
In W12 in the apple landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Apple production has declined in key regions such as Chile, Moldova, and the EU, leading to tighter supply. However, favorable weather in Chile has improved fruit quality, while Portugal and India face issues related to climate and agricultural inputs, such as substandard pesticides affecting Kashmir’s orchards.
- Moldova’s expansion into the Indian market, North Korea’s apple exports to Russia, and Portugal’s increased focus on the Middle East highlight evolving trade routes. Meanwhile, India’s potential tariff reductions could alter domestic market competition, affecting local growers.
- Kashmir’s apple industry is under pressure from potential tariff reductions and inconsistent product quality, highlighting the need for modernization to enhance product consistency, improve competitiveness in export markets, and mitigate tariff-related risks. Similarly, Moldova’s long-term production decline underscores structural challenges despite recent export gains.
- Delays in the Red Sea impacted Portugal’s shipments, while concerns over fruit firmness influenced market competition in Europe. Meanwhile, Chilean exports to Europe remain uncertain due to high stock levels and rising costs, reflecting broader logistical and economic pressures.
1. Weekly News
Chile
Lower Apple Supply and Higher Prices Expected from Chile
Chile's apple production is expected to decline in the 2024/25 season due to a reduction in planted acreage, as some growers shift to more profitable crops like cherries and walnuts, with lower volumes of Royal Gala and Granny Smith. However, fruit sizes are slightly larger, ranging from 100 to 135. The season is until September, with strong demand from South America, India, and the Middle East, while European demand remains uncertain due to stock levels and rising costs. Supply constraints are expected to keep prices high. Meanwhile, this year’s Royal Gala has developed a deeper red color due to high temperatures and favorable weather, contrasting with last year’s heavy rainfall.
India
Kashmir Apple Growers Concerned Over Potential Tariff Reductions
As India considers reducing import duties on apples in Kashmir Valley, local growers fear increased competition from higher-quality global imports. Historically, high tariffs have safeguarded local apple producers, but a reduction could weaken their competitiveness in the market. Experts note that only 25% of Kashmir’s apple production meets high-quality standards, compared to 80% in Italy, making local apples less competitive. With consumer preferences shifting toward consistent quality, growers are encouraged to adopt high-density plantation methods to improve productivity and resilience.
Kashmir Apple Growers Alarmed Over Substandard Pesticides
Kashmir’s apple growers are facing significant threats to their crops due to the influx of substandard and misbranded pesticides, which have proven ineffective against pests and diseases. The Quality Control and Chemist Laboratories of the Agriculture Department has identified several misbranded pesticide products, including Indofil M-45 and CAPTAF, raising concerns over declining fruit quality and increased crop vulnerability. Farmers are urging the government to enforce stricter regulations and curb unregulated pesticide sales as annual losses escalate. In response, authorities have intensified inspections and sampling efforts to ensure the availability of genuine pesticides, advising growers to verify product authenticity before purchase.
Korea
North Korean Apples Enter Russian Market as Trade Expands
North Korean apples have recently entered supermarkets in Russia's Far East, particularly in Khabarovsk, marking a new development in regional agricultural trade. North Korean apples are priced at USD 2 per kilogram (RUB 169/kg), making them one of the most affordable options in Russia. Exported in 20-kg boxes by North Korea’s foreign trade company, Hwanggumsan, these apples reflect expanding trade ties following discussions between Russian and North Korean authorities on boosting agricultural exports, including apples and ginseng. Russia’s Rosselkhoznadzor has confirmed North Korea’s growing interest in the market, signaling a potential shift in regional supply dynamics.
Moldova
Moldova Expands Apple Exports Despite Production Decline
Despite the decline in apple production in recent years, Moldova remains one of the world’s top 10 apple exporters, shipping around 130 thousand tons in the 2024/25 season. This is an increase from previous years but nearly 50% below the 2021/22 level. In a significant development, Moldova has secured free access to India, the world’s largest apple importer, with the first shipment delivered as planned on March 19, 2025, under new trade regulations. This expansion aligns with a global production decline of 350 thousand tons to 84 million tons, driven by reductions in the European Union (EU), the United States (US), Turkey, and Russia, while China continues to dominate the market.
Portugal
Portugal Concludes Apple Export Season with Strong Middle East Focus
Portugal's apple export season has concluded, with traders shifting focus to the Middle East in the final months, particularly ahead of Ramadan. Early in the season, Brazil was the primary market. However, unexpected price competition from France and Italy, driven by concerns over fruit firmness due to a heatwave, posed challenges. While local stocks mainly consist of smaller-sized apples, traders import larger apples from Serbia to meet domestic demand. Logistical disruptions, including delays in the Red Sea, impacted shipments to South America and the Far East, but overall, the season remained stable. Looking ahead, favorable rainfall supports tree development, though future market strategies will depend on evolving global conditions.
Turkey
Turkey Faces Sharp Apple Production Decline but Strong Export Demand
Due to adverse weather, Turkey's apple production has declined by 50% this 2024/25 season, but high-quality fruit has sustained strong demand, particularly from India. Exporters are moving shipments at a slower pace, while ongoing logistical challenges in the Red Sea continue to affect trade. As the season progresses, the availability of export-quality apples will decrease after March, with only major exporters expected to continue shipments.
2. Weekly Pricing
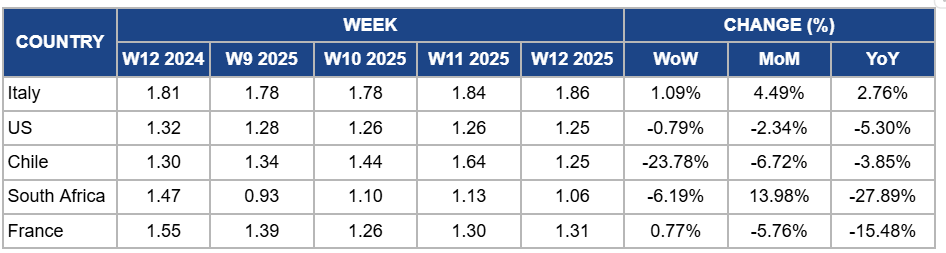
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W12 2024 to W12 2025)
Italy
In W12, Italy's apple prices increased slightly by 1.09% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 1.86/kg, with a 4.49% month-on-month (MoM) increase and a 2.76% year-on-year (YoY) increase. This upward trend is due to reduced apple production in key regions such as Bolzano and Trento, largely due to spring frosts that affected yields. Despite these production challenges, the Italian apple market has maintained stability, supported by strong exports, which increased by 14% in the 2023/24 campaign, reaching approximately 875 million kg. This export growth has helped balance domestic supply and demand dynamics, contributing to the observed price increases.
United States
US apple prices declined slightly by 0.79% WoW to USD 1.25/kg in W12, reflecting a 2.34% MoM drop and a 5.30% YoY decrease. The price decline is due to sluggish demand and high carryover stocks, as total apple storage stood at 113 million bushels as of March 1, 2025. While this represents a 5% YoY decline, it remains 13% above the five-year average, ensuring sufficient supply and preventing upward price pressure. Additionally, weaker demand for processing apples, which saw a 7% YoY decline in storage to 32 million bushels, has contributed to overall price softness. Meanwhile, unseasonably warm weather in Michigan has raised concerns about potential frost damage, but since most crops remain dormant, this has not yet influenced immediate pricing trends.
Chile
In W12, Chile's apple prices fell by 23.78% WoW to USD 1.25/kg, showing a 6.72% MoM decrease and a 3.85% YoY drop due to increased market supply as the harvest season progresses, leading to higher availability and downward pressure on prices. Additionally, a projected 1.1% decrease in apple production for the 2024/25 season has influenced market expectations, contributing to price fluctuations.
South Africa
South Africa's apple prices declined by 6.19% WoW to USD 1.06/kg in W12, reflecting a 27.89% YoY decrease. This downward trend is due to increased supply as the apple harvest season progresses. The South African apple season begins in January and extends through May, with peak supply occurring in June. Additionally, favorable growing conditions, including cooler nights, have contributed to higher yields, leading to greater market availability and exerting downward pressure on prices. However, on an MoM basis, apple prices increased by 13.98%, possibly due to short-term fluctuations in demand or temporary supply constraints earlier in the season.
France
Apple prices in France experienced a modest WoW increase of 0.77% in W12, reaching USD 1.31/kg. This slight uptick is likely due to the tail end of the apple storage period, as supplies from the previous harvest diminish, leading to tighter market availability. However, prices have decreased by 5.76% MoM and 15.48% YoY. The MoM decline is due to the seasonal consumption patterns where demand typically wanes post-winter. The YoY decrease reflects a stable production in 2024, with France maintaining an apple yield of 1.4 million tons, consistent with the three-year average. This stable supply has contributed to lower prices compared to the previous year.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Optimize Export Timing and Alternative Routes
Turkish apple exporters should accelerate shipments before the end of Mar-25 to capitalize on strong demand from India while quality remains high. Exploring alternative shipping routes, such as via Mediterranean ports, can help mitigate Red Sea disruptions and ensure timely deliveries.
Diversify Market Strategies for Next Season
Portuguese apple traders should strengthen ties with Middle Eastern buyers ahead of Ramadan while securing alternative shipping routes to avoid Red Sea delays. Expanding sourcing options, such as securing larger apples from Serbia earlier, can help maintain domestic supply without relying on imports mid-season.
Sources: Tridge, JoongAng Daily, Freshplaza, Greater Kashmir, Moldova Fruct, The Kashmir Monitor





