W42 2024: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
1. Weekly News
Argentina
Argentina to Launch Livestock Electronic Traceability System by Mar-25
Argentina plans to implement a mandatory electronic traceability system for cattle, buffalo, and deer starting March 1, 2025. This new system will replace the existing manual method and is financed by a World Bank loan. It aims to ensure individual traceability by recording all movements of these animals. Producers will have free access to the electronic devices until June 30, 2026, with an estimated cost of approximately USD 0.75 per device. The tender for these devices is set to close on November 13, 2024, and will be organized into 11 regions. During the transition period, electronic and visual traceability systems will be maintained until all herds are fitted with chips.
Brazil
Meatpacking Profit Margins Shrink Amid Rising Prices in Brazil
According to the Center for Advanced Studies in Applied Economics (Cepea), Brazil’s beef cattle market has reached a turning point in recent weeks, impacting meatpacking plants with shrinking profit margins. As of October 16, 2024, the average price of an arroba of beef cattle in São Paulo rose to USD 51.29 (BRL 292.19), a 14.4% increase from the previous month. Beef carcasses in Greater São Paulo also saw an 11.7% month-on-month (MoM) rise, reaching USD 3.52 per kilogram (BRL 20.05/kg). The price gap between the wholesale of married ox carcass (15 kg) and the arroba price paid to ranchers narrowed, with the difference shrinking from USD 2.67 (BRL 15.19) in Sep-24 to USD 1.42 (BRL 8.10) in Oct-24. From Jan-24 to Sep-24, the average difference was USD 2.24 (BRL 12.76), with a peak of USD 2.67 (BRL 15.23) in Jun-24 and a low of USD 1.39 (BRL 7.93) in Jan-24.
Despite efforts by meatpacking plants to resist raising cattle purchase prices, a cattle supply shortage has led to further increases across most regions. In São Paulo, cattle prices ranged from USD 51.61 (BRL 294) to USD 53.76 (BRL 312) on October 16, 2024, while Paraná, Minas Gerais, Mato Grosso do Sul, and Goiás recorded prices above USD 50.90 (BRL 290), with some deals reaching USD 52.66 (BRL 300). Wholesale bone-in beef carcasses in Greater São Paulo increased 12.4% MoM in Oct-24 to USD 3.69/kg (BRL 21.01/kg). The Cepea/B3 Beef Indicator closed at USD 52.71 (BRL 300.30) on October 16, 2024, its highest since Feb-23 and rising 29% since Jan-24.
China
China's Calf Production Expected to Decline in 2025
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) forecasts a slight decline in China's calf production in 2025 due to lower beginning cow stocks. Although high cattle prices and government policies previously boosted herd growth, economic challenges, as well as low dairy and beef prices, have reduced motivation. Increased culling of dairy cows in 2023 and 2024 further pressured beef prices, leading to losses for many small breeders with around 10 heads.
In Jun-24, China's Ministry of Agricultural and Rural Affairs (MARA) issued a notice to stabilize beef cattle production, including expanding cow herds, improving feed efficiency, and offering subsidies. Local governments are encouraged to support farms through financial aid and eliminate low-yield cattle to improve herd efficiency. As a result of low cattle prices, producers are culling more cattle, leading to revised lower estimates for calf production in 2024 and reduced inventory in 2025.
Philippines
Philippines Lifts Ban on Imports of Beef and Cattle from the UK
The Philippines has officially lifted its ban on livestock and meat imports from the United Kingdom (UK), a decision welcomed by British exporters. Active since 2021 due to concerns over bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), the ban was removed after a thorough review of the UK's safety protocols and animal health standards. The Philippines' Department of Agriculture expressed confidence in the UK's control measures, paving the way to reopening a crucial market for British beef and cattle producers. While this presents new opportunities for UK exporters, they will face strong competition from major beef-exporting countries such as the United States (US), Australia, and Brazil. However, the UK's reputation for high-quality beef could provide a competitive edge as British producers work to re-establish supply chains and partnerships in the Philippine market. The resumption of exports is expected to boost the UK agricultural sector, which has faced challenges in the post-Brexit trade landscape.
United States
US Cattle Herd Decline Opens Opportunities for Australia
Drought has reduced the US cattle herd to its lowest level since the 1950s, leading to increased beef imports and reduced export potential. As US farmers focus on rebuilding their herds, competitors have opportunities to fill the gap. However, major beef exporters like Brazil face challenges due to the expected decline in domestic production in 2025 and limited access to key markets. This shift has created an opening for Australia, capitalizing on favorable weather and a growing cattle herd to increase beef exports, particularly to the US and Asia.
Australia has gained market share in Japan in 2024, rising from 38% to 47%, and South Korea, from 35% to 45%. Meanwhile, US market shares fell in Japan in 2024 from 40% to 34% and South Korea from 55% to 48%. In China, Australia's share grew from 7% to 8% in 2024, while the US fell from 7% to 5%. Meanwhile, Australia's beef exports are forecasted to grow from 1.08 million metric tons (mmt) in 2023 to 1.36 mmt in 2024, with a projected slight increase to 1.37 mmt in 2025 before a decline in 2026.
2. Weekly Pricing
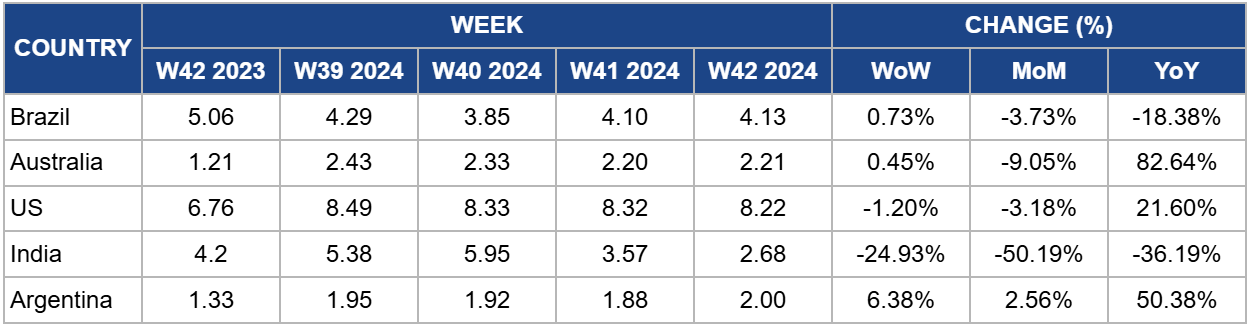
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
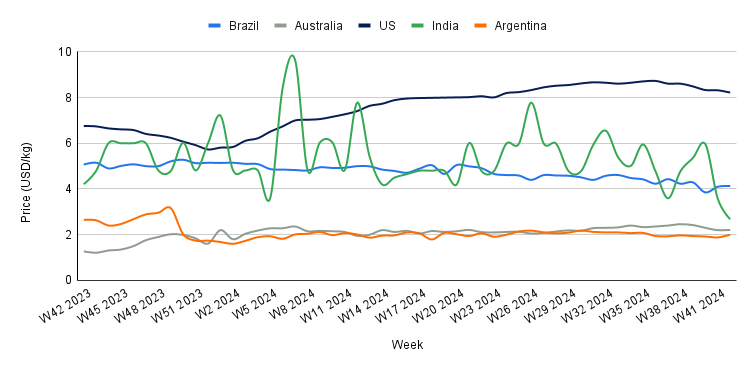
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W42 2023 to W42 2024)
Brazil
In W42, Brazil's wholesale price for boneless rear beef averaged USD 4.13/kg, marking a 0.73% week-on-week (WoW) increase but an 18.38% year-on-year (YoY) decline. The WoW rise is driven by growing demand and a limited market supply caused by tight slaughter schedules. According to Cepea, the price increase is being supported by strong sales in domestic and international markets. Safras and Mercado also point to the restricted availability of slaughter schedules, currently at their worst point this season, as a factor in the price rise. This dynamic could impact the prices of competing proteins, particularly chicken, which may increase due to the limited beef supply.
Australia
Australia's national young cattle indicator averaged USD 2.21/kg in W42, reflecting a modest 0.45% WoW rise but a significant 82.54% YoY increase. While the WoW gain was slight, Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA) reported a downward trend in the finished cattle market in W42, though young cattle remained the least affected. Yardings remained stable compared to W41 despite the resumption of two sales. Rainfall in New South Wales and Queensland reduced throughput in certain regions. Processor demand weakened in several southern saleyards, but export buyers showed increased interest. Quality varied more widely across markets, leading to a larger disparity between cattle lines.
United States
In W42, the average price of lean beef (92% to 94% lean) in the US stood at USD 8.22/kg, marking a 1.20% WoW decline but a significant 36.19% YoY increase. This marks the sixth consecutive week of price decreases, bringing lean beef prices to their lowest point since W24. The continued decline is likely due to the seasonal drop in beef demand as winter approaches, following the peak summer season. Despite the recent price reductions, lean beef prices remain relatively high, mainly due to reduced domestic production driven by a shrinking cow herd, which has constrained overall supply.
India
The average price of cow beef in India dropped to USD 2.68/kg in W42, reflecting a sharp 24.93% WoW decline and a significant 36.19% YoY decrease. These fluctuations underscore the volatility of India's beef market, which has been particularly pronounced over the past year. The instability is largely driven by shifting domestic and international regulations, along with fluctuations in domestic supply. Consequently, prices remain unpredictable, heavily influenced by evolving policies and supply chain dynamics.
Argentina
In W42, the average price of steer beef in Argentina rose to USD 2.00/kg, reflecting a 6.38% WoW increase. This rise can be attributed to a slight rebound in beef demand following the celebration of the Day of Respect for Cultural Diversity on October 12, 2024. However, beef prices have remained subdued generally due to weakened domestic demand, as beef consumption has reached historic lows amid Argentina's ongoing economic crisis. According to the Chamber of Industry and Commerce of Meat and Derivatives of the Argentine Republic (CICCRA), per capita beef consumption in Argentina averaged 46.8 kg during the first nine months of 2024, down 12.3% from the same period in 2023. This represents a decline of 6.6 kg per inhabitant per year. Additionally, the moving average for the last twelve months showed per capita consumption of 47.5 kg in Sep-24, 10.9% lower than in Sep-23, equivalent to a decrease of 5.8 kg per inhabitant per year.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhance Traceability to Boost Market Confidence
Argentina should implement robust training programs for producers on the new electronic traceability system. This would facilitate a smooth transition from the manual system and ensure producers maximize the benefits of individual animal tracking. Additionally, creating awareness campaigns about the advantages of electronic traceability can help gain producer buy-in and improve market confidence.
Implement Cost Management Strategies for Meatpackers
Meatpacking plants in Brazil should focus on cost management and efficiency optimization. This can include negotiating better supply contracts, investing in technology to reduce operational costs, and exploring alternative sourcing strategies. Implementing lean manufacturing principles could also help maintain profit margins despite rising input costs.
Leverage UK Beef Quality to Compete in the Philippines
UK beef exporters should capitalize on their reputation for high-quality beef by promoting their products through targeted marketing campaigns in the Philippines. Establishing partnerships with local distributors and participating in trade fairs can enhance visibility and help re-establish supply chains. Additionally, offering competitive pricing and emphasizing quality control measures can help UK exporters gain a foothold in this newly reopened market.
Capitalize on Emerging Markets for Australian Beef Exports
Australia should strategically target its beef exports to growing markets, particularly in the US and Asia, where its market share is increasing. Building strong relationships with importers and establishing promotional campaigns highlighting Australian beef's quality and sustainability can further enhance its market position. Additionally, expanding logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery and maintain product quality will be essential in meeting rising demand.
Sources: Beefpoint, Agromeat, The Cattle Site, Milknews, Defrentealcampo, Canal Rural, Suenaacampo


