W38 2025: Tomato Weekly Update

In W38 in the tomato landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Moldova is set for stable growth in tomato exports to the EU under a trade framework aimed at gradually eliminating tariffs and aligning with EU agri-food standards by 2027.
- Morocco continues to maintain strong cherry tomato exports despite a single contaminated batch, while overall tomato shipments in 2024/25 reached a record high.
- In Pakistan, Punjab authorities have launched emergency measures to stabilize supply and curb rising prices caused by limited domestic and cross-border availability.
- Turkey's autumn season has spurred high demand for tomatoes and peppers for homemade paste, supporting cultural culinary practices and post-disaster economic recovery.
1. Weekly News
European Union
Moldovan Tomato Exports to EU Set for Stable Growth Under New Trade Framework
The European Union (EU) is advocating for the long-term elimination of tariffs on Moldovan agricultural exports, including tomatoes. They are currently covered by temporary trade liberalization measures introduced in 2022 following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. This move aims to provide stability, boost trade flows, and support Moldova’s gradual alignment with EU agri-food standards by 2027, while safeguarding sensitive EU agricultural sectors. Moldova’s association with the EU through the Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area (DCFTA) and broader agreements promotes economic integration and political dialogue, further supporting its candidacy for EU membership.
Morocco
Moroccan Cherry Tomato Exports to EU Continue Despite Single Batch Contamination
On September 10, Dutch authorities issued a Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASSF) alert for a single batch of Moroccan cherry tomatoes due to metal contamination, which was withdrawn from the market. Contrary to widespread media reports claiming a suspension of all Moroccan cherry tomato imports to the EU, the Moroccan food safety authority (ONSSA) clarified that only this isolated batch was affected and that imports are continuing normally. Alerts for Moroccan fresh produce are rare, accounting for just 1.8% of all 2025 fresh produce alerts, highlighting compliance with international health standards. Despite seasonal low exports, shipments of Moroccan cherry tomatoes to Europe continue without issues, maintaining stable trade flows.
Morocco Breaks Seasonal Tomato Export Record in 2024/25
Morocco set a new seasonal record for tomato exports in 2024/25, shipping 745 thousand metric tons (mt) and generating nearly USD 1.2 billion in revenue. This represents an 8.3% increase from the previous season and surpasses the 2022/23 record. Tomatoes remain the country’s top fresh produce export, accounting for over 30% of sector earnings, positioning Morocco as the world’s third-largest tomato exporter after Mexico and the Netherlands. Exports occur year-round, peaking between November and March, with France as the largest importer, followed by the United Kingdom (UK), the Netherlands, and Spain. Emerging markets in Europe and West Africa, including Belgium, Scandinavia, Mauritania, and Senegal, contributed significantly to growth, while secondary markets added 15 thousand mt compared to last season. Despite challenges such as drought and labor shortages, Morocco’s tomato trade continues to expand, complementing record cucumber exports and reinforcing its role as a major global supplier of greenhouse produce.
Pakistan
Emergency Measures Launched to Curb Tomato Price Surge in Punjab
Punjab authorities have taken urgent measures to stabilize tomato supply and curb rising prices in the province. The Price Control Department has instructed all market committee secretaries to hold emergency meetings with commission agents, monitor supply closely, and act against hoarding and profiteering. The surge in prices is attributed mainly to limited tomato supplies from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Balochistan, and Afghanistan, prompting authorities to ensure timely clearance of tomato trucks arriving through the Torkham and Chaman borders. Daily reports on supply and pricing are being submitted to the Punjab Agricultural Marketing Regulatory Authority (PAMRA) for oversight. Suppliers and transporters are required to maintain close communication with authorities to prevent delivery delays. In parallel, a province-wide crackdown on profiteering continues, with thousands fined or arrested for overpricing essential goods, reflecting the government’s zero-tolerance approach to ensure fair pricing of tomatoes and other staples.
Turkey
Tomato and Pepper Paste Season Heats Up in Turkey
As autumn arrives in Turkey, the demand for tomatoes and peppers for homemade paste has surged, particularly in Bilecik, Hatay, and Gaziantep. Residents in Bilecik are buying tomatoes in large quantities, paying between USD 3.62 (TRY 150) and USD 5.55 (TRY 230) per 20-kilogram (kg) crate to 25 kg crate, while dried tomatoes produced by women affected by the Hatay disaster are sold at USD 6.03 (TRY 250) per jar, contributing to local livelihoods and post-disaster economic recovery. In Gaziantep, a gastronomic hub, the busy season for pepper and tomato paste production is underway, with local businesses working by appointment to process 30 mt of peppers daily into paste, which is then sun-dried on rooftops. Across these regions, the seasonal rush reflects both cultural culinary practices and the importance of supporting local producers, while ensuring households are well-stocked for winter.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
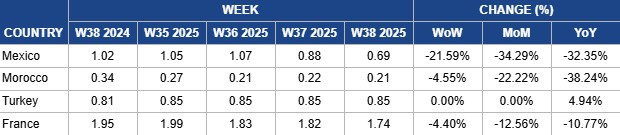
Yearly Change in Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (W38 2024 to W38 2025)
Mexico
In W38, Mexico’s wholesale tomato prices averaged USD 0.69/kg, marking a 21.59% week-on-week (WoW) decline, a 34.29% month-on-month (MoM) drop, and a 32.35% year-on-year (YoY) fall. The decline reflects weakened demand in key export markets, particularly the United States (US), following the mid-Jul-25 termination of the Tomato Suspension Agreement and the imposition of a 17.09% duty on Mexican imports. The resulting trade disruption forced exporters to reroute volumes and adjust pricing strategies, while the government’s minimum export price policy, implemented on August 8, 2025, set at USD 0.95/kg for round/bola tomatoes, USD 0.88/kg for Roma, and USD 1.70/kg for specialty varieties, provided a price floor, stabilizing prices around current levels. Despite initial market uncertainty, Mexican producers continued harvesting crops planted before the policy change, generating a temporary oversupply. Additionally, Mexico’s increasing adoption of Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) has boosted yields of greenhouse and vine-ripened tomatoes, further increasing supply and contributing to the price decline. Seasonal production peaks in late summer and early autumn also coincided with these trends, reinforcing the downward pressure on prices.
Morocco
In W38, Moroccan wholesale tomato prices averaged USD 0.21/kg, reflecting a 4.55% WoW drop, a 22.22% MoM decline, and a 38.24% YoY plunge. The price drop reflects abundant domestic supply and record seasonal exports in 2024/25, with Morocco shipping 745 thousand mt of tomatoes, an 8.3% YoY increase, ensuring sustained availability in European markets. Although a single batch of cherry tomatoes triggered a contamination alert in early Sep-25, exports continued uninterrupted, maintaining a steady supply. Strong export flows efficiently meet EU demand, yet the rapid movement through the supply chain exerts downward pressure on wholesale prices. Combined with ample production, competitive pricing, and the presence of lower-cost imports, Moroccan tomato prices remain relatively low, challenging higher-cost producers in the European market.
Turkey
In W38, Turkish wholesale tomato prices remained stable at USD 0.85/kg for the fifth consecutive week. This stability is underpinned by consistent domestic demand, the late-summer peak in harvesting, and abundant supply, which together moderate price fluctuations. According to the World Processing Tomato Council (WPTC), as of September 19, harvesting is complete in the South, with a maximum of ten days remaining in the Bursa area, while the Konya region will continue until mid-Oct-25, albeit with reduced surfaces this year. Factories are operating at low capacity, processing tomatoes of average to good quality, and weather conditions remain favorable, with no rain forecast. Local culinary traditions and cultural consumption patterns sustain demand, helping maintain steady prices despite seasonal variations in exports. The modest 4.94% YoY increase reflects inflationary pressures and rising costs in labor, energy, and packaging, slightly pushing up overall market rates.
France
In W38, French wholesale round tomato prices declined 4.40% WoW to USD 1.74/kg, reflecting a 12.56% MoM drop and a 10.77% YoY fall. The decrease is largely driven by weaker domestic consumption, as cooler weather reduces demand for summer salads, particularly cherry tomatoes. At the same time, imports of lower-priced Moroccan tomatoes continue to suppress domestic prices, limiting market access for French growers and contributing to accumulating stockpiles. Increased competition from international suppliers, coupled with persistent challenges in domestic consumption patterns, further explains the YoY decline. Domestic supply is also on the rise. According to WPTC, by the end of W37, 140 thousand mt had been processed, representing 80% of contracted volumes, with 7% penalties and an average Brix of 5.08. While overall quality remains good, a growing share of green fruits is being delivered to factories. Some smaller plants have already closed, but harvesting is expected to continue for another two to three weeks, aiming to reach the forecast of between 175 thousand mt and 180 thousand mt.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Leverage EU Trade Liberalization for Moldovan Tomato Exports
Moldovan tomato exporters should strategically align with EU agri-food standards ahead of the 2027 integration timeline, ensuring product quality, certification, and compliance with DCFTA regulations. Establishing long-term supply contracts with key EU buyers, particularly in France, Germany, and the Netherlands, will help secure stable market access and reduce the risk of trade disruptions. Additionally, exporters should diversify varieties to meet niche EU consumer preferences, such as cherry, truss, and specialty tomatoes, to maximize revenue under tariff-free conditions.
Strengthen Quality Assurance for Moroccan Cherry Tomatoes
Moroccan exporters should proactively maintain and communicate rigorous food safety measures to reinforce trust in European markets, minimizing the impact of isolated contamination alerts. Investments in traceability systems, quality audits, and rapid response protocols will ensure that shipments continue without interruptions, particularly during peak export months (November to March). Targeting emerging markets in Europe and West Africa through tailored marketing campaigns can further sustain export growth while mitigating reputational risk from rare incidents.
Improve Supply Chain Coordination in Punjab
To stabilize tomato prices, Punjab authorities and market committees should enhance real-time monitoring and forecasting of tomato arrivals from domestic and cross-border sources. Establishing dedicated communication channels between suppliers, transporters, and regulatory bodies can prevent bottlenecks at the Torkham and Chaman borders. Simultaneously, implementing digital reporting of supply and pricing data to PAMRA will allow authorities to act swiftly against hoarding and profiteering, while educating retailers and consumers on fair pricing practices to reduce market panic during shortages.
Capitalize on Seasonal and Cultural Tomato Demand
Businesses in Turkey and similar markets should optimize production schedules to coincide with cultural and seasonal peaks in tomato consumption, particularly for paste and traditional dishes. Leveraging digital platforms for pre-orders, appointment-based paste processing, and subscription models can streamline operations while reducing waste. Marketing campaigns highlighting artisanal, locally produced, and high-quality tomato products will strengthen brand value and maintain steady consumer demand during peak harvest periods.
Sources: Tridge, Agrodiario, Fresh Plaza, Kamu3






