optimize Water Use to Sustain Banana Production
Banana growers in Cyprus should adopt efficient irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation and soil moisture monitoring, to maximize limited water resources. Investing in water storage solutions and exploring alternative water sources can help mitigate the impact of ongoing shortages. Collaboration with agricultural cooperatives can also improve resource-sharing and resilience against prolonged drought conditions.
Enhance Market Competitiveness for Banana Exports
Brazilian banana exporters should strengthen trade relationships and explore new markets to offset declining shipments within Mercosur. Diversifying export destinations and improving supply chain efficiency can enhance competitiveness against Bolivia and Paraguay. Additionally, optimizing production planning to balance domestic supply with export demand can help stabilize volumes throughout the year.
Sources: Tridge, Agraria, Cyprus Mail, Datamar News, Freshplaza, GMA News, Gov UK, IPP Media, Tazabek





