W51 2024: Mango Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Brazil
Tommy Atkins Mango Prices Surged in Brazil Due to a Limited Supply
Due to limited supply, Tommy Atkins mango prices soared by 34% week-on-week (WoW) in the São Francisco Valley and 26% WoW in Livramento de Nossa Senhora. In contrast, Palmer mango prices fell by 3% WoW in the São Francisco Valley due to continued high availability despite a slowed harvest.
India
Karnataka Forms Mango Development Board to Support Alphonso Growers
The state government in Dharwad, North Karnataka, has approved the creation of a Mango Development Board. This initiative aims to strengthen Alphonso mango cultivation, which is renowned in the region for meeting international standards. With over 14 thousand hectares (ha) under cultivation and annual production exceeding 100 thousand metric tons (mt), Dharwad exports mangoes to Indian cities, Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, and Europe. Headquartered in Kumbapur, the board will address issues like middlemen, who often reduce the profit for growers by purchasing mangoes at low prices and selling them at a higher cost, leading to exploitation and a lack of market transparency. By promoting direct marketing, the board aims to ensure fair pricing, support research to enhance mango varieties, and expand exports. Backed by USD 879 thousand (INR 75 million) under the "One District, One Product" initiative, the board aims to transform Dharwad into a prominent mango hub.
Peru
Peruvian Mango 2024 Campaign Faces Market and Logistical Challenges
Peru's 2024 mango campaign rebounded to 80% production after a challenging previous season of just 20% output due to poor flowering caused by El Niño. However, the early harvests in Oct-24 overlapped with Brazilian supply, leading to market saturation and putting additional pressure on Peru's exports. This overlap, combined with challenges such as smaller fruit sizes, high logistics costs, and intense competition from Brazil's cheaper mangoes, has made the European market highly competitive. Meanwhile, elevated air transport costs and customs delays further complicate exports. Peru focuses on diversifying markets, adopting advanced packing technologies, and enhancing air transport infrastructure to sustain its international standing.
Mexico
Prolonged Drought Threatens 2025 Mango Production in Sinaloa
Mango production in Sinaloa, Mexico, is expected to face significant challenges in 2025 due to prolonged drought and inadequate rainfall. These conditions are expected to delay early flowering, especially for the Ataulfo variety in Escuinapa, resulting in smaller fruit sizes and a higher risk of premature fruit drop. Although flowering is projected to begin in January, reduced soil moisture will likely lead to lower yields. While the Santa María dam and irrigation canals are nearing completion, irrigation for mango orchards is not expected to be available until mid-2025, compounding the production challenges.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Mango Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Mango Pricing Important Exporters (W51 2023 to W51 2024)
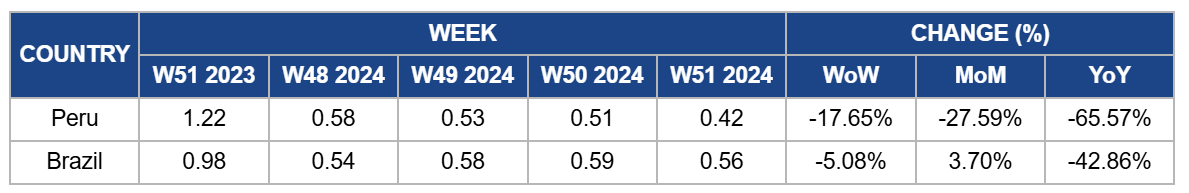
Peru
Peru's mango prices fell significantly by 17.65% WoW to USD 0.42 per kilogram (kg) in W51, with a 27.59% month-on-month (MoM) decline and a 65.57% year-on-year (YoY) drop. The price decrease is due to market saturation from overlapping early harvests with Brazilian supply, increasing competition, and price pressures. Smaller fruit sizes, high logistics costs, and customs delays have further contributed to the price drop. Despite these challenges, Peru focuses on diversifying markets and improving packing technologies to remain competitive internationally.
Brazil
In Brazil, mango prices fell by 5.08% WoW to USD 0.56/kg in W51, with a 42.86% YoY decline due to the seasonal peak in supply from other regions and increased availability from competing mango-producing areas. However, prices increased by 3.70% MoM due to limited supply from the primary regions like the São Francisco Valley and Livramento de Nossa Senhora, where Tommy Atkins mango production faced challenges, leading to a price surge.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhance Irrigation Management to Mitigate Drought Impact
Mango producers in Mexico should invest in efficient irrigation systems to optimize water usage and improve yields in anticipation of the expected drought. In the short term, producers should adopt soil moisture management practices and implement water-conserving techniques to mitigate the effects of reduced rainfall. As irrigation infrastructure nears completion, producers should work with local authorities to prioritize water access for orchards, ensuring timely irrigation to minimize the impact of delayed flowering and premature fruit drop.
Address Market Saturation through Strategic Market Diversification and Cost Efficiency
Peruvian mango exporters should focus on diversifying their export markets by exploring regions such as the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and parts of North America, where demand is rising but competition remains lower than in Europe. Additionally, tapping into emerging markets like China and India, where mango consumption is growing rapidly, can offer a new export avenue. Investments in advanced packing technologies and optimizing air transport logistics will help reduce high logistics costs and customs delays, improving competitiveness and securing better positioning in these international markets.
Manage Mango Price Fluctuations through Strategic Sourcing and Market Monitoring
Mango producers in Brazil should focus on managing price fluctuations by adjusting their sourcing strategies. Producers should reduce supply pressure for Tommy Atkins mangoes by optimizing harvests and adjusting distribution to maintain price stability. For Palmer mangoes, where high availability drives prices down, producers should consider delaying shipments or redirecting supply to less saturated markets to mitigate losses. Implementing a dynamic pricing model and closely monitoring market demand and harvest timing will enable better price volatility management.
Sources: Tridge, Agraria, Eastfruit, Freshplaza, NewsKarnataka, Portal Do Agronegocio, Oem







