
In W21 in the soybean oil landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Morocco emerged as the leading importer of EU soybean oil, reshaping trade flows as overall EU oilseed exports declined. Meanwhile, Spain maintained its position as the top EU exporter.
- Despite minor weekly volatility, US soybean oil prices remained strong due to tightening supply, robust biofuel demand, and increased domestic crushing and exports.
- China reduced imports of Russian soybean oil, with Brazil, the US, and Argentina solidifying their roles as its primary suppliers amid shifting trade patterns.
- Flooding in Argentina disrupted soybean harvesting, creating supply concerns that may reverse recent price declines and tighten global soybean oil availability.
1. Weekly News
Morocco
Morocco Emerges as Top EU Soybean Oil Importer Despite Overall Export Decline
Despite an 8% decline in overall European Union (EU) oilseed exports during the 2024/25 campaign, Morocco has solidified its position as the primary destination for EU soybean oil, importing 291,300 metric tons (mt) as of May 13, 2025. This surge positions Morocco as a key player in reshaping global soybean oil trade flows. Spain remains the EU's top soybean oil exporter with 225,600 mt, reinforcing its leadership in the vegetable oil sector. While Morocco leads in soybean oil imports, other destinations such as the United Kingdom (UK) and Norway remain significant for other oilseed products.
Russia
Russia's Soybean Oil Exports to China Plunge in Oct-24
In Oct-24, Russia's soybean oil exports to China dropped sharply to USD 7.1 million, down nearly fourfold from USD 28.2 million in the same time last year. Despite this steep monthly decline, cumulative exports for Jan-24 to Oct-24 saw a more modest decrease, falling to USD 112.8 million from USD 120.8 million in the previous year. This decline in soybean oil shipments aligns with the broader drop in Russian soybean exports to China, which halved over the same period. Meanwhile, Brazil, the United States (US), and Argentina remained China's leading soybean suppliers.
United States
US Soybean Oil Prices Climb on Tightening Supply, Renewable Fuel Demand, and Global Market Pressures
US soybean oil prices continued their upward trajectory through Apr-25 and May-25, driven by tightening soybean supplies and shifting global demand dynamics. The United States Department of Agriculture's (USDA) latest World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates (WASDE) report for the 2025/26 marketing year (MY) highlighted a nearly 15% decline in aggregate soybean supply compared to the previous season, despite a steady harvest estimate of 4.34 billion bushels. Increased domestic crushing and rising export volumes intensify competition for raw soybeans, supporting higher soybean oil prices.
Strong demand for biofuels and renewable diesel is reinforcing upward price pressure, with analysts forecasting continued bullish sentiment. US renewable energy policies, including potential changes to the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS), are expected to further stimulate soybean oil demand. At the same time, China's record-high soybean imports and sustained demand for edible oils continue to bolster global demand.. Although South American exporters have expanded raw soybean exports, they remain limited in their ability to offset US supply constraints in processed soybean oil. Logistical disruptions, such as port congestion and river shipping delays, also contribute to price volatility.
2. Weekly Pricing
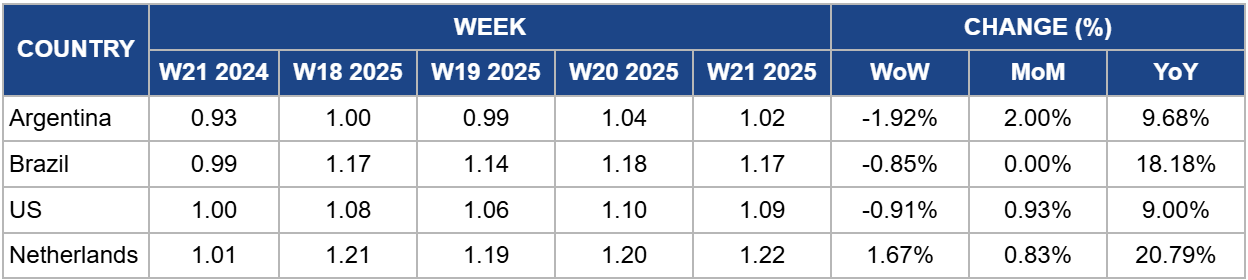
Weekly Soybean Oil Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Soybean Oil Pricing Important Exporters (W21 2024 to W21 2025)
.png)
Argentina
In W21, Argentina's soybean oil prices declined by 1.92% week-on-week to USD 1.02 per kilogram (kg), despite a 9.68% increase year-on-year (YoY) from USD 0.93/kg. The recent price dip reflects short-term market pressure, possibly linked to subdued international demand or temporary logistical constraints. However, this downward movement contrasts with mounting supply concerns triggered by severe flooding across Argentina's agricultural heartland in W21. Excessive rainfall has disrupted soybean harvesting and heightened the risk of crop losses, particularly in Buenos Aires province, where waterlogged fields remain inaccessible.
As Argentina is the world's leading exporter of soybean oil, any significant reduction in harvestable soybeans could curtail oil production and limit export volumes in the coming weeks. This supply disruption may reverse the current price decline and drive upward pressure on global soybean oil prices, particularly if market participants anticipate prolonged delays or lower-than-expected yields during the remainder of the 2024/25 season.
Brazil
In W21, Brazil's soybean oil prices declined slightly by 0.85% to USD 1.17/kg, while remaining 18.18% higher YoY from USD 0.99/kg. The modest weekly drop follows a period of strong gains, largely underpinned by expectations of increased US biodiesel demand, which has supported international soybean oil prices.
Brazil has capitalized on this price recovery, with soybean oil exports reaching 503,000 mt in Q1-2025, up 30% from the same period in 2024. The price strength reflects robust domestic and international demand, positioning Brazil as a key exporter amid tightening global supplies, particularly in light of Argentina’s weather-related disruptions. While current demand may keep near-term prices firm, rising production and stock levels could moderate price increases in the medium term.
United States
US soybean oil prices declined slightly in W21, down 0.91% WoW to USD 1.09/kg, though they remain 9% higher YoY from USD 1/kg. This minor weekly dip reflects short-term volatility amid broader bullish fundamentals. Export demand remains exceptionally strong, up nearly 1,000% YoY, while domestic consumption is supported by proposed federal mandates to raise biomass diesel blending volumes to 5.25 billion gallons by 2026. At the same time, a weaker US dollar (USD) and elevated global palm oil prices have made American soybean oil more competitive on the world market. With inventories at decade-lows and global vegetable oil supply tightening, the recent pullback is likely temporary. If policy developments and export momentum persist, soybean oil prices may resume an upward trajectory in the coming weeks.
Netherlands
Soybean oil prices in the Netherlands rose by 1.67% WoW to USD 1.22/kg in W21, marking a 20.79%YoY increase from USD 1.01/kg. This upward trend reflects sustained export demand, particularly from the UK, which continues to rely heavily on Dutch soybean oil. In 2024, the Netherlands supplied 80% of the UK's soybean oil imports by volume, underlining its strategic export role.
The price increase is further supported by robust EU oilseed dynamics. Elevated rapeseed oil prices have lifted soybean oil valuations, while softer sunflower oil prices have shifted some demand toward soybean oil as a more competitively priced alternative. With UK consumption projected to grow steadily through 2035 and Dutch exports increased by an average of 5.3% annually since 2013, continued export momentum may reinforce current pricing levels. While increased global supply from South America may temper long-term price growth, firm EU demand fundamentals suggest near-term prices will likely remain supported.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhance Market Diversification in Response to Shifting Trade Flows
Exporters and traders should strengthen commercial ties with Morocco, which has emerged as the leading importer of EU soybean oil, while also expanding outreach to underexploited destinations such as North and West Africa. Proactive engagement in these markets, especially where Russian supply has declined, can help mitigate risk from traditional demand centers and capitalize on evolving trade dynamics.
Adopt Risk Management Tools Amid Volatile Price and Supply Conditions
Given ongoing price fluctuations, tightening US supplies, and logistical disruptions in Argentina and Brazil, importers and processors should implement flexible hedging strategies using futures and options to manage procurement costs. Strategic purchases during temporary price dips, particularly in Q3-2025, can secure margins ahead of potential seasonal or policy-driven rebounds.
Monitor Biofuel Policy and Feedstock Supply in Key Producing Countries
With strong biofuel-driven demand in the US and rising environmental pressures influencing future Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) revisions, stakeholders should closely track regulatory developments that may affect soybean oil consumption. Parallel monitoring of South American weather events and crop conditions is essential for anticipating supply shocks that could affect global availability and pricing.
Sources: Tridge, APK-Inform, ChemAnalyst, Food Business News, Rue 20, Reuters, Bichos del Campo, Ukr AgroConsult




