W10 2025: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
In W10 in the beef landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- The EU's beef sector faces uncertainty as trade talks with Mercosur and Ukraine aim to cut reliance on US imports but spark farmer concerns over competition.
- Brazil's beef exports are projected to reach a record 3.88 mmt in 2025, driven by strong global demand, particularly from China, despite temporary plant suspensions.
- China’s new tariffs on US beef and the suspension of some Mercosur suppliers are poised to reshape global supply chains, creating uncertainty.
- Paraguay’s beef exports surged in early 2025, with strong demand from Chile, Taiwan, and the US, while Uruguay has redirected exports to the US and EU as Chinese demand declines.
- Brazil, Australia, and Argentina experienced weekly price declines due to exchange rate fluctuations, and trade disruptions, while US prices rose amid supply concerns.
1. Weekly News
European Union
EU’s Beef Sector Faces Uncertainty Amid Trade Talks with Mercosur and Ukraine
The European Union (EU) is considering new trade agreements with Ukraine and the Mercosur bloc (Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay) to strengthen its agricultural sector and reduce dependence on United States (US) imports. However, these agreements face resistance from European farmers, particularly due to concerns about increased competition in the beef sector. While the EU aims to expand exports of strategic products like wine and dairy, the potential influx of beef from Mercosur countries poses a risk to local producers. To address this, the EU plans to implement safeguards to protect sensitive sectors, including beef, from market disruptions. Despite opposition from countries like France and Poland, the European Commission (EC) believes these agreements will enhance the EU’s global trade position while maintaining stability in the beef industry.
Brazil
Brazilian Beef Exports Poised for Record Growth in 2025
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) expects Brazil’s beef exports to reach a record high of 3.88 million metric tons (mmt) in 2025, a 7% increase from 2024. This projected growth is driven by rising production, strong global demand, and a weaker Brazilian real. Brazil will maintain its status as the world’s largest beef exporter, with exports accounting for 33% of its total production. China remains the primary market, despite the temporary suspension of three Brazilian meatpacking plants due to regulatory non-compliance identified by Chinese authorities. In collaboration with industry stakeholders, the Brazilian government is actively addressing these issues to resume exports. The government downplayed the impact, emphasizing that Brazil still has 126 plants authorized for export to China. Additionally, the Brazilian Association of Meat Exporting Industries (Abiec) is working with the Ministry of Agriculture to ensure a swift resolution, reinforcing confidence in Brazil’s agricultural health standards.
China
China’s Tariffs on US Beef and Mercosur Plant Suspensions Bring Uncertainty to Global Supply Chains
China’s new tariffs on US farm products are set to shift global trade patterns, particularly in the beef sector, as the country seeks alternative suppliers. With a 10% tariff imposed on US beef, imports from South America and Europe are expected to rise. However, China has simultaneously suspended beef imports from several processing plants in Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay, citing regulatory non-compliance, despite these countries being its key suppliers. Occurring amid an oversupply in the Chinese beef market, this suspension signals potential trade protectionism. As China continues to diversify its agricultural imports, the impact on global beef trade remains uncertain, with both policy shifts and market dynamics playing crucial roles.
Paraguay
Paraguayan Beef Exports Surge in Early 2025 Driven by Strong Global Demand
According to the National Service of Quality and Animal Health (Senacsa), Paraguayan meat exports have seen significant growth, generating USD 419.35 million by Feb-25, a 40% increase compared to the same period in 2024. Beef remains the highest-value export, with 60.65 thousand metric tons (mt) shipped to 39 countries, bringing in USD 339.81 million. Chile leads as the top buyer with 18.11 thousand mt worth USD 111.03 million, followed by Taiwan, the US, Israel, and Brazil. Paraguay also exported 11.5 thousand mt of bovine offal, generating USD 20.3 million, with Russia, Egypt, and Taiwan as major buyers. Additionally, Singaporean auditors continue evaluating Paraguayan meat processing facilities, signaling potential expansion in exports. Senacsa highlighted growing interest from South Korea, Taiwan, and the Philippines in Paraguayan meat, with the Philippines set to inspect 14 meat-packing plants in Apr-25 before finalizing import agreements.
Uruguay
Uruguay Boosts Beef Exports to the US and EU as China’s Demand Falls
Uruguay has fulfilled 66% of its Hilton beef quota in the first two months of 2025, marking a 10% decline from the previous year amid falling exports to China. To meet the remaining 1,880 mt allocation by Jul-25, the country must process around 100,000 heavy cattle. The Hilton quota price has surged due to a shortage of export steers in Argentina, driving European demand for premium beef. Meanwhile, China’s beef imports have dropped to a nearly two-year low, with Jan-25 purchases falling below 200 thousand mt and Feb-25 imports from Uruguay declining 21% year-on-year (YoY). Additionally, China suspended Uruguay’s Sirsil meat plant over fluazuron residue concerns; similar actions were taken against Brazil, Argentina, and Mongolia. In contrast, Uruguay’s meat exports to the US and the EU have risen sharply, with US purchases growing 86% YoY and European sales increasing by 26% YoY. Additionally, Uruguay’s live cattle exports tripled, with new markets like Israel and Algeria emerging.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
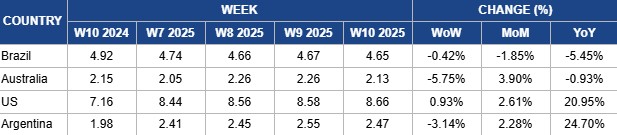
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W10 2024 to W10 2025)
Brazil
In W10, Brazil’s wholesale price for boneless rear beef declined slightly by 0.42% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 4.65 per kilogram (kg). This also represented a 1.85% month-on-month (MoM) drop and a 5.45% YoY decline. Despite this WoW decrease in USD terms, prices remained stable in local currency at BRL 27/kg for the fourth consecutive week, reflecting the impact of exchange rate fluctuations. According to Safras and Mercado, wholesale beef prices had risen slightly, with consumption during Carnival holiday being considered satisfactory. They explained that meat sales had been strong during the holiday, leading to expectations that prices would continue to rise, driven by the entry of salaries into the economy and subsequent replenishment across the supply chain.
Australia
Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator averaged USD 2.13/kg in W10, reflecting a 5.17% WoW drop, a 0.93% YoY decline, but a 3.90% MoM rise. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), the cattle market experienced a shift in W10, with yardings decreasing by 18% WoW to 72.21 thousand heads. MLA also reported that Queensland yardings and prices were affected by Tropical Cyclone Alfred, which led to disruptions in the region. As a result, the Port of Brisbane suspended incoming ships on March 2, and outgoing vessels on March 4, disrupting trade logistics. Additionally, major processors across southern Queensland temporarily shut down operations for parts of the week, with return dates yet to be announced.
United States
In W10, US lean beef (92% to 94% lean) averaged USD 8.66/kg, rising 0.93% WoW and marking its ninth consecutive weekly increase. Prices reached their highest level since W36 2024, when the record high of USD 8.73/kg was registered. Additionally, prices rose 2.61% MoM and surged 20.95% YoY, primarily due to a tightening domestic supply amid a shrinking US cow herd. According to the USDA, the total cattle and calf inventory stood at 86.7 million heads as of January 1, 2025, reflecting a 0.6% YoY decline and marking the sixth consecutive year of herd contraction. As a result, US beef production in 2025 is projected to decline by 4.4% YoY, while per capita beef consumption is expected to drop by 2.68% to 58 pounds (lbs) per person.
Argentina
Argentina’s average steer beef price rose to USD 2.47/kg in W10, reflecting a 3.14% WoW decline, but a 2.28% MoM increase and a significant 24.70% YoY surge. Despite the WoW drop, prices remained elevated due to supply concerns. The sharp YoY increase is attributed to weak beef consumption in 2024, driven by economic challenges. According to the Argentine Meat Exporters Consortium (ABC), cattle slaughter in Jan-25 totaled 1.14 million heads, marking an 8.1% MoM decline and a 2% YoY drop. This decline resulted in a 6% MoM decrease and a 1.5% YoY drop in beef production, which fell to 263.9 thousand mt. The supply of light cattle categories declined in Jan-25 compared to Dec-24, while steer and cow availability increased.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Balance EU Beef Trade Agreements with Farmer Protections
To address farmer concerns while expanding trade with Ukraine and Mercosur, the EU should implement a tiered tariff rate quota (TRQ) system for beef imports, ensuring controlled market access without overwhelming local producers. Additionally, financial support through direct subsidies or price stabilization funds should be allocated to beef farmers affected by increased competition. The EU should also invest in marketing campaigns that promote high-quality, sustainably produced European beef, differentiating it from imports. Transparent dialogue with farmer associations and gradual implementation of agreements will help mitigate resistance while fostering a balanced trade environment.
Navigate China’s Shifting Beef Import Policies
With China imposing new tariffs on US beef and suspending imports from some meatplants from Mercosur countries, exporters must adapt by diversifying markets and strengthening trade partnerships. South American suppliers should prioritize compliance with China’s regulatory standards to prevent further suspensions and negotiate predictable trade terms. Additionally, exporters should leverage opportunities in Southeast Asia and the Middle East, where demand for premium beef is rising. Given China’s beef market oversupply, suppliers may also explore value-added beef products, such as processed and marinated meats, to differentiate their offerings and maintain stable demand.
Expand Paraguay’s Beef Export Opportunities
Paraguay’s strong early-year beef export performance highlights its potential to secure additional markets. To capitalize on global demand, Paraguay should enhance bilateral trade agreements with key buyers such as the US, South Korea, and the Philippines. Expediting meat processing facility approvals from new markets, particularly in Asia, will be essential for long-term growth. Additionally, strengthening livestock health programs and increasing slaughterhouse capacity will ensure consistent supply. Paraguay should also invest in digital traceability technologies to improve transparency and meet stringent import regulations in high-value markets.
Sources: Tridge, Agri, Agromeat, Bichos de campo, Canal Rural, UkrAgroConsult,


