W33 2024: Tomato Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Egypt
Egypt's Tomato Exports Totaled USD 23.13 Million from Jan-24 to May-24
According to the Central Agency for Public Mobilization and Statistics (CAPMAS), Egypt's tomato exports from Jan-24 to May-24 totaled USD 23.13 million. The largest recipients were Russia, with exports valued at USD 3.13 million, and Saudi Arabia with USD 2.86 million. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) followed with USD 1.98 million, and Hungary rounded out the list with USD 1.93 million in exports. This data highlights the significance of foreign trade in Egypt's economic development by reflecting changes in trade balance and overall economic growth.
Fresh Tomato Prices Surged by 40% MoM in Aug-24 Due to Inflation and Rising Production Costs
In Aug-24, fresh tomato prices rose sharply by 40% month-on-month (MoM) to USD 712.78 per metric ton (EGP 35,000 EGP/mt), compared to USD 509.13/mt (EGP 25,000/mt) in Jul-24. This increase is due to inflation and the rising costs of production and agriculture.
Israel
Israel Faces Tomato Crisis Amid Export Bans, Heatwave, and Agricultural Challenges
Israel is facing a tomato crisis due to several factors. Turkey's suspension of vegetable exports, including tomatoes, has disrupted supplies. At the same time, the Israeli Ministry of Health has banned tomatoes from Jordanian greenhouses due to cholera bacteria found in the Yarmouk River, which waters these crops. Additionally, extreme heat is expected to reduce the tomato harvest by 50% in the coming weeks, compounded by war-related damage to farming areas. Israel's Ministry of Agriculture has increased the duty-free import quota for tomatoes to 5 thousand mt until the end of Sept-24 and allocated USD 3.24 million (ILS 12 million) in subsidies to encourage local tomato cultivation. An additional USD 4.05 million (ILS 15 million) will be invested in biotechnology to boost yields and enhance agricultural technology.
Morocco
Morocco Overtakes Spain as Top Tomato Supplier to the EU in Q1-24
In Q1-24, Morocco surpassed Spain to become the leading supplier of tomatoes to the European Union (EU), exporting over 210 million kilograms (kg) and capturing more than 30% of the EU's total tomato imports. This marks a substantial increase of over 13 million kg compared to the same period in Q1-23. The value of these exports reached over USD 404.65 million, a rise of more than USD 5.57 million from the previous year, driven by a higher average selling price for Moroccan tomatoes in the EU market. Morocco's competitive advantage stems from its proximity to Europe and ability to supply tomatoes during the European winter, establishing it as a crucial revenue source for the North African country.
Philippines
Philippines Tomato Prices Drop Over 50% MoM in Aug-24
Tomato prices in the Philippines have plummeted by over 50% MoM, falling from USD 3.55/kg in early Jul-24 to USD 1.42/kg in W33. This sharp decline has led some farmers in Nueva Vizcaya to discard their tomato harvests due to the low prices. The Department of Agriculture (DA) coordinates with regional field offices in the Cordillera Administrative Region and Cagayan Valley to address the surplus. They are exploring options to either donate the excess tomatoes to Kadiwa stores or transport them to Metro Manila, with support for trucking to aid distribution.
Turkey
Turkish Tomato Farmers Protest Low Prices, Secure Higher Purchase Rate
On August 8, tomato farmers in Turkey's Bursa province blocked the Bursa-Balikesir highway to protest low purchase prices from tomato paste factories. Farmers used their tractors to block both directions of the road and eventually were promised a purchase price of USD 0.10/kg . The protest lasted about 3.5 hours and ended after local officials, including the Governor of Bursa and other authorities, intervened. The highway was reopened following the agreement on the new price.
2. Weekly Pricing
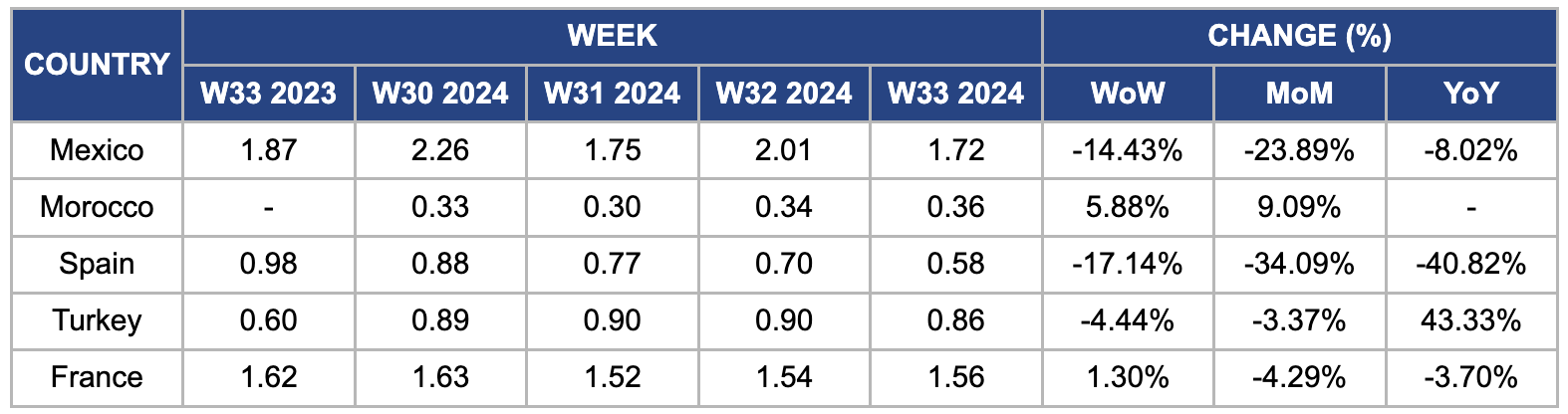
Weekly Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
* Varieties: All tomato pricing is for round tomatoes.
Yearly Change in Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (W33 2023 to W33 2024)
* Varieties: All tomato pricing is for round tomatoes
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
Mexico
In W33, wholesale tomato prices in Mexico fell significantly by 14.43% week-on-week (WoW), from USD 2.01/kg to USD 1.72/kg. Despite this drop, Mexican prices remain the highest compared to Morocco, Turkey, Spain, and France. Prices also declined 23.89% MoM and 8.02% year-on-year (YoY). The decrease is due to an increased supply of Roma and Round tomatoes from ongoing tomato production in northern Mexico, which are about a month behind schedule. Although demand remains strong, favorable warmer weather has boosted production, contributing to lower prices. The market is expected to stabilize in the upcoming weeks.
Morocco
In W33, Moroccan tomato prices rose 5.88% WoW and 9% MoM to USD 0.36/kg. This significant increase is due to several factors, including adverse weather conditions that have reduced tomato production, leading to tighter supply. Supply and demand fluctuations and rising production and transportation costs have further driven up prices. Additionally, policies affecting imports and exports and limited market availability have exacerbated the price surge.
Spain
In W33, Spain's wholesale tomato prices declined, dropping by 17.14% WoW to USD 0.58/kg from USD 0.70/kg in W32. This marks a significant YoY decrease of 40.82%. The conclusion of the greenhouse tomato campaign in Almería has led to expectations of an earlier start for the 2024/25 season. Additionally, increased tomato imports from Morocco have further driven prices down. The influx of supplies from multiple origins has intensified the downward pressure on prices in Almería during the winter tomato campaign.
Turkey
Turkey's tomato prices declined slightly by 4.44% WoW to USD 0.86/kg but surged 43% YoY. The price drop is due to an overproduction of tomatoes in 2024 and an ongoing export ban on tomato paste, leading to surplus and reduced prices. However, the YoY increase is driven by drought conditions caused by climate change, severely impacting agricultural output and driving up diesel fuel and transport costs. Consequently, farmers are staging frequent protests in provinces such as Bursa, Kahramanmaras, Balikesir, Aksaray, and Nigde, using tractors to block roads and draw attention to their economic hardships. Despite higher consumer prices due to inflation, farmers suffer financial losses, often receiving lower prices for their produce than retail prices. In Gaziantep, some farmers have protested by dumping unsold tomatoes on the road, highlighting their struggles with rising costs and declining profits.
France
In W33, tomato prices in France rose by 1.3% WoW to USD 1.56/kg from USD 1.54/kg the previous week. After a difficult start to the season, the French tomato market is showing signs of recovery with increased consumption and moderated production. However, forecasted high temperatures across Europe will likely lead to additional production losses and further price increases. This trend is expected to persist, particularly in the Mediterranean region, where extreme heat could further impact tomato crops grown in tunnels, shelters, or open fields.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Target Market Expansion and Strategic Partnerships
For Egypt, optimizing its export strategy is essential to mitigate the impact of fluctuating prices and production costs. The country should focus on expanding into new and emerging markets like Russia and Saudi Arabia. Developing strategic partnerships and trade agreements with countries in Africa and Asia could open up new avenues for export and reduce dependency on a few key markets. This approach will help stabilize Egypt's tomato export market and support its agricultural sector by diversifying revenue sources and managing market risks effectively.
Implement Support Programs and Price Stabilization Measures
The Philippines should focus on implementing support programs for farmers affected by the price drop. The DA can lead efforts to subsidize transportation costs to improve distribution and provide financial aid to offset losses from unsold harvests. Additionally, the National Food Authority (NFA) can assist by purchasing surplus tomatoes and distributing them to markets or food banks, helping to stabilize prices and manage excess supply. The Philippine Crop Insurance Corporation (PCIC) can offer crop insurance to mitigate financial losses from unsold produce. Local Government Units (LGUs) can support local distribution efforts and coordinate community-based initiatives. Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) like the Philippine Red Cross can help distribute excess tomatoes to needy communities or process them into value-added products. Agricultural cooperatives and associations can work with farmers to manage surplus and explore processing options, while the private sector and agribusinesses can invest in infrastructure and logistical support. These measures will aid farmers in coping with market fluctuations and ensure a more balanced supply chain.
Adapt to Market Conditions and Enhance Recovery Efforts
Focusing on adaptive strategies to manage production and pricing is essential in France, where tomato prices are recovering but are still impacted by high temperatures. Investments in cooling technologies and adaptive farming practices, such as heat-resistant tomato varieties and improved irrigation systems, can mitigate the impact of extreme weather. Adjusting pricing strategies to reflect current market conditions and ensuring stable supply chains will also support recovery efforts. This includes providing support through subsidies for technology upgrades and research into climate-resilient farming techniques. Local agricultural cooperatives and industry associations can facilitate training programs on adaptive practices and coordinate efforts to stabilize supply chains. By addressing these factors, France can stabilize its tomato market and support domestic consumers and producers amidst changing climate conditions.
Sources: Tridge, Akhbarelyom, Agrotimes, Eastfruit, Gmanetwork, Agronews, PTvidarural, Sondakika, Fresh Plaza , NTV, Turkiye Today






