
In W6 in the mango landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Global mango production faces mixed prospects, with strong flowering in Bangladesh and pest threats in Cambodia affecting yield potential.
- India and Cambodia experience weather-related challenges, with fog, temperature fluctuations, and soil moisture deficits affecting fruit development.
- Pest infestations in Cambodia and India highlight the need for sustainable management to prevent crop losses.
- Peru’s mango exports to South Korea due to logistical constraints, rising production costs, currency depreciation, and reduced profitability.
- The recent farm fire in Ghana and climate-induced challenges in India highlight the urgent need for strong prevention strategies. Implementing fire control measures, such as firebreaks and safe burning practices, can mitigate farm destruction, while adaptive farming techniques, like moisture conservation and protective coverings, help counteract climate-related risks.
- Export markets remain competitive, with Peru and India facing strict quality standards and trade barriers affecting profitability.
1. Weekly News
Bangladesh
Strong Mango Bloom in Bangladesh Signals Promising Harvest
Mango trees in orchards across Bangladesh, particularly in Rajshahi, Naogaon, and Chapainawabganj, are experiencing abundant flowering, signaling the potential for a strong harvest if favorable weather persists. In Rajshahi, 60 to 65% of trees have already sprouted, while Chapainawabganj stands at 45 to 50%, with full bloom expected by mid-Mar-25. Naogaon has surpassed Chapainawabganj in production, driven by orchard expansion and modern high-density planting techniques. Farmers are actively addressing pest threats, supported by agricultural officials providing training to maximize yields and ensure safe production through the best uses of modern pest management technologies and sustainable farming practices. With approximately 3.5 million mango trees spread across 23 thousand hectares (ha), the industry remains a primary driver of the regional economy.
Cambodia
Rising Pest Threats Challenge Cambodia’s Mango Production
Mango farmers in Cambodia, particularly in Oddar Meanchey, Kampong Speu, and Battambang, are facing rising pest threats, including mealybugs, thrips, flower webworms, and mango gall midge, as identified by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The organization emphasizes the importance of timely pest monitoring and sustainable management practices, advocating for ecological solutions over chemical reliance. February is a crucial period for mango flowering, with soil moisture deficits further affecting growth. Additionally, the FAO warns of potential market saturation in Mar-25 and advises farmers to delay harvesting until Jul-25 to Aug-25 for better prices.
Ghana
Fire Destroys Mango Farm in Ghana's Eastern Region
A fire in Okwenya, a suburb of Somanya in Ghana's Eastern Region, destroyed 5 ha of a 10-ha mango farm, causing losses exceeding USD 8.5 thousand. Ignited by an uncontrolled fire set to burn a snake, the blaze quickly spread due to dry harmattan conditions, which is a seasonal dry and dusty trade wind from the Sahara that lowers humidity and increases fire risk. The Ghana National Fire Service responded swiftly, preventing further damage to the remaining farmland. In response, authorities urge farmers to implement fire prevention measures, such as creating fire belts, to protect their crops during the dry season.
India
Weather Conditions Threaten Mango Yield in Andhra Pradesh
Mango growers in Andhra Pradesh are concerned that prolonged foggy weather and low morning temperatures are hindering fruit setting, with dew causing significant flower drops in orchards. Despite above-normal flowering across key mango-producing districts such as Krishna, Nandamuri Taraka Rama Rao (NTR), Chittoor, and Vizianagaram, delayed fruit development could impact overall yields. Cultivating mangoes on 375 thousand ha with an estimated production of up to 5 million metric tons (mmt), the state is known for premium export varieties like Banginapalli and Suvarnarekha. Experts caution that insufficient heat exposure and high moisture levels may reduce the expected average yield of 10 to 12 mt/ha this season.
Peru
Challenges and Opportunities for Peruvian Mango Exports to South Korea
Peru has encountered challenges exporting its mangoes to South Korea this season due to increased volumes, logistical constraints, rising production costs, and the depreciation of the Korean won (KRW). Although South Korea offers a promising market for diversification, exporters have struggled with strict quality standards, extended hydrothermal treatments, and limited shipping space, restricting potential growth by 20%. Additionally, the weakened KRW has reduced profitability despite strong demand. Adverse weather conditions in Piura further affected fruit quality, leading to a higher percentage of overripe mangoes. However, exporters anticipate price improvements later in the season as supply declines, with sea exports maintaining a significant market share.
2. Weekly Pricing
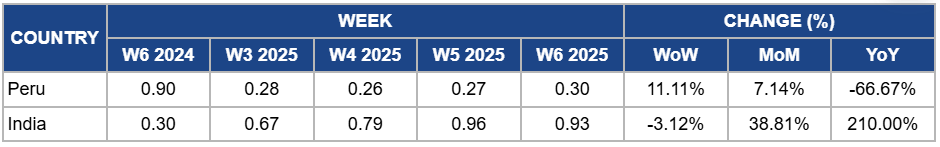
Weekly Mango Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Mango Pricing Important Exporters (W6 2024 to W6 2025)
Peru
In Peru, mango prices rose by 11.11% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 0.30 per kilogram (kg) in W6, with a 7.14% month-on-month (MoM) increase due to a gradual reduction in supply as the harvest season progresses. Some growers have slowed harvesting to manage volumes, reducing immediate market availability and supporting prices. Additionally, more fruit was redirected to domestic markets, easing export-related pressures and boosting local demand. These factors contributed to the slight price recovery. However, year-on-year (YoY) prices dropped significantly by 66.67% due to continued oversupply and weak export demand. In previous months, abundant harvests led to excess volumes, keeping prices low despite steady demand. Logistical constraints, high production costs, and currency depreciation have made exports less profitable. Additionally, adverse weather conditions in Piura have affected fruit quality, leading to an increased share of overripe mangoes, further weighing on prices compared to last year.
India
India's mango prices dropped by 3.12% WoW to USD 0.93/kg in W6 due to an increase in local supply as the harvest progressed, leading to higher market availability and intensified competition among traders. Prices are also adjusting downward after reaching a peak in W5. Additionally, logistical disruptions in primary export routes temporarily slowed international shipments, contributing to the short-term price decline. However, MoM and YoY prices surged significantly by 38.81% and 210%, respectively, due to strong export demand, particularly for premium varieties from Maharashtra’s Nashik region. The impact of adverse weather on mango production in Andhra Pradesh has also shifted some consumer demand toward grapes, further supporting prices. Additionally, improved post-harvest handling and cold storage facilities have enhanced fruit quality, driving higher prices in both domestic and export markets.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Optimize Quality and Logistics for South Korea
Peruvian mango exporters should enhance quality control measures to meet South Korea’s strict standards and minimize losses from overripe fruit. Streamlining logistics and securing reliable shipping options will help maintain freshness and profitability despite currency fluctuations. Strengthening market positioning through targeted promotions can further maximize demand in this competitive market.
Strengthen Flower Retention for Higher Yields
Mango growers in Andhra Pradesh should implement moisture management strategies, such as mulching, drip irrigation, and humidity regulation, along with targeted nutrient applications to counteract flower drops caused by prolonged fog and low temperatures. Enhancing orchard microclimates through protective coverings and regulated irrigation will help improve fruit setting and maintain yield potential for premium export varieties
Sources: Tridge, Akipress, Bss News, Freshplaza, Khmer Times, Modern Ghana, Timesofindia






