W2 2025: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
In W2 in the beef landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Global beef production faces constraints as major exporters, including Brazil, the US, and Australia, grapple with declining livestock numbers and economic challenge.
- China’s rising demand, alongside reduced slaughter rates, is driving uncertainty, with imports expected to grow significantly by 2025. Despite supply limitations in major exporting countries, import demand remains strong, particularly from China and South Korea, indicating steady global growth.
- Beef prices varied across major exporters, with US prices rising by 28.94% YoY due to shrinking cattle numbers, while Brazil saw a small increase of 2.84% WoW. Australia experienced a drop in prices by 7.66% WoW, reflecting a post-holiday slowdown, and Argentina’s prices surged by 30.59% YoY, despite a sharp 9.34% WoW decline.
- Argentina and Uruguay face weak domestic demand and economic instability, impacting beef sales. In particular, Argentina is struggling with high inflation and declining consumption, while Uruguay deals with limited export demand.
- Brazil and Australia continue to see strong export performance, suggesting that market diversification and strategic expansion will be key to mitigating challenges and capitalizing on opportunities.
1. Weekly News
Global
Global Beef Market Faces Uncertainty in 2025 as China Launches Dumping Investigation and Supply Constraints Loom
The global livestock market faces heightened uncertainty as 2025 starts, largely due to a dumping investigation initiated by Chinese organizations into beef imports. The matter, referred to the World Trade Organization (WTO), highlights China's growing dependency on beef imports to meet domestic demand. In 2024, China’s beef imports reached 2.6 million metric tons (mmt), up 4% compared to 2023. Projections from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) suggest China will import 3.83 mmt in 2025, marking a 40% increase since 2020. However, the investigation has sparked concerns about its potential to suppress beef prices, as Chinese importers and officials reportedly aim to curb costs amid limited supply and rising demand.
Compounding the situation is a forecasted decline in livestock numbers among key beef-exporting countries, including Brazil, the United States (US), and Australia, with year-on-year (YoY) reductions ranging from 1% to 3%. Coupled with retention trends and diminished slaughter rates, this points to constrained global supply. While countries like Uruguay show slight growth in livestock production, these marginal gains are unlikely to offset broader reductions. Recent price declines, particularly in Argentina, driven by currency devaluation and strategic price adjustments by exporters, may provide temporary relief. However, persistent supply shortages and China's robust demand are poised to dominate the market, likely driving beef prices higher in the near future.
Australia
Strong Demand Drove Australia’s Beef Export Boom in 2024
Australia achieved a record-breaking beef export volume of 1.34 mmt in 2024, marking a 24% increase over 2023 and surpassing the previous record set in 2014 at 1.29 mmt. The surge in exports was largely driven by higher demand from South Korea and China, with the latter becoming a key market. The US also saw significant shipments, reflecting the tight supply of ground beef in the country’s domestic market. Despite typically slower export months during December and January, Australia's beef industry experienced strong performance during these periods in 2024.
The national cattle herd in Australia stood at 30.2 million heads in 2024. However, the cattle population is projected to decline by 2% to 29.6 million heads by 2025 due to the evolving livestock cycle. Slaughter numbers reached 8.2 million heads in 2024, the highest since 2019, with an expected increase of 200 thousand heads in 2025. While rebuilding its beef production after a period of herd decline, Australia has become the second-largest beef exporter globally. However, it is not considered a direct competitor to Brazil as the two markets offer slightly different types of meat on the international stage.
Brazil
Brazil’s Record-Breaking Beef Exports in 2024 and 2025 Outlook
According to the Brazilian Association of Meat Exporting Industries (Abiec), Brazil’s beef exports reached a record 2.89 mmt, valued at USD 12.8 billion in 2024. This represents a significant 26% increase in volume and a remarkable 22% rise in value compared to 2023. China remained Brazil’s largest market, importing 1.33 mmt and contributing USD 6 billion in revenue. The US, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the European Union (EU), and Chile also played significant roles.
Looking ahead, Brazilian beef exports are projected to exceed 4.032 mmt in 2025 and potentially reach 4.35 mmt by 2030, driven by strong demand and expanding market access. Efforts to open new markets in Japan, Vietnam, Turkey, and South Korea are expected to support further growth. According to trade associations, Brazil’s livestock sector continues to benefit from robust Chinese demand and favorable trade conditions. Industry leaders anticipate sustained growth in production and revenue, reinforcing Brazil's role as a key global meat supplier.
Brazil’s Beef Prices Set to Rise in 2025 Amid Strong Export Demand and Livestock Cycle Changes
Beef prices in Brazil are projected to rise by 8% YoY in 2025, driven by cyclical livestock changes, strong export demand, and macroeconomic factors such as exchange rates and interest rates. The reduced slaughter of female cattle will constrain supply, further pushing prices upward. Export volumes, which reached record levels in 2024 are expected to remain strong, fueled by demand from key markets like China and the US, where local production has declined. A stronger dollar will incentivize producers to prioritize exports, tightening domestic availability and contributing to higher local prices.
However, rising beef prices are anticipated to suppress domestic consumption, with projections expecting a 6% to 7% YoY decline in 2025 as consumers shift to more affordable protein options such as chicken and pork. Despite these challenges, the beef industry aims to remain competitive by adapting to cost pressures and leveraging export-driven growth. Robust external demand and favorable exchange rates will continue to position Brazil as a dominant player in the global beef market, even as domestic consumption adjusts to evolving economic dynamics.
Indonesia
Indonesia Plans to Import Cows in 2025 to Support School Meals Program
Indonesia is aiming to import 400 thousand breeding cows in 2025 to support its domestic livestock sector and meet the growing demand for meat and milk for its free school meals program. Launched in W2, the program initially distributed 570 thousand meals to schools and will be expanded to feed over 80 million children and pregnant women, with an estimated cost of USD 28 billion. The agriculture ministry plans to import 350 thousand cattle for fattening in 2025 and expects half of the 400 thousand cows to be dairy cows. Over the next five years, Indonesia aims to import 2 million breeding cows, with the goal of transitioning to local supply for the school program. Currently, Indonesia imports cattle from Australia and milk from New Zealand, while considering expanding sources to include Brazil.
Uruguay
Uruguay’s Meat Export Market Outlook in 2025 Amidst Global Pressures
Uruguayan meat exports face a challenging yet opportunistic outlook for 2025. While China remains Uruguay’s top destination, low prices are causing concerns. Additionally, China’s investigation into meat imports over an alleged oversupply and its dual strategy of meeting domestic demand while keeping imports available adds further uncertainty. Meanwhile, Uruguay’s competitiveness is hindered by high cattle costs, with Brazil’s massive production capacity and Argentina’s market struggles intensifying the pressure.
Despite these challenges, Castiglioni, an Uruguayan meat export company, sees potential in alternative markets such as the US, Europe, and Southeast Asia, including the Philippines, Vietnam, and Thailand. Although still in a testing phase, these markets present opportunities for Uruguay’s meat exports. Looking ahead to 2025, Castiglioni expects a slow start but believes diversification and strategic market placements will help maintain Uruguay’s competitiveness in the global market.
2. Weekly Pricing
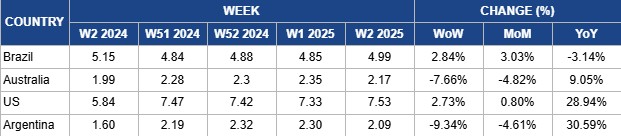
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W2 2024 to W2 2025)
Brazil
In W2, Brazil's wholesale price for boneless rear beef rose by 2.84% week-on-week (WoW), reaching USD 4.99 per kilogram (kg). This also represented a 3.03% month-on-month (MoM) increase, though it was still down 3.14% YoY. While weekly prices in USD terms saw an uptick, they remained stable in Brazilian real at BRL 30/kg for the ninth consecutive week, with exchange rate fluctuations driving the variation in USD pricing. According to the Center for Advanced Studies on Applied Economics (Cepea), strong domestic meat consumption continues to support wholesale prices, prompting meatpacking plants to resume buying and offer higher prices for new batches of beef cattle. However, Safras and Mercado note that the outlook for the first two months of 2025 suggests limited room for further price adjustments, as the population faces financial pressures, including property taxes, vehicle taxes, and school supplies purchases. This is likely to shift consumer focus toward more affordable protein options such as chicken, sausages, and eggs.
Australia
Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator averaged USD 2.17/kg in W2, marking a 7.66% WoW drop. This also represented a 4.82% MoM decrease, but a 9.05% YoY increase. The price drop can be attributed to the market adjusting to the post-holiday period, as high consumer demand leading up to Christmas and New Year 2025 had driven prices higher from W46 of 2024 to W1 of 2025. Prices are expected to stabilize in the coming weeks as the market finds balance.
United States
In W2, the price for lean beef (92% to 94%) in the US averaged USD 7.53/kg, reflecting a 2.73% WoW increase, marking the first rise in the past seventeen weeks. This price also showed a slight 0.80% MoM rise and a significant 28.94% YoY increase. The YoY surge is attributed to a tightening domestic supply caused by a shrinking cow herd. The consistent price decline since W36 of 2024 aligned with the seasonal dip in winter demand following the peak summer consumption period. However, limited production continues to support relatively high lean beef prices. The WoW rebound could also be linked to concerns surrounding the incoming US administration, with the inauguration scheduled for January 20.
Argentina
In W2, Argentina's average steer beef price dropped to USD 2.09/kg, reflecting a 9.34% WoW decline and a 4.61% MoM drop. Despite this, the price marked a notable 30.59% YoY increase. This second consecutive weekly drop can be attributed to the market returning to its actual price level after heightened demand during the Christmas and New Year holiday periods. Argentina's beef consumption in 2024 faced significant challenges due to economic pressures. According to the Chamber of Industry and Commerce of Meat and Derivatives of the Argentine Republic (CICCRA), beef consumption fell by 12% YoY, marking the worst year for beef sales in two decades. Per capita consumption dropped to 47.4 kg, an 11.1% decrease compared to 2023, with the 12-month moving average until Nov-24 reflecting a 12.4% YoY decline. Apparent domestic beef consumption in 2024 totaled 2.038 mmt, 10.1% less than in 2023, reaching its lowest levels in 22 years.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Mitigate Risks in the Global Beef Market Amid China's Dumping Investigation and Supply Constraints
To address the heightened uncertainty in the global beef market, stakeholders should focus on diversifying export markets. Countries like Brazil, Australia, and the US should explore new markets, such as those in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa, to offset the potential decline in Chinese beef imports. Additionally, beef producers should consider increasing production efficiencies through technological advancements and sustainable practices to lower costs, ensuring competitiveness even amid rising prices. Collaboration with the WTO to ensure fair trade practices and the resolution of the dumping investigation will also help stabilize market conditions.
Enhance Brazil’s Beef Industry Amid Price Increases and Export Demand
Brazil should focus on enhancing its supply chain efficiency to maintain its strong position in the global beef market. This could include investing in meat processing technologies and improving traceability systems to meet growing export demands. Brazil should also increase its focus on expanding markets in Japan, Vietnam, and Turkey to reduce dependency on China. To counter domestic price increases, the government should introduce subsidies or support for local consumers to mitigate the effects of higher beef prices. Strengthening the domestic beef supply chain will also be key in managing price fluctuations driven by cyclical changes in livestock.
Strengthen Indonesia’s Strategic Livestock Imports for the School Meals Program
Indonesia’s livestock import plan can be strengthened by ensuring that the imported cows meet long-term sustainability goals, such as enhancing local breeding programs and improving herd management. The government should prioritize creating incentives for farmers to adopt more efficient practices in raising dairy and beef cattle. Additionally, fostering partnerships with international suppliers like Brazil, alongside expanding local dairy production, will ensure that Indonesia can meet its ambitious school meals program while eventually reducing reliance on imports. Long-term infrastructure development for cold chain logistics and processing capacity will also be crucial.
Sources: Tridge, Agro Forum, Agromeat, Bichos de campo, Canal Rural, NoticiasAgricolas


