
In W20 in the apple landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- China has officially granted market access to Dutch apples through a new import protocol signed during a high-level meeting in Beijing on May 15, 2025.
- India faces rising trade tensions as apple traders in Pune protested against Turkish imports, urging a ban to protect domestic growers from cheap foreign apples.
- Moldova’s apple prices surged by 10 to 15% due to low stocks, smaller harvests, and increased local demand following spring frost damage.
- US apple volumes in storage declined by 5% YoY but remain 16% above the five-year average, with fresh and processing apple holdings showing decreases.
1. Weekly News
China
China Grants Market Access to Dutch Apples
During a high-level meeting in Beijing on May 15, 2025, China and the Netherlands signed a new apple protocol that officially permits the import of Dutch apples into the Chinese market. The agreement was signed by the Vice Minister of the Dutch Ministry of Agriculture and the Vice Minister of Chinese Customs. Building on the existing pear protocol, this agreement allows Dutch exporters to broaden their top fruit offerings, giving Chinese consumers increased access to high-quality apples from the Netherlands. Representatives from both the Dutch Ministry of Agriculture and Chinese Customs endorsed the agreement.
India
India's Apple Trade Tensions Rise as Calls to Ban Turkish Imports Grow
In India, apple traders in Pune have intensified protests against Turkish apple imports following Turkey’s criticism of India’s actions in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir. At the Pune Agriculture Produce Market Committee (Marketyard), traders publicly discarded Turkish apples, citing political tensions and national security concerns. This protest has gained strong backing from Himachal Pradesh apple growers, who demand a complete ban on apple imports not only from Turkey but also from Iran, Iraq, and China. India imports about 30 million apple boxes annually to meet a local demand of 150 million boxes, with roughly 60% coming from Turkey and Iran. Local growers argue that these cheaper imports undermine domestic markets by suppressing prices, making it difficult for farmers to compete. The imports particularly affect those in Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand, which collectively produce around 120 million boxes annually. They believe banning Turkish imports would boost domestic prices, support local producers, and encourage greater investment in India’s apple industry.
Moldova
Apple Prices Surge in Moldova Due to Low Stocks and Smaller Harvest
Wholesale apple prices in Moldova increased by 10 to 15% in late Apr-25 and early May-25, averaging USD 0.69 per kilogram (MDL 12/kg). Meanwhile, retail prices rose to USD 0.87 to 1.04/kg (MDL 15 to 18 MDL/kg, despite consumer feedback indicating average or below-average fruit quality. This represents the highest price level for this period in five years and is mainly driven by shrinking stock levels, as most export-quality apples were sold by mid-April, leaving only lower-grade fruit for the domestic market. Additionally, a delayed start to the fruit season and spring frost damage to berry and stone fruit crops have heightened local demand. Moldova exported just over 13 thousand metric tons (mt) of apples in Apr-25, down from over 18 thousand mt in Mar-24 and 20 thousand mt in Apr-24, reflecting a smaller 2024 harvest of about 440 thousand mt and reduced availability of export-grade apples. Total apple exports from Apr-24 to May-25 reached approximately 90 thousand mt.
United States
US Apple Volumes in Storage Decline 5% YoY but Remains Well Above Five-Year Average
In the United States (US), apple storage as of May 1, 2025, totaled 72 million bushels, marking a 5% decline compared to the 76 million bushels recorded at the same time last year, though still 16% above the five-year average. Fresh apple holdings stood at 52 million bushels, down 2% year-over-year (YoY), while processing apple holdings dropped more sharply by 12% to 20 million bushels. Representing over 95% of national storage capacity, the data highlights a moderate reduction in supply despite overall strong stock levels.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
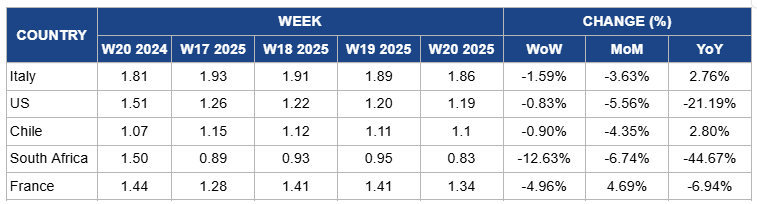
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W20 2024 to W20 2025)
Italy
Italy's apple prices dropped by 1.59% WoW to USD 1.86/kg in W20, marking a 3.63% MoM decrease due to increased availability from ongoing local harvests and strong competition from imported apples in European markets, particularly from Poland and France. However, YoY prices increased by 2.76% due to lower overall production during the 2024 harvest season, which was affected by spring frosts and hailstorms in Northern Italy, resulting in tighter supplies and firmer prices compared to the previous year.
United States
US apple prices decreased slightly by 0.83% WoW to USD 1.19/kg in W20, reflecting a 5.56% MoM decrease and a 21.19% YoY drop due to ample supply from the 2023/24 harvest, which was one of the largest in recent years, especially in Washington state. Additionally, softer export demand, partly due to increased global competition and higher shipping costs, has led to more apples being sold domestically, putting further downward pressure on prices. The YoY decline also reflects normalization after the elevated price levels seen last year, when adverse weather reduced crop volumes and pushed prices up.
Chile
Chilean apple prices decreased by 0.90% WoW to USD 1.10/kg in W20, with a 4.35% MoM decrease due to the gradual normalization of harvest volumes and logistics after early-season delays caused by heavy rainfall and labor shortages. However, prices rose by 2.80% YoY due to a smaller overall crop this season compared to 2024, driven by adverse weather conditions during flowering and fruit set. Additionally, strong international demand, particularly from Latin American and Asian markets, has contributed to the upward YoY price trend despite short-term fluctuations.
South Africa
Apple prices in South Africa decreased by 12.63% WoW to USD 0.90/kg in W20, reflecting a 6.74% MoM decrease and a 44.67% YoY decline due to a combination of factors. The 2025 apple season has seen a 5% increase in export volumes, reaching approximately 51 million cartons, driven by favorable weather conditions and the maturation of new orchards. However, severe disruptions at Cape Town port have led to logistical bottlenecks, causing two weeks' worth of apple shipments to arrive simultaneously in multiple markets, leading to price fluctuations. Additionally, reduced export demand, particularly from markets like Tanzania, which imposed a sudden ban on South African produce, and Nigeria, where currency issues have made transactions challenging, have further pressured prices downward. These factors, combined with increased local supply and intensified global competition, have contributed to the significant YoY price decline.
France
In France, apple prices dropped by 4.96% WoW to USD 1.34/kg in W20, with a 6.94% YoY decrease due to increased local availability and sluggish demand as consumers shifted to summer fruits. However, prices rose by 4.69% MoM due to reduced cold storage inventories from the 2023 harvest and logistical challenges affecting the internal distribution of remaining stocks, which created temporary upward pressure on prices.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Improve Fruit Quality Management to Maintain Competitive Pricing
Apple producers in Moldova and similar regions should prioritize post-harvest quality management to avoid price drops caused by lower-grade fruit flooding the local market. Producers must invest in better sorting, grading, and storage technologies, such as controlled atmosphere storage and improved packaging, to extend shelf life and preserve fruit quality. For example, farmers can adopt optical sorting machines to separate export-grade apples from lower-quality ones early, ensuring only premium fruit reaches high-value markets, while redirecting lower grades to processed products or local sales. This approach helps stabilize prices and meets consumer expectations despite smaller harvests or adverse weather impacts.
Strengthen Local Market Position Through Quality and Branding
Apple producers in India and similar markets should focus on enhancing fruit quality and developing strong regional branding to compete effectively against cheaper imports. Farmers and cooperatives can invest in better orchard management practices, like precision pruning, pest control, and controlled harvesting, to produce premium apples that justify higher prices. Additionally, marketing efforts should emphasize unique local varieties and certifications such as organic or geographic indication labels. For example, Himachal Pradesh growers could promote the distinct flavor and quality of their apples through targeted campaigns in urban centers and export markets. This strategy helps build consumer loyalty and offsets price pressure from imports.
Sources: Tridge, ANI News, Freshplaza, Logos, News Drum, Newindianexpress, US Apple Association





