W36 2024: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Brazil Registers Increased Beef Exports as of Aug-24
According to Ministry of Development, Industry, Trade and Services (MDIC) data, Brazil’s beef exports reached 1.8 million metric tons (mmt), valued at USD 7.9 billion, from Jan-24 to Aug-24, marking a significant 27.9% increase in volume and an 18.7% rise in value compared to the same period in 2023. In Aug-24, Brazil exported 248.06 thousand metric tons (mt) of beef, generating USD 1.07 billion, representing year-on-year (YoY) growth of 16.5% in volume and 13.7% in value.
The Brazilian Beef Exporters Association (ABIEC) attributes this consistent export growth to the collaborative efforts of the Brazilian beef sector and the government, supported by the Brazilian Export and Investment Promotion Agency (ApexBrasil) through the Brazilian Beef project. This initiative has facilitated Brazil's access to more than 150 global markets. China remains the largest importer, with total shipments amounting to 797 thousand mt. Other key markets include the United States (US), with 122 thousand mt, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) with 113.5 thousand mt, and Hong Kong with nearly 83 thousand mt.
Brazil's beef exports to the European Union (EU) also saw significant growth in Aug-24, with the free-on-board (FOB) value increasing by 27.9% YoY to USD 57.6 million and volumes rising by 27.7% YoY to 7.96 thousand mt. This growth is largely driven by increasing European demand for Brazilian in natura beef, which dominates export categories. Additionally, the anticipation of European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) rules, set to take effect in Jan-25, has further fueled demand from importers, leading to a surge in shipments.
USDA Expects Gradual Phase Change in Brazil’s Livestock Cycle in 2025
Despite the typical expectation of a steep decline following rapid growth, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) predicts only a moderate contraction in Brazil's beef production for 2025. In its first projections for 2025, the USDA anticipates only a moderate reduction in production alongside an increase in export volumes. This contrasts with the expectation of a sharp contraction, reflecting a more stable outlook for the sector.
There is broad consensus that 2024 represents the peak of Brazil's cattle herd liquidation phase. The substantial increase in slaughter and beef production in 2024 has been significant. According to the USDA, Brazil's cattle slaughter is expected to rise by 3.59 million heads in 2024, an 8% increase compared to 2023. This surge has resulted in a record production of 11.85 mmt of beef, setting new highs for the industry. Despite the anticipated moderation in 2025, Brazil's beef sector remains poised for continued strong export performance. The USDA expects a modest drop in slaughter to 47.5 million heads and a slight decline in production to 11.75 mmt.
Despite this expected dip in production, the USDA foresees improved positioning for the export sector, boosted by Brazil's weak exchange rate. The result would be a reduction in domestic consumption, absorbing the production decrease while exports grow. The USDA predicts domestic consumption in Brazil will decline by 120 thousand mt in 2025 to 8.21 mmt, while exports will increase by 25 thousand mt, reaching 3.6 mmt.
Should this forecast materialize, it would suggest robust international demand for Brazilian beef, particularly from China, whose market recovery would drive higher prices and import volumes. However, if Chinese demand falls short, more beef will remain available for Brazil's domestic market.
China
Structural Growth is Expected in China’s Beef Market
In its Q3-24 report, Rabobank expects strong growth potential in China's beef market. Despite slower economic growth and a declining population, Rabobank indicates that China’s beef consumption continues to rise. However its per capita consumption is still lower than other developed Asian nations. Over the past five years, China has dominated the global beef market. While current trends show oversupply, stagnant demand, and rising inventories, Rabobank views these conditions as cyclical rather than permanent. The market is expected to bottom out in 2024 and then experience renewed growth, particularly in the food service sector, which has shown an annual growth rate of 3.2% over the last decade.
South Korea
Official Launch of Irish Beef in South Korea
On September 6, 2024, Ireland’s Minister for Agriculture, Food and the Marine launched Irish beef into the South Korean market. This follows the South Korean market opening to Irish beef in May-24. The Minister emphasized the importance of this achievement, highlighting South Korea’s high meat consumption, especially among the countries with the highest per capita consumption in Asia, and its growing demand for beef.
Despite having its own native Hanwoo beef, South Korea relies heavily on beef imports due to insufficient domestic production. Australia and the US are currently the primary suppliers of imported beef. However, there is growing interest in grass-fed beef, which presents a key opportunity for Irish beef producers.
Anglo Beef Processors (ABP), an Irish meat processing company, was one of the first to launch its beef products in South Korea through the K-Meat franchise, which operates restaurants, butcher shops, and stores nationwide. This move opens a new avenue for Irish beef in the South Korean market. However, Irish farmers are eager to see if this development will translate into tangible benefits for them in terms of higher prices and profitability. Access to bone-in beef products, like short ribs, which are popular in South Korea, is expected to drive demand, with industry leaders like Dawn Meats, Kepak, and Liffey preparing to expand trade.
United States
US Increased Live Cattle and Beef Imports in H1-2024
According to the USDA, live cattle imports to the US reached 1.12 million heads in the first half of 2024, marking a 19% increase compared to the same period in 2023. Additionally, frozen and chilled beef imports grew significantly, with frozen beef imports rising by 29% YoY to 365.07 thousand mt and chilled beef imports increasing by 11% YoY to 331.55 thousand mt. These import spikes were primarily driven by elevated domestic prices and a dwindling cattle herd, which has hit its lowest point since the 1950s.
The decline in the US cattle herd, exacerbated by prolonged drought in key states, high production costs, and reduced cattle slaughter, has resulted in a shortage of lean meat, particularly used in ground beef production. This has made the US an increasingly attractive market for beef imports.
Mexico has been the primary supplier of live cattle to the US, capitalizing on the shrinking US herd and high cattle prices. Mexico and Canada remain top exporters of fresh and chilled beef to the US. On the other hand, market shares for Australia and New Zealand have declined, as Brazil has captured a more significant portion of the US market. Brazil's increased exports to the US were partly due to the opportunity created by China’s temporary ban on Brazilian meat imports in 2021.
2. Weekly Pricing
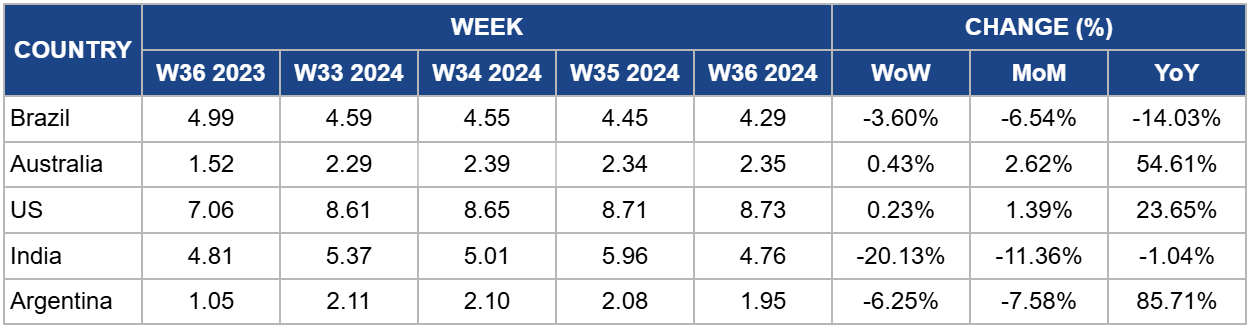
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
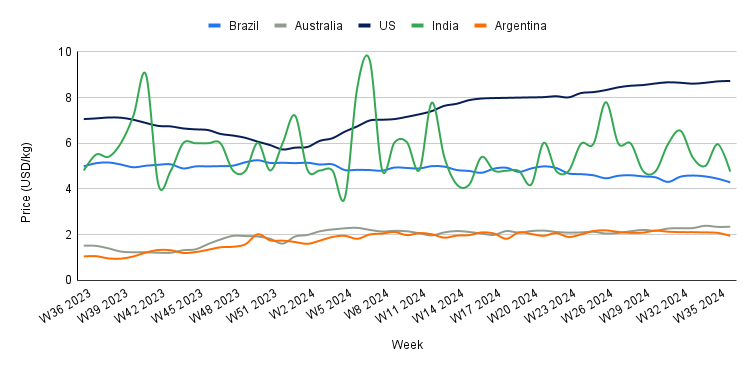
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W36 2023 to W36 2024)
Brazil
In W36, the wholesale price of boneless rear beef in Brazil averaged USD 4.29 per kilogram (kg), a 3.60% week-on-week (WoW) decrease and a 14.03% YoY decline. These declines are due to an increased beef supply from higher production levels. The USDA projects that Brazil's cattle slaughter will rise by 3.59 million heads in 2024, an 8% increase from 2023, leading to a record 11.85 mmt of beef production. In addition, the National Supply Company (CONAB) forecasts a 4.2% YoY rise in domestic beef availability in 2024, reaching 6.82 mmt.
Australia
Australia's national young cattle indicator averaged USD 2.35/kg in W36, a 0.43% WoW rise, and a significant 54.61% YoY increase. Reduced yardings and higher demand largely drove the weekly price rise. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), yardings fell by 5.9 thousand heads to 48.64 thousand heads during the week. The restocker yearling heifer indicator also saw an uptick, with the highest prices recorded at Tamworth, Carcoar, and Wagga Wagga, contributing 13% to the overall indicator. In some areas like Wagga Wagga and Tamworth, demand for heifers surpassed steers, driven by interest in restocking and feedlots, further pushing prices up.
United States
In W36, the average price of lean beef (92% to 94% lean) in the US was USD 8.73/kg, reflecting a 0.23% WoW rise and a notable 23.65% YoY increase. These price increases are primarily attributed to reduced domestic beef supply due to a shrinking cattle herd. The USDA reported that the US cattle population at the start of 2024 was 87.2 million heads, the lowest since 1951, primarily caused by prolonged drought and rising supply costs. This has led to a shortage of lean meat, particularly for ground beef production, pushing prices higher. Additionally, strong summer demand further contributed to the record-high prices.
India
The average price of cow beef in India dropped to USD 4.76/kg in W36, marking a 20.13% WoW decline and a 1.04% YoY decrease. These price drops reflect the ongoing volatility in the Indian beef market, which has been particularly pronounced over the past year. This instability is primarily driven by domestic and international regulations, alongside fluctuations in supply within the Indian market.
Argentina
In W36, the average price of steer beef in Argentina fell to USD 1.95/kg, a .6.25% WoW drop, reaching its lowest point since W24. This price reduction is mainly due to weakened demand, as Argentina's beef consumption has hit historic lows amid a severe economic crisis. According to the Chamber of the Meat and Cattle Industry and Commerce (CICCRA), per capita beef consumption averaged 44.7 kg in the first half of 2024, a 16.7% decrease compared to the same period in 2023.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Expanding Brazilian Beef’s Market Differentiation and Brand Value
Brazil's strong beef export performance, particularly in 2024, underscores a growing demand. Exporters should focus on market diversification by increasing value-added beef products to maintain momentum. To meet European and Asian consumer preferences, emphasize quality, sustainability, and traceability. Additionally, leveraging the premium appeal of grass-fed and organic beef in markets like South Korea and Europe could provide a competitive edge. Marketing campaigns highlighting health and environmental benefits would strengthen Brazil’s position in high-demand markets.
Strengthening Partnerships in China's Food Service Sector
Rabobank’s projection of structural growth in China’s beef market presents a lucrative opportunity for beef exporters. Exporters should intensify partnerships with China’s food service providers, as this sector is poised for growth. Offering tailored beef cuts and innovative packaging options to meet consumer demands in restaurants and retail outlets can boost market penetration. Furthermore, enhancing marketing efforts through targeted campaigns focused on beef quality, traceability, and food safety will align with rising health-conscious consumer trends in China.
Leveraging Irish Beef’s Entry into South Korea
Irish beef’s recent entry into the South Korean market can be maximized by capitalizing on the growing interest in grass-fed beef. Irish exporters should invest in educational campaigns highlighting grass-fed products' health benefits and superior taste to differentiate them from competitors. Collaborating with local influencers, chefs, and health experts can help build awareness and trust. Ensuring continuous dialogue with South Korean regulators to expand plant approvals will further facilitate market access for Irish beef processors. Irish exporters can also take advantage of the upcoming Chuseok holiday to promote their products, as premium beef is a highly consumed product during the holiday.
Diversifying Supply Chains to Meet US Ground Beef Demand
With the US beef market facing lean meat shortages and increased imports, beef importers should diversify supply chains to ensure a consistent flow of beef to meet demand. Collaborating with US retailers and food processors to provide tailored beef cuts for ground beef production can boost export volumes to the US. Additionally, leveraging Brazil’s strong export growth to the US by emphasizing competitive pricing and beef quality will help maintain a strong presence in the US market. Ensuring sustainability practices align with evolving consumer preferences for ethically sourced meat products.
Sources: Agromeat, Noticias Agricolas, Nieuwe Oogst, AgriLand



