W30 2025: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
In W30 in the beef landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Argentina's beef exports have rebounded following a slow start in 2025, fueled by strong Chinese demand and better margins, with Jul-25 expected to hit the year's peak volume.
- Brazil’s beef exports to the US have sharply declined due to new tariffs, prompting exporters to shift focus toward China and other markets.
- Australia has reopened to US beef, reversing a long-standing ban, while Japan is easing tariffs to strengthen trade ties. In contrast, South Korea continues to resist market access to US beef from cattle aged over 30 months, citing food security concerns.
- Paraguay grapples with rising domestic beef prices and debates over FMD vaccination timelines, while continuing to grow its exports.
- Uruguay continues to benefit from high international beef prices and is expanding market access through trade agreements.
1. Weekly News
Argentina
Argentina’s Beef Exports Rebound Amid Global Demand and Market Shifts
Argentina’s beef exports had a sluggish start in 2025. However, recent months have shown a promising recovery, with Jul-25 projections reaching 85 thousand metric tons (mt) of bone-in beef, potentially the highest monthly volume this year. This rebound is driven by stronger global demand, particularly from China, improved exchange rate competitiveness, and a decline in raw material costs, enabling better margins across the livestock chain. Jun-25 marked a turning point, with exports rising 12.7% month-on-month (MoM) in volume and 7.2% MoM in value. This was largely supported by high international prices, especially from China, which accounted for 77% of total shipments.
Although exports remained 16.4% lower year-on-year (YoY) in H1-2025, optimism for H2-2025 is growing, especially if Argentina’s government lifts the 6.75% beef export tax. Meanwhile, industry players are embracing trends like vacuum packaging to improve quality, convenience, and access to both domestic consumers and export markets such as Israel, pointing toward an evolving meat industry focused on innovation and diversification.
Australia
Australia Reopens Market to US Beef After Decades-Long Ban
Australia announced that it will fully lift restrictions on United States (US) beef imports, allowing the entry of both fresh and frozen products following a decade-long scientific and risk-based assessment. While Australia had partially opened its market to US beef since 2019, concerns over bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) had previously limited access to certain products. The Australian Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry (DAFF) confirmed that enhanced US biosecurity measures now meet required standards. The National Cattlemen's Beef Association (NCBA) welcomed the move, citing it as a long-overdue correction of a trade imbalance that had favored Australian exports to the US. The announcement comes at a critical time as both countries are in the midst of trade negotiations covering broader issues, including tariffs on steel, aluminum, and pharmaceuticals.
Brazil
Tariff Hikes Trigger Sharp Decline in Brazil’s Beef Exports to the US
Brazil's beef exports to the US have declined between Apr-25 and Jun-25, dropping nearly 62%, following the implementation of a 10% tariff in May-25 and ahead of a planned 50% hike set for August 1. Although Brazil achieved a record high in Apr-25 by exporting nearly 48 thousand mt of beef to the US, volumes declined significantly in the subsequent months. The upcoming tariff increase could raise total duties to 76.4% on shipments exceeding the quota, potentially causing further contraction in exports. This move has sparked concerns among Brazilian stakeholders, as the US is Brazil's second-largest beef buyer. Despite the downturn, Brazil posted a record 156 thousand mt of beef exports to the US in H1-2025, indicating possible stockpiling ahead of the tariff escalation.
In response, Brazilian exporters are shifting focus to other markets, notably China, which now absorbs over half of Brazil’s beef exports. The Brazilian government has formally protested the tariffs and is pursuing diplomatic channels. Brazil is also expanding trade partnerships, including a new deal with Mexico for processed bone exports. Experts warn that sustained tariffs could disrupt global supply chains, pressure US food prices, and threaten both American agribusiness and Brazilian producers unless policy changes are made.
Paraguay
Paraguay’s Beef Sector Confronts Rising Prices, Expanding Exports, and a Critical Health Policy Choice
Paraguay’s beef sector is marked by rising prices, market concentration concerns, growing exports, and a key national debate over animal health policy. The Paraguayan Rural Association (ARP) has raised concerns about market dominance by major meat processors, which has contributed to a 22% YoY increase in beef prices as of Jun-25, and nearly 70% since the onset of the pandemic. These rising prices are straining producers and consumers due to the monopolization of the market.
Despite these challenges, the sector remains resilient. Beef export volumes rose 17% YoY in H1-2025, while export revenues surged nearly 38% YoY, generating an additional USD 289.8 million. Looking ahead, meat exports, including beef, poultry, and pork, are projected to rise by USD 500 million by year-end.
At the same time, Paraguay is engaged in a national debate over suspending foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) vaccination by 2027 to attain the highest level of international animal health recognition. While government agencies and industry experts support the 2027 timeline, citing an absence of virus circulation, many producers advocate for a delay until 2030. They emphasize the need for stronger surveillance systems, greater trust in institutions, and coordinated planning to protect long-term sustainability and global competitiveness. Although there is alignment on the strategic goal, stakeholders remain divided on the timeline.
South Korea
South Korea Holds the Line on US Beef Access in Trade Talks
South Korea has firmly excluded beef market access from its trade negotiations with the US, citing food security and the sensitivity of the sector. While the US is pushing for expanded access, particularly for beef from cattle over 30 months old, the South Korean government has designated this issue a red line, emphasizing potential domestic backlash and international trade constraints. The government’s stance highlights a strategic effort to protect its beef industry while steering negotiations toward less sensitive items such as biofuel-related agricultural imports. This position contrasts with other nations, like Japan, that have been more flexible in using beef access to gain broader trade concessions.
United States
US–Japan Beef Trade Deal to Boost Exports and Tariff Cuts
The newly signed US-Japan trade agreement is expected to significantly enhance US beef exports by improving market access and reducing tariffs. Under the deal, Japan will cut tariffs on US agricultural imports, including beef, from 25% to 15%, helping US producers regain price competitiveness, especially against competitors like Australia. Already the largest market for US beef, Japan imported approximately USD 2.3 billion worth in 2023, and the updated agreement is projected to boost this to between USD 2.4 billion and USD 2.5 billion in 2025. The package builds on the 2019 bilateral deal, which gradually lowered beef tariffs and aligned US access with other major exporters under broader trade frameworks. In addition to tariff reductions, the agreement is expected to streamline sanitary regulations and stabilize quotas, providing predictability for US beef exporters. While implementation details are pending, the deal offers renewed momentum for US beef exports in a market facing rising food prices and declining domestic livestock production.
Uruguay
Uruguay Taps Global Demand and Trade Deals to Boost Exports
According to the National Institute of Meats (INAC), Uruguayan beef export prices have surged to USD 5,969/mt in Jul-25, marking their highest average since May-22 and continuing the sharp upward trend seen in recent weeks. This price rally has supported strong export performance in H1-2025, with average prices up nearly 19% YoY. China remains the top destination, with a 33% increase in export revenue, while the US saw reduced volumes and the European Union (EU) nearly doubled its imports from Jul-24. Uruguay has exported 102.72 thousand mt of beef so far this year, a 28.3% YoY increase, earning USD 543.1 million.
Alongside traditional markets, Uruguay is pursuing new opportunities through agreements with Ukraine and Vietnam and broader trade deals like Mercosur-European Free Trade Association (EFTA) and Mercosur-EU. These agreements are expected to lower tariffs, expand market access, and enhance competitiveness. Notably, the Mercosur-EU deal will immediately eliminate the 20% Hilton tariff, with phased quotas offering more flexible export terms. Meanwhile, the EFTA agreement opens high-value niche markets like Switzerland and Norway, potentially boosting export prices above USD 12,000/mt.
2. Weekly Pricing
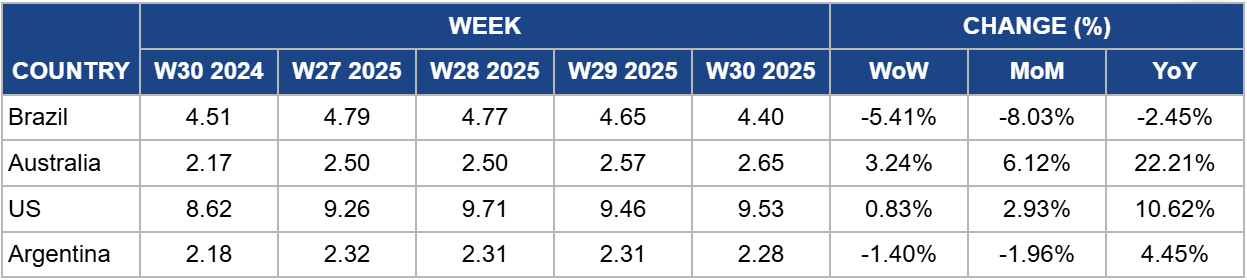
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W30 2024 to W30 2025)
Brazil
In W30, Brazil’s wholesale price for boneless rear beef declined by 5.41% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 4.40 per kilogram (kg), reflecting an 8.06% MoM drop and a 2.45% YoY decrease. According to Safras and Mercado, the wholesale market signals a continued short-term downward trend, driven by slower restocking between wholesale and retail channels in the latter half of Jul-25. Chicken meat continues to be price-competitive compared to beef and pork, further weighing on beef demand. In the physical cattle market, slaughter volumes remain steady due to adequate supply and strong inflows of confined cattle. Meanwhile, the outlook for Brazilian beef exports to the US remains bleak, as the recent tariff hike has rendered shipments economically unviable. However, the domestic market is expected to see a modest recovery in early Aug-25, with beef prices likely to firm ahead of Father’s Day, a key driver of seasonal consumption.
Australia
Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator (NYCI) rose to USD 2.65/kg in W30, marking increases of 3.24% WoW, 6.11% MoM, and 22.21% YoY. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), overall market sentiment remained positive, although cattle yardings declined by 6.09 thousand heads. The feeder steer Indicator strengthened as fewer heavy export cattle were available, prompting increased purchasing by lot feeders. A shortage of well-finished stock supported price increases in New South Wales (NSW) and Victoria. The processor cow indicator also climbed, with most states, including NSW and Victoria, recording higher prices. Demand was particularly strong for heavy cows, especially in Wagga Wagga, while interest in plain-conditioned cows remained limited.
United States
In W30, US lean beef (92% to 94%) averaged USD 9.53/kg, up 0.83% WoW, 2.93% MoM, and 10.62% YoY. Prices remain historically high, driven by strong seasonal demand and tight supplies. The US cattle inventory has fallen to its lowest level since 1952, primarily due to prolonged droughts that have depleted natural grazing resources. As a result, many farmers have turned to costly industrial feed, significantly reducing their profit margins. Despite record-high prices, consumer demand for beef remains resilient, signaling that Americans are still willing to pay for their preferred protein. However, market analysts warn that if economic conditions worsen, this loyalty may weaken. This would spell further challenges for producers, who are already grappling with rising input costs and shrinking margins. The US beef industry appears to be at the peak of its current price cycle, and any drop in prices could pose serious risks for those holding large inventories. There is no immediate sign of relief, and a market correction will largely depend on shifts in consumer spending power and sentiment. If demand softens, downward pressure on prices could follow.
Argentina
Argentina’s average steer beef price fell by 1.40% WoW to USD 2.28/kg in W30, representing a 1.96% MoM decline but a 4.45% YoY increase. The weekly drop points to sluggish demand, while the annual rise reflects a modest recovery in beef consumption after the historic lows recorded in 2024. In Jun-25, Argentina’s per capita beef consumption stood at 50.1 kg annually, up 5.2% YoY and nearing 2021 levels at 49.3 kg. In contrast, the 2024 average was just 47.7 kg per person, a 9% decline from 2023 and the second-lowest level in history, surpassed only by 1920. The steep decline in beef intake has coincided with a sharp rise in chicken consumption. Price sensitivity played a key role. For example, Argentinians could buy three kg of chicken or two kg of pork for the price of one kg of beef. This situation drives a shift toward more affordable protein alternatives.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strengthen Resilience Through Market and Product Diversification
To sustain its export rebound and reduce vulnerability to fluctuations in Chinese demand, Argentina should actively diversify its export portfolio by expanding into high-value markets such as the EU, Israel, and the Middle East. Accelerating the adoption of vacuum packaging and other value-added innovations will enhance product quality and shelf life, meeting evolving consumer expectations. Also, lobbying for the removal or reduction of the 6.75% beef export tax could enhance competitiveness and incentivize production. Public-private collaboration is essential to promote new market access agreements and co-invest in logistics and processing infrastructure for premium cuts.
Positioning US Beef in Australia and Japan’s High-Value Segments Amid Market Reopening and Expansion
To capitalize on the reopening of the Australian market, US beef exporters should prioritize strict adherence to Australian biosecurity requirements while promoting the quality, safety, and traceability of their products to build consumer trust. Collaborating with Australian trade bodies on joint marketing campaigns can help reshape consumer perceptions and boost demand, particularly in premium retail and foodservice segments where grain-fed US beef holds a competitive edge.
In Japan, exporters should increase production planning for premium and chilled cuts to meet growing demand under the bilateral trade agreement. Tailored marketing strategies aligned with Japanese preferences, such as ideal portion sizes and marbling, alongside investments in cold-chain logistics, will ensure consistent quality and timely delivery. Additionally, US policymakers should actively monitor the trade agreement’s implementation to ensure tariff reductions and sanitary measures are applied fairly, preventing non-tariff barriers from undermining market access.
Mitigate Tariff Impacts Through Diplomatic and Market Diversification Strategies
In response to steep US tariff hikes, Brazil should intensify its diplomatic efforts to negotiate equitable trade terms while accelerating its pivot toward alternative markets such as China, Mexico, and the Middle East. Signing more bilateral agreements for processed and high-value beef cuts will help stabilize revenue. The government should also invest in cold-chain infrastructure to maintain product quality across long shipping distances and support private sector innovation in processed beef offerings. Engaging with multilateral trade organizations to contest protectionist measures could also be a viable medium-term strategy.
Optimize Trade Deals and Enhance Niche Market Penetration
Uruguay should actively promote its beef through storytelling marketing campaigns in high-value markets like Switzerland and Norway, leveraging its pasture-based production model and animal welfare standards. With new trade deals eliminating key tariffs and opening niche markets, exporters should segment offerings by market, focusing on chilled cuts in the EU and high-margin frozen products in Asia. Government support for export readiness, including sanitary certifications and digital traceability platforms, will be critical in converting access into long-term market share and premium pricing.
Sources: Tridge, Agromeat, Canal Rural, Foodmate, UkrAgroConsult, Yna


