
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Brazil Faces Citrus Production Decline Amid Rising Global Orange Juice Prices
Brazil, the world's largest exporter of orange juice, is experiencing a significant drop in citrus production due to prolonged heat waves, drought, and the widespread impact of Huanglongbing (HLB), or citrus greening disease. In São Paulo's Casablanca region, a major citrus-producing area, local citrus production has fallen by 30% per hectare (ha). The Brazilian citrus industry forecasts a 24% year-on-year (YoY) decrease in production for the 2024/25 season, the lowest in 36 years. Consequently, domestic citrus prices have surged, increasing from USD 8.06 to 14.32/40-kilogram (kg) box (BRL 45 to 80/40-kg box). Although global orange juice prices have risen by over 50% since early 2024, driven by a 9.3% YoY decrease in Brazil's orange juice exports, the industry faces challenges in meeting varying market demands and maintaining supply.
São Paulo Wildfires Impact Citrus Production But Prices Remain High
Recent wildfires in São Paulo's central-north citrus region have raised concerns, but the impact on overall orange production is expected to be minimal. The fires affected only small areas, and quick response from landowners and recent rainfall helped control the situation. Despite these challenges, the orange market has seen historically high prices this year due to limited supply and strong demand. By the end of Aug-24, orange prices stood at USD 17.90/40.8-kg box (BRL 100/40.8-kg box). However, a cold wave in late Aug-24 reduced consumer activity, affecting market dynamics. Nonetheless, high prices for fresh consumption and industrial use continue, supported by ongoing supply constraints and elevated industrial contract prices.
Mexico
Orange Prices Soared in Mexico Amid Production Declines
Orange prices in Mexico surged dramatically, significantly impacting inflation. In Jul-24, the National Consumer Price Index (NCPI) recorded an 18.57% monthly increase in orange prices. The National System of Information and Integration of Markets (SNIIM) reported a staggering 382.75% rise in the price of small Valencia oranges at the Iztapalapa supply center in Mexico City, jumping from USD 0.29/kg (MXN 5.80/kg) in Jan-24 to USD 1.41/kg (MXN 28/kg) in Jul-24. Medium Valencia orange prices increased from USD 0.35/kg (MXN 7/kg to USD 1.51/kg (MXN 30/kg), and large Valencia orange prices rose from USD 0.50/kg (MXN 10/kg) to USD 1.73/kg (MXN 34.50/kg). This price spike was driven by a 50% YoY drop in production due to drought and HLB disease. Mexico, a major global orange producer, has faced severe crop losses, especially in Veracruz, disrupting its industry.
Philippines
Philippines Intercepts Illegal Orange Shipment from Thailand
The Philippine Department of Agriculture (DA) and the Bureau of Customs (BOC) recently intercepted a shipment of 3.2 thousand cartons of fresh oranges from Thailand at the Manila International Container Port. The shipment was valued at PHP 8.422 million and lacked necessary sanitary and phytosanitary import permits. The Agriculture Secretary emphasized the government's commitment to preventing agricultural smuggling to safeguard public health and protect local farmers. The oranges will be condemned to avoid market distribution, and the case has been referred to the Bureau Action Team Against Smuggling for further investigation and possible prosecution.
Spain
Valencian Citrus Campaign Begins with Lower Supply and Rising Costs
The 2024/25 citrus season in Spain's Valencian Community is starting with a lower supply due to domestic issues and fewer imports from South Africa. Prices for citrus fruits are similar to last year but adjusted for expected production decreases and higher costs caused by drought and pests. Farmers face rising expenses, with production costs increasing by 18% since 2020. Although prices for early varieties like Okitsu mandarins and Oronules remain stable, growers should check market prices before selling.
United States
California Valencia Orange Supply to End Early This Season
California’s supply of Valencia oranges is expected to conclude earlier than usual in 2024, with most shippers finishing by the end of Sep-24. This contrasts with last year, when shipments continued into late October, causing a gap before the navel orange season starts in mid to late October. The current season's lighter crop of Valencias has sold well early, but reduced acreage over the past two decades has led to a more balanced supply. Increased demand for in-store juicing and higher juice concentrate prices have also helped California Valencia growers. As domestic supplies decline, imports from Chile, South Africa, Australia, and later-harvested Valencias from the Southern Hemisphere will help fill the gap. Prices for Valencias are expected to rise significantly in Sep-24.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Orange Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
* Varieties: Spain, South Africa, and the US (Navel), Italy (Tarocco), and Egypt (overall orange average)
Yearly Change in Orange Pricing Important Exporters (W36 2023 to W36 2024)
* Varieties: Spain, South Africa, and the US (Navel), Italy (Tarocco), and Egypt (overall orange)
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
South Africa
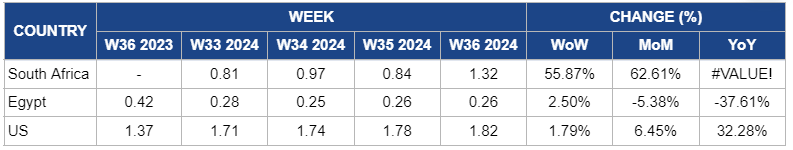
In W36, South African orange prices surged by 55.87% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 1.32/kg, with a 62.61% MoM increase. This sharp rise comes after the unexpected decline in W35 and is due to the temporary oversupply from imports and shifts in consumer demand. In W36, the anticipated effects of reduced supply and adverse weather conditions finally materialized, driving prices upward. Additionally, the limited availability of oranges following the earlier oversupply correction and a return to normal consumer demand contributed to the price rebound in the domestic market.
Egypt
Orange prices in Egypt increased by 2.5% WoW to USD 0.26/kg in W36, continuing the slight upward trend in W35. However, despite the weekly rise, the market remains under pressure, with prices falling by 5.38% month-on-month (MoM) and 37.61% YoY. This ongoing decline reflects the challenges of oversupply from a large harvest, which has kept prices lower than usual. While the domestic market faces downward pressure, Egypt's strong export performance, especially in the European Union (EU), has yet to impact local pricing significantly.
United States
In the United States (US), wholesale orange prices rose by 1.79% WoW to USD 1.82/kg in W36. Additionally, prices saw a 6.45% MoM increase and a 32.28% YoY rise. This steady price rise reflects concerns over the spread of HLB disease, driving up production costs. Despite stable output, growers are facing higher expenses related to disease management, including quarantine measures by the California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA) and additional pest control efforts. These factors add upward pressure on orange prices as producers work to mitigate the effects of HLB on their crops.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Implement Resilience Strategies for Citrus Production
The Brazilian citrus industry should immediately implement resilience strategies to address the ongoing production decline. This includes investing in heat-resistant and disease-resistant citrus varieties, such as 'Valencia' and 'Tahiti lime' for heat tolerance and 'Citrus tristeza virus-resistant' varieties for disease resistance. Additionally, adopting advanced irrigation techniques like drip and subsurface irrigation will optimize water use and reduce crop stress during heat waves. Enhancing pest and disease management practices through integrated pest management (IPM), biological controls, and disease-resistant rootstocks is essential. Furthermore, the industry should focus on diversifying export markets, targeting regions with growing demand, to mitigate risks associated with production shortfalls and stabilize supply chain fluctuations. These actions will help stabilize production levels and manage price volatility amid the challenges.
Adjust Pricing Strategy and Monitor Market Trends
Spanish citrus growers should closely monitor market prices and adjust their selling strategies accordingly. This involves regularly reviewing current citrus prices, especially for early varieties like Okitsu mandarins and Oronules, and comparing them with production costs and expected supply levels. By staying informed through market reports and industry updates, growers can make timely adjustments to their pricing strategies, ensuring they remain competitive and maximize profitability despite production decreases and rising expenses.
Adjust Supply and Negotiate to Stabilize Orange Prices
Mexican orange producers should immediately stabilize prices by adjusting supply levels and negotiating with distributors in key markets such as the US, Canada, and the European Union. Producers should carefully manage their output and avoid flooding the market to prevent market oversaturation and mitigate the impact of the recent dramatic price surge. Additionally, they should negotiate with distributors in these countries to secure better pricing agreements and ensure a more balanced supply chain. Investing in advanced disease management and drought-resistant practices is crucial to improving crop resilience and long-term stability.
Sources: Tridge, Espanol, CEPEA, MSN, Department of Agriculture, MXfruit, Freshplaza, Hortifruti





