
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Brazil's Apple Trade Deficit Hits Record Low in 2024 Amid Severe Weather Impact
Brazil's apple trade balance has turned negative in 2024, reaching record low levels from January to July. According to Comex Stat data, a Brazilian government platform tracking foreign trade, the deficit is USD 127.1 million free-on-board (FOB). This is the first time the country has seen such a trend during harvest months since 1997. Export revenues plummeted by 69% year-on-year (YoY), reaching only USD 9.2 million. On the other hand, import expenditures surged by 103% to USD 136.3 million. The sharp decline in Brazil's apple trade is primarily due to intense rainfall during spring 2023, followed by a challenging summer, which affected crop yields, apple size, and post-harvest quality. This led to an oversupply of small apples and hindered export performance, reflecting broader challenges in the sector.
Europe
South Tyrolean Apple Consortium Adapts to Challenges as European Apple Production Declines
The upcoming 2024/25 apple season in Europe will face challenges, as highlighted by Prognosfruit 2024, the annual conference where WAPA (World Apple and Pear Association) forecasts a decrease in European apple harvest by 11.3% YoY to around 10.21 million metric tons (mmt). This figure also represents a 13.6% decrease compared to the average of the past three years. Among the primary apple varieties, Golden Delicious production is expected to decline by 10.2% YoY to 1.9 mmt, while Gala apples are forecasted to decrease by 11.1% YoY, reaching 1.3 mmt. Conversely, Red Delicious production is anticipated to rise by 2.8% YoY. However, the output of Idared apples is forecasted to drop by 18.4% YoY. This was due to adverse conditions such as poor flowering, late frosts, and hail, particularly affecting central and eastern European Union (EU) countries like Poland, Hungary, the Czech Republic, and Austria.
Hungary
European Shortage Drives Price Surge as Hungarian Apple Harvest Declines Significantly
Due to a weak European apple harvest, Hungary is experiencing high demand for its apples, which is expected to drive up prices. The Hungarian Fruit and Vegetable Association (FruitVeB) forecasts a sharp decline in the apple harvest in 2024 to just 330 thousand tons, down from last year's 472 thousand tons, marking the second-lowest yield in the past decade. The domestic apple production for the fresh market is anticipated to fall short of the 110 thousand tons needed, with only 90 thousand to 100 thousand tons expected. The industrial apple sector is similarly affected, with an expected harvest of 230 thousand to 240 thousand tons, which needs to be improved for full processing capacity. As a result of the European deficit and increased demand, apple prices are projected to rise significantly, with fresh market apples potentially increasing by 10 to 15% YoY and producer prices by 25 to 35% YoY. In contrast, industrial apple prices may exceed USD 0.22 per kilogram (HUF 80/kg) at the season's start.
Iran
Iran's Annual Apple Production Reaches 3 to 4 Million Tons
Iran's annual apple production ranges between 3 to 4 million tons, with 250 thousand hectares (ha) dedicated to apple cultivation. The top apple-producing regions in Iran are West Azarbaijan, East Azarbaijan, and Tehran. From March 20 to July 21 of the current Iranian calendar year, Iran exported approximately 2.226 million tons of agricultural products worth USD 1.18 billion, marking a 32% YoY increase in value. The export volume also rose by 22% YoY.
Poland
Polish Apple Production Forecasted to Decline Due to Frost
Poland's apple production is expected to experience a significant decline in 2024, with frost events from March to May causing losses of up to 90% in some regions. Varieties such as Jonagored and Jonagold have been particularly affected, while Gala apples have remained largely unscathed. The Gala apple harvest is set to begin in W1 of Sep-24, with prices projected to increase by 15 to 20% YoY due to the overall reduction in European apple production.
Turkey
Niğde's Apple Harvest Faces 40% YoY Decline Amid Weather Challenges
Niğde, Turkey, a primary apple production center, exports to 15 countries, including Russia, Iraq, Syria, and India. However, this year's apple harvest from August to October is expected to drop 30 to 40% YoY, especially in red apples, due to insufficient rainfall and high summer temperatures. Last year's yield was around 600 thousand tons, but it is projected to be around 370 thousand tons in 2024. Despite this, prices rose to USD 0.42 to 0.56/kg (TRY 14 to 19/kg). The Niğde Apple Producers Association President emphasized the need for better export support and production planning from the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry to help stabilize the market and support producers experiencing high demand from countries like India.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
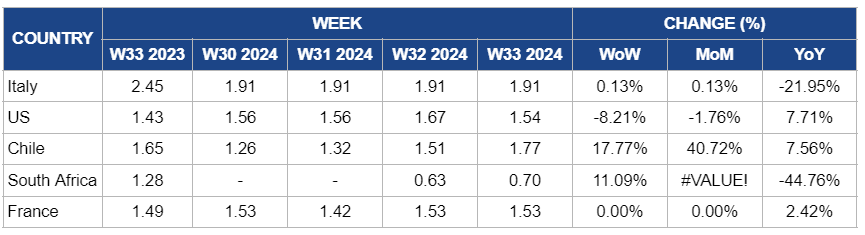
* Varieties: US and Italy (Gala), Chile, South Africa, and France (Granny Smith)
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W33 2023 to W33 2024)
* Varieties: US and Italy (Gala), Chile, South Africa, and France (Granny Smith)
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
Italy
In W33, apple prices remained steady again at USD 1.91/kg, with no week-on-week (WoW) and month-on-month (MoM) change. This continued price stability reflects Italy's consistent local apple production despite the broader decline in European apple yields. Due to adverse climate conditions, European apple production is expected to fall to around 10.2 mmt for the 2024/25 season. Italy's ability to maintain stable prices is attributed to its modest production increase and recovering consumer demand, which offset the impact of reduced yields across the continent. The strong supply conditions in Western Europe and favorable economic factors have further contributed to this stability, reinforcing Italy's position amidst the fluctuating European apple market.
United States
In the United States (US), apple prices decreased by 8.21% WoW to USD 1.54/kg in W33, down from USD 1.67/kg in W31. There is also a 1.76% decrease in MoM. This decline is mainly due to the anticipated recovery in Washington State's apple crop, projected to produce 124 million 40-pound (lb) boxes in 2024, returning to historical production levels after previous years of reduced output. The increased supply, including a rise in organic apples and other popular varieties, has eased market pressure and contributed to lower prices. The influx of additional apples into the market has surpassed current demand, resulting in the observed price decrease.
Chile
The price of Chilean apples in W33 surged by 17.77% WoW, 40.72% MoM, and 7.56% YoY, reaching USD 1.77/kg. This sharp increase is primarily due to recent flooding in Chile, which has caused substantial damage to apple orchards and disrupted production. The flooding has significantly reduced apple yields and affected the supply chain, leading to a tighter market. Consequently, the diminished supply amid steady or rising demand has increased prices. The ongoing challenges in apple production and quality due to adverse weather conditions are expected to keep prices elevated.
South Africa
Apple prices in South Africa increased by 11.09% WoW to USD 0.70/kg in W33. This surge is due to the recent storm, which caused significant damage to apple orchards, reducing yields and disrupting the supply chain. The storm's impact on production and distribution has tightened the market, leading to higher prices. However, there is a 44.76% YoY price decline. The current YoY decrease reflects the contrast between last year’s high prices and the current lower prices resulting from the storm's impact on supply and the previous year’s market conditions.
France
French apple prices remained at USD 1.53/kg in W33, showing no MoM change and a 2.42% YoY increase. Despite the lack of recent change, this price stability reflects the market's adjustment to the forecasted 3% YoY decline in production for 2024. The decrease in apple production, particularly affecting most regions except Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, is expected to exert upward pressure on prices. The higher prices compared to last year are driven by reduced supply and production challenges, which will impact the market in the coming months.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhance Export Support and Production Planning Amid Declining Apple Harvest
Private agencies and producers should take proactive steps to address the decline in Niğde's apple harvest due to weather challenges. Apple producers can collaborate with local agricultural cooperatives to secure financial support through private loans or investment programs to offset reduced yields. Additionally, they can form partnerships with international buyers and logistics companies to streamline export procedures, targeting high-demand markets like India. Producers should also focus on optimizing production practices, including advanced water management techniques, to ensure better yield stability in the face of climate challenges, helping to stabilize future harvests and prices.
Adjust Marketing and Pricing Strategies for Gala Apples
The marketing and sales teams of apple producers should adjust their strategies accordingly to address the price increase of Gala apples in Poland due to a decline in production. They should focus on promoting Gala apples as a premium product and implement a pricing strategy reflecting increased value due to reduced supply. Additionally, they should strengthen partnerships with distributors to ensure a stable supply chain and capitalize on the higher market prices during the upcoming harvest season.
Enhance Brazilian Apple Export Strategy
Apple producers should enhance post-harvest quality control by adopting best practices for sorting and grading apples and improving size and quality for the market to address Brazil's negative apple trade balance and export decline. Private agencies should invest in advanced storage solutions, such as controlled atmosphere storage, to maintain freshness and reduce spoilage. Additionally, upgrading packaging technologies to protect apples during transportation better can increase their market appeal. Producers should also focus on building strategic export partnerships to manage oversupply and open new market opportunities, helping to boost export revenues and mitigate the current trade deficit.
Sources: Tridge, Datamarnews, HF Brasil, Sondakika, Mercados, Agrotimes, Tehrantimes, Yahoo, Freshplaza, Eastfruit, Simfruit





