
1. Weekly News
Argentina
Argentina's Apple Production Expected to Rise Amid Challenges for Small Producers
Fresh apple production in Argentina for the 2024/25 marketing year (MY) is forecasted to increase slightly to 488 thousand metric tons (mt), while pear production is projected to decline to 655 thousand mt. Despite favorable weather conditions, the industry faces challenges, including escalating production costs and shrinking numbers of fruit producers. Moreover, apple exports are expected to reach 82 thousand mt in 2024/25 MY. The Río Negro province remains the country's primary apple and pear producer, contributing 82% of the total output. However, the number of apple producers has drastically declined from about 9 thousand in 2005 to 1.6 thousand in 2023 due to high production costs and increased competition for agricultural land.
Brazil
Brazil Gains Market Access for Apple Exports to Peru
Brazil has successfully entered the Peruvian market for apple exports, making it the second country, after Chile, to achieve this. The new bilateral agreement marks a significant milestone in trade relations between Brazil and Peru, highlighting a mutually beneficial exchange. Brazilian officials emphasized the importance of balanced trade, underscoring the intention to sell Brazilian apples and import Peruvian products. The discussions also covered the strategic use of the Chancay Port in Peru, built with Chinese investment, which is expected to enhance the distribution of Brazilian goods in the region.
Canada
Nova Scotia Apple Growers Concerned About Potential US Tariffs on Exports
Nova Scotia apple growers are worried about potential United States (US) tariffs following Donald Trump's presidential campaign to impose a 10% tariff on all foreign products, including apples. The US is Nova Scotia's largest export market, and any tariff could reduce demand for their high-quality Honeycrisp apples, impacting prices and orders. Although the region has sought alternative markets, such as Vietnam, these come with higher shipping costs and quality loss during transit. Growers are anxious about the political uncertainties surrounding trade policies and are looking to the Canadian government for support if the tariffs are imposed. The potential tariff could disrupt their business, especially with the US being a convenient, nearby market for perishable goods like apples.
Chile
Chile's Apple Industry Focuses on New Varieties with Changing Market Trends
At the Fruittrade 2024 event in Santiago, Chile's apple industry highlighted its strategies to adapt to shifting global market conditions. Despite reducing apple planting areas, Chile is investing in new varieties such as Honeycrisp and Ambrosia to strengthen its presence in key markets like Brazil, Colombia, and Ecuador. Although China remains the largest apple producer, its high domestic consumption limits its export capacity, placing it third globally. In contrast, Italy and Poland lead international exports, focusing on traditional varieties like Golden Delicious. Chile ranks seventh globally but excels as a top exporter of premium varieties such as Gala and Pink Lady. However, strong harvests in the US have increased global supply, putting downward pressure on prices in these primary markets.
India
India's Apple Production Increases as Import Demand Grows
India's apple production is projected to increase by 6% year-on-year (YoY) to 2.55 million metric tons (mmt) in MY 2024/25, driven by favorable weather in major growing regions such as Jammu, Kashmir, and Himachal Pradesh. Despite higher domestic production, apple imports are expected to rise by 10% YoY to 600 thousand mt due to strong consumer demand for premium-quality apples. However, limited cold chain infrastructure continues to hinder domestic distribution, affecting the supply chain efficiency. The recent removal of retaliatory tariffs has boosted US apple exports, further supporting the rise in imports.
New Zealand
New Zealand Apple Industry Recovers and Expands Despite Cyclone Damage
In the 2024/2025 MY, New Zealand's apple-planted area is projected to grow significantly to 11.1 thousand hectares (ha) as the industry recovers from damages caused by Cyclone Gabrielle in 2023. Despite the impact of floods and debris in major apple-growing regions like Hawke's Bay and Gisborne, favorable weather, improved farm practices, and increased seasonal labor availability are expected to boost apple production to 560 thousand mt. Apple exports are forecasted to reach 380 thousand mt, targeting primary markets in Asia, the US, and the United Kingdom (UK). This resurgence could push total revenue to over USD 586 million (NZD 1 billion), reflecting strong demand and enhanced export performance.
Russia
Apple Shortage Persists in Russia Despite Efforts to Increase Production
Russia continues to face a shortage of apples, as confirmed by the Russian President during a discussion with regional officials. Although North Ossetia-Alania, a primary apple-growing region, boasts the largest orchard in southern Russia, supply remains insufficient to meet domestic demand. Frosts earlier in the season significantly reduced the apple harvest, prompting authorities to look toward imports from Azerbaijan, Armenia, Turkey, Serbia, and Belarus to fill the gap. Regional efforts to expand production, including new pear plantings, are underway, but challenges persist in stabilizing the apple supply.
2. Weekly Pricing
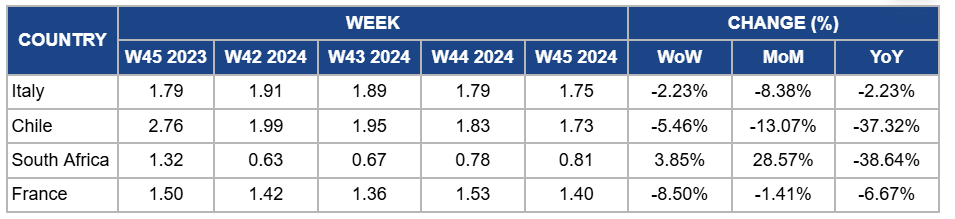
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W45 2023 to W45 2024)
Italy
In W45, apple prices in Italy decreased by 2.23% week-on-week (WoW) and YoY to USD 1.75 per kilogram (kg), with an 8.38% month-on-month (MoM) drop due to increased supply as peak seasonal production continues. The availability of various apple varieties, including Fuji and Annurca, has eased pricing pressure. Although demand remains steady, the abundant harvest drives prices down as the market adjusts to higher supply levels.
Chile
Chilean apple prices declined by 5.46% WoW to USD 1.73/kg in W45, showing a 13.07% MoM drop and a 37.32% YoY decrease due to increased market supply from new orchard plantings and improved harvest yields. The enhanced use of cold storage has increased inventory levels, putting downward pressure on prices. Additionally, weaker export demand has contributed to the prolonged price drop, intensifying the YoY decline.
South Africa
Apple prices in South Africa rose by 3.85% WoW to USD 0.81/kg in W45, showing a 28.57% MoM increase due to strong local demand and reduced supply of green apple varieties, particularly Granny Smith. However, YoY prices declined by 38.64% due to a surplus of red apple varieties like Royal Gala and Kanzi and export disruptions, including the recent suspension of shipments to Taiwan, which has pressured overall market pricing.
France
In France, apple prices fell by 8.5% WoW to USD 1.40/kg in W45, marking a 1.41% decrease MoM and a 6.67% decline YoY due to increased supply following the peak harvest period and rising competition from imported apples. Additionally, despite ongoing promotional efforts, domestic demand did not fully offset the seasonal oversupply, leading to downward pressure on prices.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Capitalize on New Zealand's Apple Production Recovery
Apple growers in New Zealand should focus on enhancing production efficiency and increasing exports by utilizing the growth in planted areas and favorable conditions post-Cyclone Gabrielle. With improved farm practices such as precision irrigation, integrated pest management, and enhanced pruning techniques for better light penetration, alongside increased labor availability, growers should prioritize scaling up production and strengthening export channels to Asia, the US, and the UK markets. Growers can also explore value-added product offerings, like organic or premium apples, to capture higher-value market segments and ensure robust revenue growth during recovery.
Expand Apple Supply through Strategic Imports and Regional Support
Apple suppliers in Russia should enhance imports from neighboring countries, such as Azerbaijan, Armenia, Turkey, Serbia, and Belarus, to bridge the gap created by local shortages. At the same time, Russian growers should accelerate efforts to stabilize domestic apple production by increasing investments in orchard management and exploring more resilient varieties to mitigate frost damage. Additionally, strengthening regional partnerships and logistics for smoother import and distribution can help ensure the steady availability of apples to meet consumer demand.
Diversify Markets and Mitigate Tariff Risks
Nova Scotia apple growers should prioritize diversifying their export markets beyond the US, especially targeting regions like Vietnam while exploring other cost-effective logistics solutions to minimize quality loss during transit. Additionally, growers should strengthen relationships with current international buyers and develop direct-to-consumer channels to reduce dependency on the US market. Exploring alternative transport routes and improving packaging to preserve apple quality can help mitigate the impact of tariffs, ensuring consistent demand and market stability.
Sources: Tridge, Agrotimes, CanalRural, Eastfruit, Freshplaza, PAJHWOK, RG, Saltwire, USDA





