W36 2025: Tomato Weekly Update

In W36 in the tomato landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Argentina’s recent alignment of tomato quality standards with Mercosur is expected to enhance competitiveness and facilitate exports.
- Brazil’s wholesale tomato prices dropped in late Aug-25 amid warmer weather and high yields. However, stability is expected after the late harvest ends in Sep-25.
- Peru recorded a significant 210% YoY surge in tomato exports in Jul-25, with shipments primarily directed to Colombia and Italy.
- Spain’s Andalusian tomato sector faces historic losses as extreme heat, pest infestations, and falling prices erode farmer profitability, prompting calls for urgent support.
- Turkey is leveraging tomato production to strengthen rural incomes, with large-scale sun-dried tomato exports and women’s cooperatives producing tomato paste, underscoring the crop’s economic and social importance.
1. Weekly News
Argentina
Argentina Aligns Tomato Quality Standards with Mercosur to Boost Exports
Argentina has updated its Tomato Quality and Identity Regulations to align with Mercosur standards, a move that strengthens market access and competitiveness while reducing technical trade barriers. Through Resolution 627/2025, national rules now incorporate Mercosur’s Resolution No. 26/2017, ensuring that tomatoes produced under Argentine regulations are recognized across member states and beyond. Fresh tomato production is concentrated in provinces such as Mendoza, San Juan, Salta, Jujuy, Corrientes, and Formosa, with exports mainly directed to Paraguay, Brazil, Uruguay, and Chile. According to the National Food Safety and Quality Service (Senasa), this regulatory harmonization facilitates smoother and more secure trade, positioning Argentina’s tomato sector more effectively in regional and international markets.
Brazil
Warmer Temperatures and High Yields Pressure Tomato Markets in Brazil
In late Aug-25, wholesale tomato prices in Brazil saw a sharp decline due to higher productivity and warmer temperatures. In São Paulo, the average price of a 3A salad tomato box dropped 19.3% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 10.49 (BRL 57), while in Campinas prices fell 11.3% WoW to USD 15.10/box (BRL 82/box). In contrast, markets in Rio de Janeiro and Belo Horizonte remained relatively stable at USD 13.44/box (BRL 73/box) and USD 11.05/box (BRL 60/box), respectively. Looking ahead, with the late tomato harvest ending in Sep-25 and supply expected to be somewhat controlled, prices are anticipated to stabilize.
Peru
Peruvian Tomato Exports Surge 210% YoY in Jul-25
In Jul-25, Peruvian tomato exports surged to 1,627 metric tons (mt), marking a significant 210% year-on-year (YoY) increase. The shipments reached 13 countries, with Colombia accounting for 33% of the total and Italy 28%, highlighting strong demand in both regional and European markets. Leading the exports was Icatom SA with a dominant 68% share, followed by Tiba Cargo Perú SAC with 15%. This sharp growth underscores Peru’s expanding role in the global tomato trade.
Spain
Andalusian Tomato Sector Faces Historic Losses Amid Heat and Price Drops
Andalusian tomato producers are facing a severe crisis, with the Coordinator of Farmers and Ranchers Organizations (COAG) Andalucía reporting historic losses in the processing tomato sector due to extreme weather, pests, and low prices at origin. Despite initial optimism following much-needed rainfall, the campaign has been marked by difficulties starting from sowing, compounded by a Jun-25 heatwave that destroyed early flowering, reduced yields by around 30%, and triggered pest infestations and plant stress. Farmers now struggle to cover production costs, as prices have fallen USD 44.55/mt (EUR 38/mt) compared to last season. This situation has left many farmers unable to cover production costs. COAG Andalucía has called for urgent price increases at source, stressing the strategic economic and social importance of processing tomatoes in the region.
Meanwhile, advances in plant biotechnology, such as the virus-specific Ribonucleic Acid interference (vsRNAi) technique developed by Spanish and Italian researchers, offer hope for future resilience. Successfully tested on tomatoes, this innovation enables rapid and precise gene silencing to improve traits like drought tolerance and disease resistance without permanently altering plant Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA). This innovation could provide a pathway to more resilient and sustainable tomato production in the future.
Turkey
Tomato Exports and Paste Production Strengthen Rural Incomes Across Turkey
Tomatoes have become a key driver of local economies in several regions of Turkey, with diverse forms of production supporting both farmers and communities. In Şanlıurfa’s Siverek district, sun-dried tomatoes cultivated on fertile lands are processed and exported globally, generating significant income and expanding agricultural diversity. This year, around 10 thousand mt of tomatoes have been planted, with dried production expected to reach 5 thousand mt. Picked in July and August, the tomatoes are sliced, salted, and dried under intense summer heat before being sent to processing facilities in İzmir and Manisa, and later exported to Europe, the United States (US), Russia, and the Middle East. Alongside this, women’s cooperatives in Hatay and Malatya are driving tomato-based production by turning fresh harvests into tomato paste using traditional methods. These initiatives, such as HAZEK in Hatay and Zeynep Ana Cooperative in Malatya, support disaster-affected and rural women, offering financial and psychological empowerment while boosting local economies.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
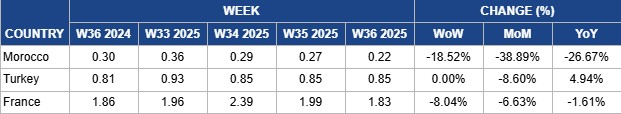
Yearly Change in Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (W36 2024 to W36 2025)
Morocco
In W36, Moroccan wholesale tomato prices fell by 18.52% WoW to USD 0.22 per kilogram (kg). This price also marks a 38.89% month-on-month (MoM) decline, and a 26.67% YoY fall. The significant monthly decline reflects abundant supply and aggressive exports to the European Union (EU), particularly Spain, where shipments from Jun‑24 to May‑25 reached 80.29 thousand mt, generating USD 135.17 million (EUR 115.35 million). While strong export flows meet rising EU demand, rapid movement through the supply chain exerts downward pressure on Moroccan wholesale prices. At the same time, the sector’s resilience amid years of drought has allowed exporters to maintain these flows, even as European producer groups increase pushback against Moroccan competition, a key policy risk that could influence future pricing.
Turkey
In W36, Turkish wholesale tomato prices remained stable at USD 0.85/kg for the third consecutive week, despite an 8.60% MoM decline. The stability reflects the typical late-summer pattern of widespread harvesting, while Turkey’s position as a major global tomato producer ensures an abundant supply, keeping prices moderate during peak availability. According to the World Processing Tomato Council (WPTC), southern regions completed harvesting by September 3, while the Bursa area was about 50% through its harvest, expected to accelerate over the next two weeks due to late planting bunching from high temperatures. Yields in the later harvest are lower, prompting a downward revision of the production forecast to 2.2 million metric tons (mmt). Harvesting in the Konya region has also begun. Strong origin supply and throughput have softened wholesale export quotes. However, 4.94% YoY price strength persists due to cost pass-through and steady external demand. Additionally, an increasing share of tomatoes is being directed to value-added products, such as dried tomato exports, supporting the overall price floor as the fresh season transitions.
France
In W36, French wholesale round tomato prices fell 8.04% WoW to USD 1.83/kg, representing a 6.63% MoM decline and a 1.61% YoY drop. The correction follows a weather-driven surge in late Aug‑25, when heatwaves and drought in southern regions, particularly Occitanie, caused severe yield losses of 60% to 80% for some growers, tightening domestic supply and sharply lifting prices. Increased harvesting progress and rising EU imports, particularly from Morocco and Spain, added supply to the market, helping stabilize prices and cap further upside. According to WPTC, 105 thousand mt had been processed as of September 3, accounting for 60% of the forecasted 175 thousand mt, with average brix at 5.17 and penalties at 6.8%. While overall quality is good, some fruits were damaged by overmaturity during the early Aug-25 heatwave. Recent heavy rains in the South-East and South-West, with more expected in the coming week, suggest a challenging start to Sep-25. Despite the recent price decline, lingering domestic shortfalls and heat-related quality issues keep prices above 2024 levels, indicating continued volatility as France navigates uneven local output alongside import flows.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strengthen Argentina’s Tomato Trade Through Harmonization
Argentina should leverage the new regulatory alignment with Mercosur by promoting greater regional branding and marketing of its tomatoes, emphasizing quality assurance and harmonized standards. Exporters can negotiate longer-term trade contracts with Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Chile, capitalizing on reduced technical barriers. Additionally, investing in cold chain infrastructure and logistics efficiency in provinces like Mendoza and San Juan would help maintain quality and expand exports beyond regional partners into premium-paying international markets.
Maximize Peru’s Export Growth Momentum
Given the 210% YoY surge in exports, Peru should focus on market diversification to reduce dependency on Colombia and Italy by targeting new destinations in Asia and North America. Companies like Icatom SA, already leading the export front, can invest in value-added processing such as sauces and canned tomatoes to capture higher margins. Strengthening phytosanitary compliance and branding Peruvian tomatoes as premium-quality products will also help sustain global demand and position Peru as a reliable supplier in competitive markets.
Revive Andalusian Tomato Competitiveness
Spain’s tomato sector needs supportive price policies and subsidies to help farmers recover from losses, while also adopting climate-resilient practices such as precision irrigation, pest management, and heat-tolerant seed varieties. Public-private partnerships should accelerate the adoption of biotechnology innovations like vsRNAi, offering farmers long-term solutions to environmental stresses. In the short term, cooperatives and producer organizations should negotiate better farmgate prices with processors and retailers to ensure farmers’ sustainability and protect the socio-economic role of tomatoes in Andalusia.
Enhance Turkey’s Rural Tomato Economy Through Diversification
Turkey should further strengthen value-added tomato production by scaling up initiatives like sun-dried tomatoes and traditional paste-making, which already support rural livelihoods. Providing financial and technical support to women’s cooperatives in Hatay and Malatya will expand their role in both economic and community recovery, especially in disaster-affected regions. At the same time, establishing direct export channels and branding for Turkish tomato products in European, US, and Middle Eastern markets will ensure producers capture higher margins, while encouraging regional clusters of small-scale processors will foster inclusive rural growth.
Sources: Tridge, Agraria, Agrodiario, Agrolink, Agromeat, Canal Rural, Kamu3







