July 2025 Outlook Report: Fruits
Bojan Mijatovic
Published Jul 18, 2025
PDF File Preview

- Key Indicators: Global freight prices averaged USD 3,395.91 per 40-foot container in Jun-25, 59.90% higher month-on-month (MoM) but still 20.69% lower year-on-year (YoY), driven by frontloading ahead of expected tariff expirations. Meanwhile, the World Bank’s Fertilizer Index rose to 142.98 points, a 7.34% MoM rise and 20.96% YoY increase, supported by rising prices in urea, diammonium phosphate (DAP), and potassium chloride.
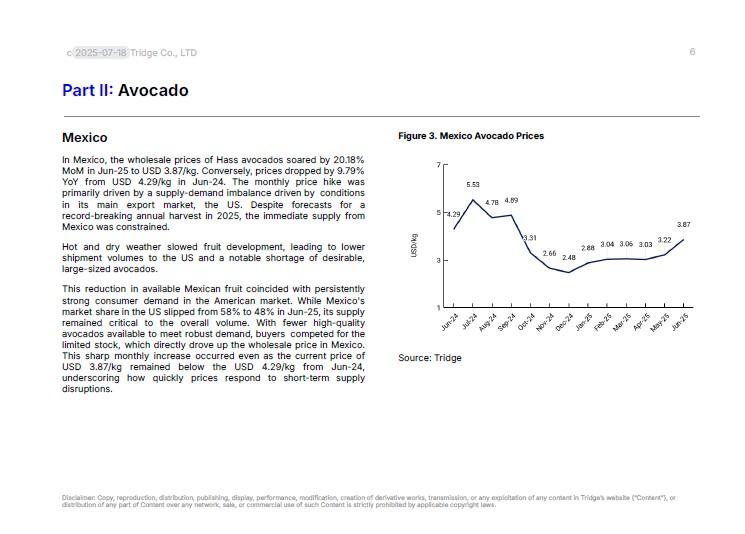
- Avocado: Avocado prices in Jun-25 showed varied trends across key markets. In Mexico, prices surged by 20.18% MoM to USD 3.87 per kilogram (kg), due to adverse weather that reduced the supply of large-sized fruit amid strong United States (US) demand. In Spain, prices climbed 32.64% MoM to USD 4.47/kg, fueled by strong end-of-season demand for high-quality local avocados, which commanded a premium despite a flood of Peruvian imports into Europe. Meanwhile, Chilean prices remained stable MoM at USD 2.53/kg, as a robust domestic market successfully balanced supply and demand from a bumper crop, even as prices were down 34.11% YoY.
- Grape: In Jun-25, fresh grape prices varied significantly among major Southern Hemisphere exporters, reflecting intense competition and shifting market dynamics. In Chile, prices dipped 4.79% MoM to USD 1.39/kg as the market grappled with saturation and intense competition from Peru, part of a broader strategic shift away from traditional grape varieties. Conversely, Peru saw prices jump 45.94% MoM to USD 1.08/kg due to a combination of strong demand and insufficient supply. Similarly, South Africa experienced a price surge of 41.82% MoM to USD 2.95/kg, driven by strong demand from North America as the country works to diversify its export markets amid fierce competition from its South American rivals.
- Mango: In Peru, mango prices experienced a significant monthly rebound, skyrocketing by 60.41% MoM in Jun-25 to USD 0.77/kg. However, this surge did little to offset the YoY price suppression, with prices remaining 59.47% lower than the previous year due to an enormous supply overhang. While a post-season uptick in demand fueled the monthly price hike, the sheer volume from this bumper crop was the dominant factor, keeping overall prices heavily subdued compared to the prior year.
- Avocado: Avocado prices in Jun-25 showed varied trends across key markets. In Mexico, prices surged by 20.18% MoM to USD 3.87 per kilogram (kg), due to adverse weather that reduced the supply of large-sized fruit amid strong United States (US) demand. In Spain, prices climbed 32.64% MoM to USD 4.47/kg, fueled by strong end-of-season demand for high-quality local avocados, which commanded a premium despite a flood of Peruvian imports into Europe. Meanwhile, Chilean prices remained stable MoM at USD 2.53/kg, as a robust domestic market successfully balanced supply and demand from a bumper crop, even as prices were down 34.11% YoY.
- Grape: In Jun-25, fresh grape prices varied significantly among major Southern Hemisphere exporters, reflecting intense competition and shifting market dynamics. In Chile, prices dipped 4.79% MoM to USD 1.39/kg as the market grappled with saturation and intense competition from Peru, part of a broader strategic shift away from traditional grape varieties. Conversely, Peru saw prices jump 45.94% MoM to USD 1.08/kg due to a combination of strong demand and insufficient supply. Similarly, South Africa experienced a price surge of 41.82% MoM to USD 2.95/kg, driven by strong demand from North America as the country works to diversify its export markets amid fierce competition from its South American rivals.
- Mango: In Peru, mango prices experienced a significant monthly rebound, skyrocketing by 60.41% MoM in Jun-25 to USD 0.77/kg. However, this surge did little to offset the YoY price suppression, with prices remaining 59.47% lower than the previous year due to an enormous supply overhang. While a post-season uptick in demand fueled the monthly price hike, the sheer volume from this bumper crop was the dominant factor, keeping overall prices heavily subdued compared to the prior year.
Table of Content
Part I: Key Indicators
- Freight
- Fertilizer
Part II: Avocado
- Mexico
- Spain
- Chile
Part III: Grape
- Chile
- Peru
- South Africa
Part IV: Mango
- Peru
Related market data
Read more relevant content
By clicking “Accept Cookies,” I agree to provide cookies for statistical and personalized preference purposes. To learn more about our cookies, please read our Privacy Policy.



