W28 2025: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
In W28 in the beef landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Brazil and Australia emerged as the dominant global beef exporters in H1-2025, fueled by rising demand from China and the US.
- New US tariffs such as 25% on Japan and South Korea and 50% on Brazil, threaten beef trade stability, prompting Brazil to diversify and weakening US export competitiveness.
- Argentina solidified its EU market position by fulfilling 100% of its 2024/25 Hilton Quota, exporting premium cuts worth USD 350 million as the 2025/26 cycle begins.
- South Korea’s Hanwoo beef sector is rebounding, with prices rising amid lower slaughter, holiday demand, and government support, while export efforts continue despite key challenges.
- EFSA warns of HPAI risks to European cattle from American herds via birds and trade, urging stronger surveillance ahead of a full 2025 impact assessment.
1. Weekly News
Global
Shifting Dynamics in Global Beef Exports as Brazil and Australia Break Records, while US Faces Setbacks
In the first half of 2025 (H1-2025), Brazil reinforced its global beef export leadership with consistent growth in both volume and price. In Jun-25 alone, Brazil’s exports reached 241 thousand metric tons (mt), 11% higher month-on-month (MoM) and 22% year-on-year (YoY), with China and Mexico showing the largest demand surges. Meanwhile, Australia set a new monthly record with 135 thousand mt exported in Jun-25, driven by strong shipment to the United States (+23% YoY) and demand resurgence in China (+44% YoY), contributing to a 31% YoY rise in total exports in H1-2025. Paraguay posted a 16% YoY rise in Jun-25 exports, reaching 36 thousand mt, while also improving prices by 20% YoY and diversifying its export destinations. Despite a 10% YoY drop in Jun-25 exports, Uruguay registered a 5% YoY increase for H1-2025 shipments, with significant growth in exports to Europe (+47% YoY) and the US (+30% YoY), although exports to China fell 13% YoY and to Israel by 33.33% YoY. In contrast, US beef exports fell to 77 thousand mt in May-25, a 10% YoY drop, mainly due to trade tensions with China, where shipments plunged to one-tenth of May-24 levels.
European Union
EFSA Warns of Potential HPAI Threat to European Cattle via Birds and Trade
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has identified potential routes through which the highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) virus, currently affecting American dairy herds, could reach European cattle. The main concerns are virus transmission via migratory birds, particularly through major European stopover sites such as Iceland, the British Isles, Scandinavia, and coastal wetlands, and through commercial trade. Although no live cattle or bovine embryos were imported from the US in recent years, other imported products like fresh beef, raw milk items, and bovine semen could pose a risk if not properly treated. EFSA underscores the importance of cross-sectoral surveillance, research, and preparedness and plans to release a follow-up report by the end of 2025 to assess the virus’s potential impact and outline preventive measures.
Argentina
Argentina Meets 100% of Hilton Quota for 2024/25, Secures Strong Position in EU Beef Market
Argentina has successfully fulfilled its Hilton Quota for the 2024/25 cycle, exporting 29.35 thousand mt of high-quality beef to the European Union (EU) and an additional 111 mt to the United Kingdom (UK), effectively reaching 100% of its 29.5 thousand mt allocation for the third time in seven years. Valued at approximately USD 350 million free on board (FOB), these exports averaged USD 18,000/mt for premium cuts such as rump, loin, sirloin, and ribeye. The main European buyers included Germany, the Netherlands, Italy, Spain, Greece, and Portugal. The Hilton Quota is a tariff-rate system offering a 20% tariff preference for boneless high-value beef, with Argentina receiving the largest share at 44% of the global allocation. For the new 2025/26 cycle, 69 Argentine companies have been allocated quota shares, with 8.5% already used in Jul-25.
Brazil
Rising Tensions Threaten Brazil-US Beef Trade Amid 50% Tariff Imposition
The US announced a 50% tariff on all imports from Brazil, including beef and agricultural products, effective August 1, 2025, citing unfair trade practices and political tensions. This move places significant pressure on Brazil's export sector, particularly as US imports of Brazilian beef surged by 112.7% YoY between Jan-25 and May-25, nearly equaling the total imported in all of 2024. Brazilian industry representatives have criticized the decision as politically motivated and economically unjustified. They noted that the US relies on imported beef, especially forequarters used in hamburger production, to meet domestic demand amid high prices and a weak livestock cycle.
These tariffs are likely to cause production disruptions in Brazil, especially those which were intended for export to the US. Brazilian beef exporters are now seeking alternative markets such as China, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East. Market experts warn that the move may erode Brazil’s competitiveness in the US market relative to other exporters like Australia, Argentina, and Uruguay, potentially resulting in lost market share. In response, Brazil is accelerating efforts to diversify its export destinations, including recent approvals to export beef to El Salvador and bovine collagen to Malaysia. These developments are part of a broader strategy to reduce dependence on traditional markets and expand into high-value segments, reinforcing the strength and adaptability of Brazilian agribusiness.
South Korea
Uptick in Hanwoo Prices and Global Outreach Signal Market Optimism
The auction price of Hanwoo beef in South Korea has rebounded above USD 13.70 per kilogram (KRW 19,000/kg) for the first time in months. This rebound is attributed to reduced slaughter volumes, upcoming discount events, and expectations of increased demand due to economic recovery and government support payments. Distributors are securing inventory ahead of the Chuseok holiday, with industry analysts expecting this price trend to hold in the short term.
Meanwhile, efforts to expand Hanwoo exports are underway, with recent marketing events such as the Seoul International Liquor & Wine Expo and the Halal Hanwoo Launching Show in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), promoting Korean beef’s quality and sustainability. Although exports declined by over 20% YoY in 2024, especially to Malaysia, new markets like the UAE are showing strong potential. However, challenges persist, including a limited number of halal-certified slaughterhouses, high logistics costs, inconsistent pricing, and internal competition in key markets like Hong Kong. Stakeholders are calling for more government support, infrastructure upgrades, and targeted export strategies to stabilize supply and broaden market access.
United States
US Tariffs on Japan and South Korea Threaten Beef Export Stability
The US government's decision to impose 25% tariffs on imports from Japan and South Korea starting August 1, 2025, has raised concerns for the US beef industry. Japan and South Korea are top buyers of US beef, and the new tariffs, framed as a correction of trade imbalances, could lead to retaliatory measures or a shift in purchasing to alternative suppliers like Australia and Brazil. This may potentially reduce the US market share. At the same time, American consumers may face higher prices for premium imported beef such as Japanese Wagyu. With the US beef cattle herd already at its lowest since 1952, and beef market disruptions looming, industry stakeholders are bracing for potentially long-term impacts on both domestic pricing and export competitiveness.
2. Weekly Pricing
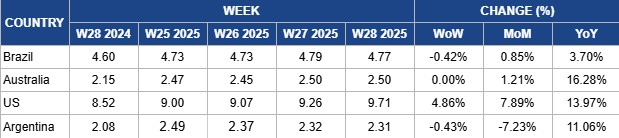
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W28 2024 to W28 2025)
Brazil
In W28, Brazil’s wholesale price for boneless rear beef declined by 0.42% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 4.77/kg. However, the price still reflected a 0.85% MoM increase and a 3.70% YoY rise. The weekly drop in US dollar terms was primarily due to exchange rate fluctuations, as prices in Brazilian real actually rose by 0.77% WoW to BRL 26.20/kg. According to Safras and Mercado, the wholesale beef market remains firm, though there is limited room for further price adjustments in the second half of the month due to weaker consumer demand. Chicken meat continues to be significantly more price-competitive than beef and other proteins. Meanwhile, the physical cattle market showed signs of weakness, with buyers attempting to negotiate lower prices. Uncertainty persists in the Brazilian beef sector following the newly imposed US tariffs, which have eroded Brazil’s export competitiveness against key rivals like Argentina, Uruguay, and Australia.
Australia
In W28, Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator (NYCI) held steady WoW at USD 2.50/kg, reflecting currency-related stability, as prices in local terms rose by 1.05% WoW to AUD 3.84/kg. Despite that, the price registered a 1.21% MoM increase and a 16.28% YoY gain. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), while both the dairy and processor cow indicators increased during the week, the overall cattle market remained relatively subdued. Total cattle yardings rose by 5.24 thousand heads to 61.32 thousand heads, mainly driven by an influx of processor cows, restocker heifers, and steers. The heavy steer indicator declined, particularly in Victoria, although Leongatha registered the highest price for that category. Winter conditions continue to affect cattle quality, contributing to softer prices for export and trade cattle. Meanwhile, leaner cows were increasingly favored by processors, especially in Victoria, where this preference supported notable price gains in the processor cow indicator.
United States
In W28, US lean beef (92% to 94%) prices reached a record high of USD 9.71/kg, representing a 4.86% WoW increase, a 7.89% MoM rise, and a 13.97% YoY gain. This price surge is largely driven by strong seasonal demand tied to summer grilling and outdoor activities, compounded by structural supply constraints. US cattle inventory has fallen to its lowest level since 1952 due to prolonged drought, pandemic-related disruptions, and meatpacking plant closures. Adding further pressure, a screwworm outbreak led to the suspension of live cattle imports from Mexico, tightening supply. While border reopening has begun, with cattle from Sonora and Chihuahua cleared for export, volumes remain constrained. The 10% import tariff hike implemented in Apr-25 has further limited beef inflows. Looking ahead, the planned 50% tariff on Brazilian products, effective Aug-25, could tighten supplies further, as Brazil has been a key beef supplier to the US. These factors are likely to sustain elevated beef prices in the near term.
Argentina
In W28, Argentina’s average steer beef price declined by 0.43% WoW to USD 2.31/kg. This slight drop in USD terms was mainly due to exchange rate fluctuations, as the local currency price rose by 4.05% WoW to ARS 2,913.66/kg. Despite the weekly decline, prices were still 11.06% higher YoY, although down 7.23% MoM, indicating a slow yet possible recovery in demand following the 2024 economic downturn. The Argentine beef sector showed relative stability in slaughter levels and moderate gains in production, alongside evolving herd structure dynamics. In Jun-25, approximately 1.126 million heads of cattle were slaughtered, unchanged from May-25 but 9.2% higher YoY. Slaughter in H1-2025 totaled 6.60 million heads, a 0.5% YoY increase. The share of females in total slaughter was 48.0% in Jun-25, slightly below the 49.8% in Jun-24, and averaged 47.2% for H1-2025, down from 48.1% in the same period last year. This decline in adult female slaughter may suggest early signs of retention in the maternal herd. Beef production in Jun-25 reached 260.3 thousand mt (bone-in), showing a marginal 0.4% MoM decline but a strong 11.7% YoY increase. Cumulative production for Jan-25 to Jun-25 totaled 1.518 million metric tons (mmt), up 1.8% YoY. The average carcass weight in Jun-25 stood at 231.2 kg, 0.5% lower than in May-25 but 2.3% higher YoY. For H1-2025, the average carcass weight was 230.2 kg, reflecting a 1.3% YoY increase.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversify High-Risk Markets to Sustain Growth Amid Tariff Shocks
With the US imposing a 50% tariff on Brazilian beef and introducing 25% tariffs on Japanese and South Korean imports, affected countries like Brazil and the US should intensify efforts to diversify their export markets. Brazil should expand partnerships in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa, building on recent approvals for El Salvador and Malaysia. Meanwhile, the US should focus on penetrating emerging markets such as Vietnam, the Philippines, and Indonesia, where demand for premium beef is rising. Investing in market intelligence, local partnerships, and cultural adaptation of products will be critical for reducing overdependence on volatile trade partners and minimizing exposure to geopolitical disruptions.
Leverage Value-Added and Premium Beef Segments to Stay Competitive
Exporting countries facing trade barriers or saturation in traditional markets, such as Uruguay, Argentina, and the US, should invest more in value-added beef segments like organic, grass-fed, Wagyu-style, or halal-certified beef. Argentina’s success in the EU Hilton Quota shows the profitability of targeting high-value segments. Exporters should enhance traceability, sustainability certification, and branding strategies to appeal to premium consumers in Europe, the Gulf, and East Asia. This approach supports better pricing and helps shield exporters from commodity price volatility.
Promote Export Infrastructure and Halal Certification to Unlock Hanwoo’s Potential
South Korea should capitalize on growing interest in Hanwoo beef by addressing key bottlenecks. This includes expanding halal-certified slaughterhouses, developing cold chain infrastructure, and offering targeted logistics subsidies for long-distance exports. Building centralized pricing systems and digital platforms can ensure price transparency and buyer trust in markets like the UAE, Malaysia, and Hong Kong. Government support through export promotion agencies and trade missions should also be expanded to reinforce Hanwoo’s global branding as a premium, sustainable beef option.
Enhance Surveillance and Biosecurity to Protect Against Disease Risks
With EFSA highlighting the threat of HPAI transmission, EU nations should immediately enhance cross-border disease surveillance, strengthen border inspections for high-risk products, and coordinate risk mitigation with the poultry and livestock sectors. Investments in early warning systems, digital traceability, and rapid response mechanisms are critical to preventing outbreaks that could devastate both domestic production and export credentials. Additionally, enhancing sanitary protocols for imports such as bovine semen, raw milk, and fresh beef is vital to maintain herd health.
Sources: Tridge, Aflnews, Agrinet, Agromeat, Agropopular, Canal Rural



