W42 2024: Sugar Weekly Update
.jpg)
1. Weekly News
Global
Global Sugar Market Faces 2 MMT Shortfall Due to Brazilian Supply Decline and Export Restrictions
According to a forecast by Sucres et Denrées (Sucden), the global sugar market is projected to face a shortfall of nearly 2 million metric tons (mmt) due to factors such as dry weather, extensive sugarcane fires in Brazil, and export bans from major producers like India and Russia. Brazil's sugar supply is forecasted to decline by 40% year-on-year (YoY) in Q4-2024 and Q1-2025, contributing to rising raw sugar futures, which recently hit a six-month high at around USD 23 per pound (lb). While sugar beet and sugarcane production is expected to increase in the Northern Hemisphere, it will not compensate for the losses in Brazil. The International Sugar Organization (ISO) has projected a global deficit of 3.58 mmt for the 2024/25 crop year, and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) anticipates a decrease in global sugar inventories to a 13-year low. Facing domestic supply pressures, India has limited exports but is urged to lift restrictions as production is expected to rise. Meanwhile, Thailand is forecasted to increase sugar production by 18% in the 2024/25 marketing year (MY), which may help stabilize prices.
Brazil
Decrease in Sugar Vessels at Brazilian Ports in Oct-24
In W42, the number of vessels waiting to load sugar at Brazilian ports decreased to 74 from 80 the previous week, according to Williams Serviços Marítimos Ltda, and the volume scheduled for shipment dropped to 2.886 metric tons (mt) from 3.348 mmt. The Port of Santos holds the largest share of 1.889 mmt. Brazil's sugar exports in Oct-24 totaled 1.645 mmt, generating USD 767.6 million in revenue, with an average price of USD 466.40/mt. Despite a 33.6% rise in export volume compared to Oct-23, the average price per mt fell by 13.1% year-on-year (YoY).
Brazil's Sugar Production Forecast Adjusted Amid Extreme Weather Events and Wildfire Concerns
Brazil is expected to experience extreme weather events in 2024, including severe drought and increased temperatures, which will impact sugarcane production. While direct losses from wildfires are forecasted to be minimal, the USDA has revised its forecast for Brazil's sugar production in the 2024/25 crop year down to 43 mmt raw, primarily due to reduced cane quality and unfavorable weather conditions. The Center-South region is expected to contribute 40 mmt to this total.
From Apr-24 to Sep-24, Brazil's cumulative sugar production in the Center-South region reached 30.3 mmt, a 3.6% increase from the previous year, with São Paulo State accounting for approximately 65% of this output. The USDA maintains its 2024/25 domestic consumption forecast at 9 mmt, ensuring Brazil's capacity to meet domestic needs and export demands, with exports projected at 34.5 mmt raw.
Despite the challenges posed by wildfires and adverse weather, Brazil continues to hold a significant share of the global sugar market, supported by competitive pricing resulting from the depreciation of the Brazilian real (BRL). Major importers of Brazilian sugar include China, Indonesia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Global sugar supplies are anticipated to become more balanced by mid-2025 as weather conditions improve in other producing countries.
Türkiye
Sivas, Türkiye Achieves Record Agricultural Production of Sugar Beets Harvested Despite Drought Challenges
In Sivas, Türkiye, agricultural production reached new highs despite challenges from drought. The region harvested around 850 thousand mt of sugar beets on 162 thousand acres, supplying five sugar factories. Despite adverse weather conditions, sugar beet production remained strong, with yields improving slightly compared to the previous year. The President of the Sivas Chamber of Agriculture noted that farmers successfully overcame climate challenges, contributing significantly to the country's agricultural output.
Sugar Beet Harvest in Kahramanmaraş Boosts Local and National Economy
In the Kahramanmaraş districts of Elbistan, Afşin, Pazarcık, and Türkoğlu, sugar beet harvest is underway. An expected yield of 518 thousand mt of beets from 80 thousand acres is anticipated, resulting in approximately 71 thousand mt of crystal sugar.
Half of the beets have already been processed, contributing significantly to the local and national economy.
Ukraine
Significant Sugar Production Increase in Ukraine's Ternopil Region
In the Ternopil region of Ukraine, sugar production has significantly increased, according to the director of the Department of Agro-industrial Development. Sugar plants processed over 782 thousand mt of sugar beets, resulting in the production of more than 109,000 mt of sugar this season. This is a notable rise from the 75,649 mt produced by the same time last year, attributed to an earlier start to the season and higher quality raw materials. With over 2 mmt of sugar beets contracted, the region is forecasted to produce approximately 240,000 mt of sugar, with improved efficiency and better crop quality.
Vietnam
Vietnam's Sugar Industry Achieves Top Productivity in ASEAN
Vietnam's sugar industry has achieved the highest productivity in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) region for the first time, according to the Vietnam Sugarcane and Sugar Association (VSSA). The 2023/24 crop yielded 6.79 mt of sugar per hectare (ha), surpassing key regional producers such as Thailand and Indonesia. This growth is due to increased mechanization, Industry 4.0 technologies, and trade defense measures. Sugarcane output has risen by 166%, with sugar production increasing by 161% over the past four years. The purchase price for sugarcane has also increased significantly, ranging from USD 47.23 to 51.17/mt (VND 1.2 to 1.3 million/mt), supporting sustainable growth in the industry.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Sugar Pricing Important Producers (USD/kg)
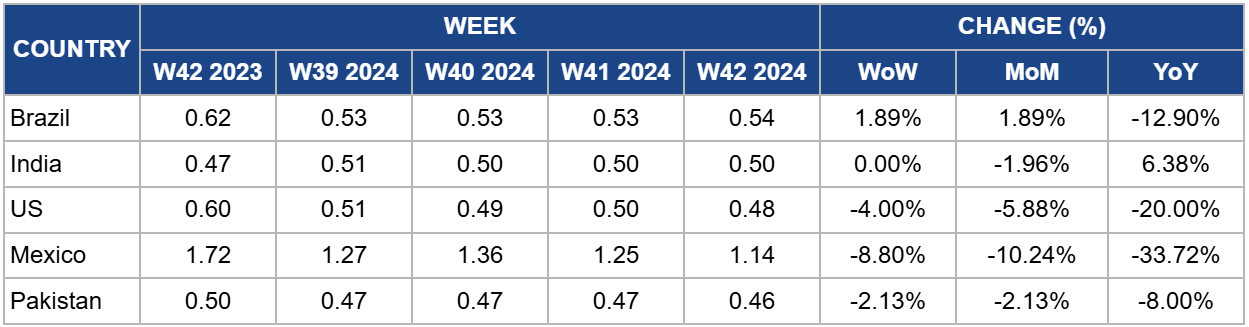
Yearly Change in Sugar Pricing Important Producers (W42 2023 to W42 2024)
.png)
Brazil
Brazil's sugar prices rose to USD 0.54 per kilogram (kg) in W42, reflecting a 1.89% increase both week-on-week (WoW) and month-on-month (MoM). This price movement is primarily due to unfavorable weather conditions and concerns over potential crop failures, reduced production forecasts, and strong domestic demand, which have significant implications for international sugar markets.
India
India's sugar prices remain stable at USD 0.50/kg for the third consecutive week, with a 6.38% increase YoY. Total sugar production for the 2024/25 season is forecasted to decrease to 32.50 mmt, with 4 mmt allocated for ethanol, resulting in net sugar production of 28.50 mmt. As of W42, the sugarcane crop is underperforming, particularly in Maharashtra, leading to a shorter crushing season of about 115 to 120 days. The Central Government has set the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) for sugarcane at USD 4.04 per quintal (INR 340/quintal). Sugar exports remain restricted, and the government will likely continue this policy due to low stock levels.
United States
In the United States (US), sugar prices decreased to USD 0.48/kg, reflecting a 4% WoW decline and a significant 20% drop YoY. This shift is influenced by the global economic expansion, which typically supports sugar demand. However, falling energy prices and potential recession risks could lead to further declines in sugar prices. Key sugar-producing countries, including Brazil and India, provide subsidies that impact global prices and can lead to fluctuations. Recent global sugar deficits have tightened stocks-to-use ratios, indirectly supporting US prices, particularly for raw sugar. Furthermore, Mexico's sugar exports to the US are severely affected by drought, with expected shipments at a 15-year low of 497 thousand mt, further straining domestic supplies.
Mexico
Mexico's sugar prices have decreased to USD 1.14/kg, representing an 8.8% WoW decline and a substantial 33.73% YoY drop. The recent rainy season positively impacted sugarcane production in Morelos but rising inflation poses a risk to producers as it undermines profit margins despite the good harvest. Despite favorable production conditions, challenges persist in Mexico's sugar industry. Rising costs for fertilizers and machinery have impacted profitability, while outdated irrigation systems contribute to significant water losses. Poor transportation infrastructure further complicates logistics and production efficiency. With approximately 36% of Mexico's sugar mills located in Veracruz, the state plays a crucial role in the national sugar economy. Although local producers have invested in road maintenance, escalating costs and low yields from inadequate fertilization continue to pose significant difficulties for the sector.
Pakistan
In W42, Pakistan's sugar prices fell to USD 0.46/kg, reflecting a 2.13% decline in both WoW and MoM, along with an annual decrease of 8% from USD 0.50/kg. The Pakistan Sugar Mills Association (PSMA) announced that the sugarcane crushing season will commence on November 21, 2024, ensuring adequate stock despite the government's approval for an additional 500 thousand mt of sugar exports. In addition, a PSMA spokesperson indicated there would be enough surplus sugar to meet over a month of domestic consumption, even post-export. However, the commitment to crushing hinges on the export approval and a forthcoming stock assessment by the Sugar Advisory Board (SAB) on November 1. The PSMA anticipates a surplus of 300 thousand to 500 thousand mt.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversify Supply Chains and Secure Alternative Sources
To mitigate the projected shortfall in global sugar supply, importers and food manufacturers should diversify their sourcing strategies by securing alternative suppliers from regions forecasted to increase production, such as Thailand and the Northern Hemisphere. Establishing partnerships with these emerging producers will help stabilize supply chains and reduce dependence on Brazil, which faces significant production declines. Additionally, exploring alternative sweeteners or sugar substitutes can minimize risk and manage costs as global sugar prices rise.
Invest in Strategic Stockpiling and Long-term Contracts
Given the anticipated global sugar deficit and price volatility, businesses should consider investing in strategic stockpiling to build up reserves during periods of relative market stability. Additionally, entering into long-term contracts with key suppliers, particularly in regions less affected by adverse weather conditions, can help secure a steady supply of sugar at more predictable prices. This approach will provide greater stability in meeting domestic and international demand, especially as prices fluctuate.
Sources: Agro Portal, Son Dakika, Ekonomi, WTO Center, Portal Do Agronegócio, Vinanet, Agro Info, Rural Voice, Farm Progress, El Sol de Cuautla, Imagen de Veracruz




