W4 2025: Tomato Weekly Update

In W4 in the tomato landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- The spread of ToBRFV in Australia threatens crop yields, prompting strict quarantine measures.
- Morocco has expanded its tomato production, strengthening its EU market position, but faces rising domestic prices and trade tensions with Spain.
- Nigeria and Mexico have experienced significant tomato price drops due to bumper harvests, while Mexico also faces potential trade disruptions with the US.
- Spain and France continue to struggle with production declines, leading to fluctuating prices and increasing competition from Morocco and Türkiye.
1. Weekly News
Australia
Tomato Brown Rugose Fruit Virus Detected in Victoria, Prompting Quarantine Measures
The detection of tomato brown rugose fruit virus (ToBRFV) in Victoria, Australia, has raised concerns for the tomato industry, as it follows its earlier outbreak in South Australia. The virus, which severely reduces crop yields by up to 70%, was found in a Goulburn Valley after seedlings were moved from South Australia. In response, Agriculture Victoria Services, under the Department of Jobs, Precincts and Regions (DJPR) implemented quarantine controls and destroyed affected plants. Although the virus does not pose a food safety risk, mandatory crop destruction and import bans have been imposed in South Australia. The virus's spread within Victoria appears contained, with no further outbreaks reported. Victoria, responsible for 70% of Australia's processing tomatoes, is confident in the measures taken to control the virus's impact.
Kazakhstan
Russia Lifts Temporary Tomato Import Restrictions from Kazakhstan
The Russian Federation has lifted temporary restrictions on tomato imports from Kazakhstan, effective January 16, 2025. This decision follows an analysis by the Federal Service for Veterinary and Phytosanitary Surveillance (Rosselkhoznadzor) and the Federal State Budgetary Institution (VNIIKR), as well as negotiations with Kazakhstan's Ministry of Agriculture. The ban was lifted for tomatoes from 36 greenhouse complexes in Kazakhstan, which have been recognized as free from quarantine threats. Ongoing discussions aim to remove restrictions on other plant products. This development may positively impact trade and tomato supply dynamics between the two countries.
Morocco
Morocco Boosts Tomato Production by 17.36% Over the Past Decade
Over the past decade, Morocco has significantly expanded its tomato production by 17.36%, positioning itself as a key player in the global tomato market. This growth contrasts with declines in major European producers, such as Spain and the Netherlands, where production fell by 18.83% and 19.93%, respectively during the same period. Meanwhile, Türkiye remains the dominant producer, with a 12.24% increase in output. Morocco's proximity to Europe, along with favorable policies and agricultural practices, has enabled it to become a stronger competitor in the European Union (EU) market. However, the country faces challenges with rising domestic prices, particularly as tomato prices surge ahead of Ramadan.
Rising Tensions Between Moroccan and Spanish Tomato Growers Over Legal Threats and EU Agreement Disputes
Tensions between Moroccan and Spanish tomato growers have escalated following a statement from Spain's Coordinator of Farmers' and Ranchers' Organizations (COAG), which announced plans to pursue legal action against Moroccan tomato importers for alleged tax fraud. This comes after the European Court of Justice ruled to invalidate agricultural agreements between the EU and Morocco. Moroccan representatives, including the president of the Moroccan Interprofessional Federation for Fruit and Vegetable Production and Export, dismissed the legal threat as an attempt by Spanish growers to secure more subsidies. In addition, he emphasized that Moroccan tomato exports to Europe continue unaffected, and negotiations with the EU on new agricultural agreements are ongoing. Furthermore, Morocco rejects the labeling of tomatoes from the disputed Sahara region, asserting that they should be recognized as Moroccan products.
Nigeria
Tomato Prices in Daura, Katsina State, Plummet After Bumper Harvest
Tomato prices in Daura, Katsina State, Nigeria, have significantly dropped following a bumper harvest during the irrigation farming season. Market surveys revealed that a basket of tomatoes now costs USD 3.93 (NGN 6,000), down from USD 22.91 (NGN 35,000) in Oct-24. Residents have expressed optimism that this price drop will extend to other farm products, improving the affordability of essential commodities.
2. Weekly Pricing
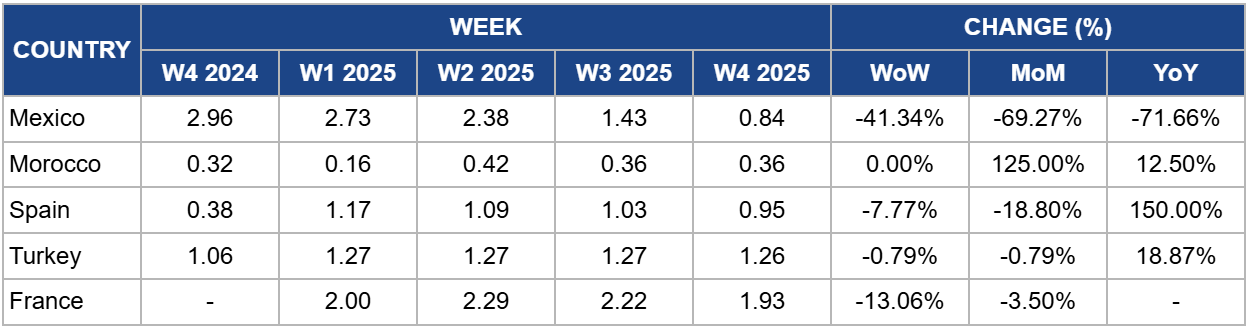
Weekly Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
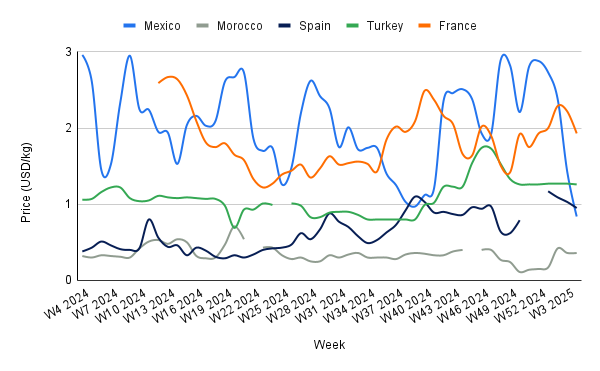
Yearly Change in Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (W4 2024 to W4 2025)
Mexico
Mexico's tomato prices have dropped significantly to USD 0.84 per kilogram (kg) in W4, marking a 41.34% week-on-week (WoW) decline and a 71.66% year-on-year (YoY) decrease. This sharp fall is primarily driven by increased domestic supply, particularly from key producing regions like Sinaloa and Baja California, where favorable weather has boosted yields. Additionally, reduced export demand, especially from the United States (US), has contributed to downward pressure on prices.
Furthermore, ongoing trade tensions between the US and Mexico could influence future price movements. If new tariffs are imposed on Mexican tomatoes under Trump's "America First Trade Policy," exports to the US could decline further, increasing domestic supply and exerting additional downward pressure on prices in Mexico. However, if trade restrictions lead to higher US tomato prices, alternative export markets or domestic demand could stabilize or lift Mexican prices in the longer term. Retaliatory measures by Mexico on US agricultural imports may also shift market dynamics, affecting supply chains and pricing trends.
Morocco
Morocco's tomato prices remained stable at USD 0.36/kg in W4, reflecting a significant 125% month-on-month (MoM) increase from USD 0.16/kg. The price surge is primarily driven by lower-than-usual production following a high supply period from Oct-24 to Dec-24. In addition, post-holiday seasonal demand has increased, putting further upward pressure on prices.
Cold weather has slowed harvests across all tomato varieties, limiting supply and sustaining higher prices. With temperatures expected to remain low in the coming weeks, production constraints could persist, potentially driving prices higher. If adverse weather continues, global tomato supply—especially for round, cherry, and plum varieties—may tighten further, affecting export availability and pricing in key markets such as the EU. However, any recovery in production or shifts in trade policies could moderate price increases in the near term.
Spain
Spain's tomato prices fell to USD 0.95/kg in W4, marking a 7.77% WoW decrease but a 150% YoY increase. The price trend reflects broader structural challenges in Spain’s tomato sector, which has seen an 18.83% production decline from 2014 to 2023, pressured by rising competition from Morocco and Türkiye, higher production costs, and strict environmental regulations.
The ongoing production decline, coupled with increasing competition, puts Spain’s position in the European market at risk. If these trends persist, Spanish tomato prices may remain volatile, with potential upward pressure due to reduced domestic supply. However, further expansion of Moroccan and Turkish tomato exports at lower prices could limit Spain's ability to sustain higher prices in the long term. Industry experts emphasize the need for investment in technology and sustainability to restore Spain’s competitiveness and prevent further market share loss.
Türkiye
Türkiye's tomato prices declined slightly to USD 1.26/kg in W4, reflecting a marginal 0.79% WoW and MoM decrease. However, the price remains elevated compared to the previous year due to reduced domestic supply, as cold weather, heavy rainfall, and storms have significantly impacted greenhouse production in Antalya, the country’s primary tomato-producing region.
France
In W4, France's tomato prices fell to USD 1.93/kg, reflecting a 13.06% week-on-week and 3.50% MoM decrease. The price drop is largely due to a 9% YoY decline in greenhouse tomato production, which reached 436,236 metric tons (mt) in 2024. While outdoor production increased by 19% over the previous year, it has not fully offset the overall supply reduction.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strengthen Biosecurity and Quarantine Measures
To mitigate the risk of further outbreaks of ToBRFV in Australia, authorities and industry stakeholders should enhance biosecurity protocols. This includes stricter regulations on seed and seedling movement, mandatory testing for nurseries supplying commercial farms, and expanded surveillance in high-risk areas. Establishing long-term containment strategies, such as greenhouse hygiene programs and resistant crop varieties, can prevent future disruptions in production and trade.
Diversify Export Markets to Reduce Trade Risks
Given ongoing trade tensions and potential tariff risks affecting Mexican tomato exports to the US, Mexican producers should proactively expand their export reach. Targeting alternative markets in Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America can reduce reliance on a single trading partner and mitigate the impact of sudden policy changes. Collaborating with trade associations and leveraging free trade agreements can facilitate smoother entry into these markets while ensuring price stability.
Sources: Tridge, Agrosektor, Morocco World News, ABC, Horti Daily, Fresh Plaza, Tabasco Hoy






