W46 2024: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
1. Weekly News
Global
Global Beef Market Outlook for 2025: Challenges and Opportunities
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) projects global beef production to decline by 500 thousand metric tons (mt) to 60.9 million metric tons (mmt) in 2025 after five years of growth, driven by reductions in the United States (US), Brazil, and the European Union (EU). Brazil’s output is forecasted to drop by 100 thousand mt to 11.75 mmt, marking its first significant decline in a decade. The EU’s production is expected to fall to 6.5 mmt, while the US faces the steepest decline, with a 4% year-on-year (YoY) reduction due to a cattle stock shortage. These changes are reshaping global market dynamics, especially with rising US import demand.
Despite reduced production, beef export markets are expected to remain resilient, with global exports holding steady at 12.9 mmt in 2025. Despite production challenges, Brazil, the world’s leading exporter, will sustain a record 3.6 mmt of exportable surpluses. Meanwhile, Argentina and Australia are poised to benefit from increased global demand and favorable policies, with the latter achieving a record 2.6 mmt in production, driven by a 2% YoY growth. Accounting for 34% of global imports, China will see a 1% YoY increase in beef imports to 3.825 mmt, even as domestic production marginally declines. Conversely, the US is forecast to set a new import record of over 2 mmt, driven by limited domestic supply, creating lucrative opportunities for major exporters.
The USDA expects the tight global supply to support higher beef prices in 2025. Shifts in import demand will see the US emerge as a major driver, alongside steady demand from China and growth in markets such as South Korea and Taiwan. Despite constrained production, global consumption will remain robust, reinforcing strong trade flows and profitability for exporters.
European Union
EU Beef Sector Faces Challenges Amid Declining Production, Rising Prices, and Regulatory Pressures
The European Commission (EC) predicts a decline in EU beef production through 2024 and 2025 due to high costs, disease outbreaks like bluetongue (BTV) and epizootic hemorrhagic disease (EHD), falling demand, and new regulations. Tight supplies have driven cattle prices above 2023 levels, but the sector remains unprofitable due to labor shortages, high energy costs, and regulatory uncertainty. Significant reductions in cattle populations are expected in France, Germany, the Netherlands, and Belgium, exacerbated by calf losses, poor forage production, and adverse weather conditions.
In Eastern Europe, cattle farming is growing, supported by EU policies like the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), which favors smaller producers and a shift from dairy to beef production. Poland, Romania, and the Balkans benefit from export opportunities and the adoption of local breeds. Despite these regional gains, overall EU cattle numbers are shrinking, with France and Germany seeing the largest declines.
High beef prices are likely to persist as falling feed costs encourage cattle fattening, but droughts and heat waves in Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria have reduced slaughter weights. EU beef imports fell 3.4% YoY in early 2024, particularly from Brazil, due to tariffs and supply chain regulations like the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). While demand is recovering in tourism-driven markets such as Spain and Greece, declining exports and tight supplies will keep prices elevated into 2025.
Argentina
Argentina's Beef Export Prices Resurges Driven by Strong Chinese Demand
Argentina's beef export prices to China, the country’s largest export market, have continued to rise. Currently, cuts like Garrón and Brazuelo are fetching USD 5,000/mt, marking a 20% increase from the first half of the year. Other beef cuts are trading between USD 4,600/mt and USD 5,800/mt, reflecting a 24% rise over recent months. This increase is driven by China's continued demand and reduced beef supply from Brazil, which retains cattle. Additionally, the US has increased import competition in the global market since it is rebuilding its livestock stocks, driving up export prices. As a result, beef prices are expected to strengthen further as China ramps up imports ahead of the 2025 Lunar New Year.
The rise in beef export prices has also positively impacted cattle prices within Argentina. Beef cattle are now sold for USD 3.39 per kilogram (ARS 3,400/kg), a 21% increase from earlier in the year. Manufactured cows, which are seasonal, saw a 66% price increase, rising from USD 1.80/kg (ARS 1,800/kg) from Mar-24 to Jun-24 to USD 3.09/kg (ARS 3,100/kg). However, exports to Europe are facing a different trend. At the SIAL in Paris, prices for high-quality Hilton cuts dropped by 19%, from USD 16,000/mt to USD 13,000/mt. Meanwhile, the price of steers, a scarce category, has remained steady at USD 3.99/kg (ARS 4,000/kg) on the hoof.
Brazil
Brazil Aims to Expand Beef Exports to Turkey Amid Growing Trade Opportunities
Brazil is taking steps to expand its beef exports to Turkey, one of the few major markets still restricted to Brazilian beef. During a mission in Ankara, the Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock, and Food Supply (MAPA) officials highlighted the quality of Brazilian beef and its compliance with halal standards, aiming to position Brazil as a strategic supplier for Turkey's growing food demand. Discussions also addressed lifting restrictions on poultry meat and expanding trade in agricultural products. Turkey is already the seventh-largest destination for Brazilian agricultural exports, valued at USD 0.45 billion (BRL 2.6 billion) in the first nine months of 2024.
The mission announced the establishment of an agricultural attaché in Ankara by the end of 2024 to strengthen trade ties. Brazil has also opened Turkish markets for new products like gelatin and bovine heparin. MAPA emphasized Turkey's strategic importance and Brazil's commitment to forging lasting trade agreements that boost gross domestic product (GDP), create jobs, and strengthen the national economy.
Brazil Sanctions New Law Regulating Animal Genetic Material and Cloning
On November 13, Brazil’s President sanctioned Law No. 15,021/2024, regulating the control and supervision of animal genetic material and cloning of domestic animals in Brazil. Derived from Bill No. 5,010/2013, the law covers the production, handling, import, export, and commercialization of genetic material and clones of animals like cattle, goats, and birds. Only registered suppliers are authorized to handle such material, with the federal government overseeing the process through veterinary services and maintaining a public database for tracking genetic material.
The law imposes penalties for violations, including fines, seizure, or destruction of genetic material, with fines ranging from USD 259.62 (BRL 1,500) to USD 0.26 million (BRL 1.5 million), depending on the severity. It also requires prior authorization to clone wild animals from Brazil. The President vetoed a section on tax incentives to ensure constitutional compliance. The law will take effect 90 days after publication, bringing greater regulatory certainty and efficiency to Brazil's animal genetic material industry.
United States
US Beef Industry Faces Challenges as Drought Impacts Herd Expansion and Production
The resurgence of drought in US cattle-producing regions has stalled plans to rebuild the nation's cattle herd, which is at its lowest level in seven decades. According to the US Drought Monitor, 62% of cattle were in drought-affected areas at the end of Oct-24, up from just 8% in Jun-24. Ranchers, particularly in Nebraska and Oklahoma, are grappling with dry pastures and delayed planting of grazing crops like wheat, forcing them to send young heifers and calves to feedlots earlier than usual. This trend, combined with a lack of pasture and high cattle prices, has delayed herd expansion, leaving analysts predicting it could take years to recover. Farmers in Nebraska report slaughtering 10% more of their herd last year due to the drought's impact on grazing conditions.
The tight cattle supply is hitting meat processors like Tyson Foods hard, with its beef division posting a loss in Q3-2024 and margins expected to worsen to negative 2.2% in Q4-2024, according to an investment research firm, Center for Financial Research and Analysis (CFRA). Early feedlot deliveries of young cattle are projected to reduce beef production in the first half of 2025 and tighten supplies further in the second half. This situation keeps beef prices elevated for consumers while delaying the industry’s recovery. For ranchers, rebuilding herds remains out of reach until weather conditions improve.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
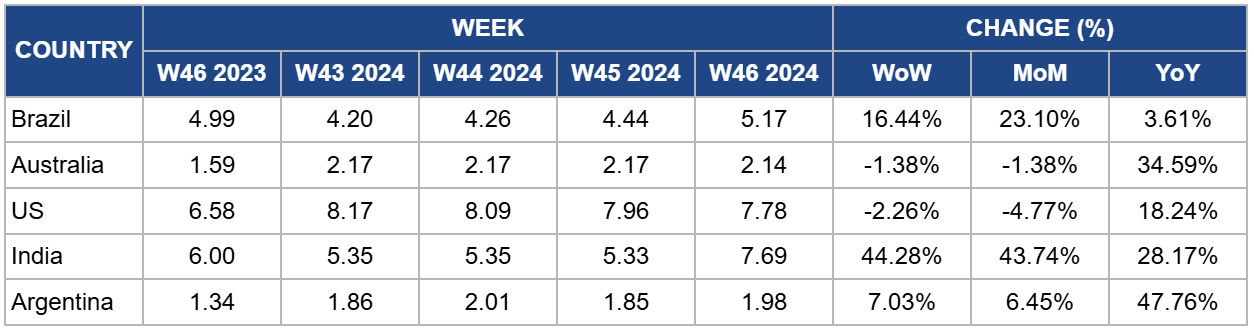
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W46 2023 to W46 2024)
.png)
Brazil
In W46, Brazil's wholesale price for boneless rear beef surged to USD 5.17/kg, a significant 16.44% week-on-week (WoW) increase and reaching its highest level since W50 of 2023. The prices also registered a substantial 23.10% month-on-month (MoM) rise and a 3.61% YoY increase. According to the Center for Advanced Studies on Applied Economics (Cepea), the Brazilian livestock market is experiencing heightened activity, characterized by continuous price increases and an accelerated production pace driven by strong domestic and international demand. Reduced slaughter activity at meatpacking plants has also contributed to the price surge.
Australia
Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator averaged USD 2.14/kg in W46, reflecting a 1.38% WoW drop, a 1.38% MoM decline, and a notable 34.59% YoY rise. According to Rural Bank, a leading Australian agribusiness bank, dry conditions in southern regions have increased supply levels at local markets, prompting southern buyers to shift back to local sourcing from northern markets. However, demand for stock may ease as processing centers are already booked well in advance, with schedules extending into late Nov-24 or even the end of 2024.
United States
In W46, the price of lean beef (92% to 94%) in the US averaged USD 7.78/kg, marking a 2.26% WoW decline and the tenth consecutive week of price drops, reaching the lowest level since W16. This also represents a 4.77% MoM decrease. Despite this recent downturn, prices are still up 18.24% YoY, primarily due to a tightening domestic supply caused by a shrinking cow herd. The price drop aligns with the seasonal dip in demand as winter approaches, following the peak consumption period in the summer. However, limited production continues to keep lean beef prices relatively high overall.
India
The average price of cow beef in India surged to USD 7.69/kg in W46, reflecting a substantial 44.28% WoW increase, a 43.74% MoM rise, and a 28.17% YoY jump. These price fluctuations highlight the ongoing volatility in India’s beef market, which is influenced by changing domestic and international regulations, and variable local supply. As a result, prices have become increasingly erratic, driven by evolving policies and shifting supply chain dynamics.
Argentina
In W46, Argentina's average steer beef price rose to USD 1.98/kg, reflecting a 7.03% WoW increase and a 6.45% MoM rise. Despite this uptick, beef prices in Argentina have remained relatively low throughout 2024, driven by reduced domestic demand amid the country’s ongoing economic crisis. According to data from the Chamber of Industry and Commerce of Meat and Derivatives of the Argentine Republic (CICCRA), per capita beef consumption fell by 12.3% in the first nine months of 2024, averaging 46.8 kg, an annual decrease of 6.6 kg per person. The 12-month moving average as of Sep-24 dropped to 47.5 kg per capita, marking a 10.9% YoY decline.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Adapt to Expected Global Beef Supply Challenges in 2025
To navigate the anticipated tight global beef supply in 2025, exporters should diversify their market reach by exploring emerging regions like Southeast Asia and the Middle East, reducing dependency on dominant markets such as China and the US. Additionally, focusing on value-added beef products, such as premium cuts or ready-to-cook offerings, will enable processors to target high-income consumer segments, ensuring profitability despite reduced production volumes.
Overcome Regulatory and Production Challenges
The EU beef sector can address its production and regulatory challenges by strengthening supply chain connections with Eastern European countries, which benefit from CAP incentives. This strategy will help offset declining production in Western Europe. Adopting sustainable farming practices, supported by EU green subsidies, will enhance resilience to adverse weather and regulatory pressures. Moreover, expanding promotional campaigns in recovering tourism-driven markets like Spain and Greece can stimulate demand, particularly for high-quality EU beef products.
Maximize Gains from Export Price Surge
Argentina’s beef exporters should streamline logistics and address supply chain bottlenecks to maximize gains from rising Chinese demand and higher export prices. Diversifying exports to other lucrative regions, such as the Middle Eastern countries, can further enhance market stability, leveraging Argentina’s halal-certified beef. At the domestic level, incentivizing farmers to adopt climate-resilient cattle breeds and improved pasture management techniques will mitigate production risks and ensure long-term sustainability.
Seize New Export Opportunities
To capitalize on opportunities in Turkey’s growing beef market, Brazil should expedite compliance with Turkish import requirements and actively negotiate favorable trade terms. Enhancing halal certifications will also open doors to other Muslim-majority markets, such as Indonesia and Egypt, providing additional revenue streams. Furthermore, the recently sanctioned law on animal genetic material offers a pathway to innovating cattle breeding practices, improving yield and disease resistance, which will boost productivity and competitiveness in the global market.
Sources: Tridge, AgroForum, Agromeat, Bichos de campo, Canal Rural, Elagro


