W1 2025: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
1. Weekly News
Argentina
Argentina's Beef Industry Struggles to Stay Profitable Due to Cost Pressures
The Federation of Refrigeration Industries of Argentina (FIFRA) highlighted that 2024 closed with high beef production levels, although with a complex situation for the meat industry. Despite high production, the industry remains unprofitable, largely due to increased costs and the reduction in the price of exported meat, which has fallen by 20% compared to 2022. While the government's removal of export restrictions and tax measures improved competitiveness, FIFRA emphasized the need to fully eliminate export duties on all meats and their by-products to benefit operators and sustain the sector’s performance.
Looking ahead, FIFRA predicts a difficult 2025, with challenges such as rising production costs and the loss of value for by-products like leather and tallow. FIFRA suggests increasing rearings to improve slaughter weights and mitigate cost pressures. The situation is exacerbated by informal market practices and unfair competition, which threaten formal businesses. FIFRA called for stronger regulations, particularly in terms of compliance with labor, tax, and health obligations. Despite the challenges, FIFRA remains optimistic that with proper investment and economic reforms, Argentina’s livestock sector can thrive and support small agro-industrial growth.
Bolivia
Bolivia's Beef Industry Struggles with Rising Costs
Bolivia became a major beef producer in 2024, with 320 thousand metric tons (mt) of beef produced, of which 290 thousand mt were used for domestic consumption and 30 thousand mt for export. The country's livestock inventory of 11.4 million cattle ensures that local supply meets demand while still allowing for exports. However, beef prices have risen due to speculation by middlemen, smuggling, and temporary issues like droughts and fuel shortages. The lack of regulation over middlemen is driving up prices, emphasizing the need for better control of the supply chain to stabilize prices and optimize export potential.
To address these issues, Bolivia must regulate intermediaries by certifying all third-party suppliers and monitoring their activities, including fuel usage and profits. Despite challenges, the beef export sector has grown significantly, with nearly 36 thousand mt sold in 2024. By balancing domestic needs with export growth, Bolivia can continue to strengthen its beef industry while ensuring market stability.
China
China Launches Inquiry into Beef Imports
China has launched an investigation into beef imports amid concerns about their impact on domestic prices and the local livestock industry. Covering imports between Jan-19 and Jun-24, the inquiry targets 22 companies across ten countries, including Brazil, Argentina, and Australia, which supply over 30% of China's market. The investigation follows complaints from livestock associations citing serious damage from increased import volumes, which have pressured prices. With China’s beef imports reaching USD 14.2 billion in 2023, the government aims to determine whether safeguards like tariffs or quotas are needed to protect domestic farmers.
The investigation could significantly disrupt global beef trade, particularly affecting Brazil and Argentina, which rely heavily on exports to China. This move may reflect China’s efforts to shield its market amid economic challenges and potential trade disputes. Exporters fear tariffs or quotas could be imposed regardless of the findings, with some viewing the investigation as a signal to consumers to expect higher prices. If safeguards are enacted, they could reshape global meat trade and deepen uncertainties for exporting nations.
Colombia
Colombia Emerges as Key Global Beef Exporter
According to the National Federation of Cattle Ranchers (Fedegan), Colombia’s beef exports reached 17.29 thousand mt, valued at USD 71.6 million in 2024. This performance illustrates Colombia’s growing position as a key exporter of sustainably produced meat from natural pastures, producing over 900 thousand mt annually. The main export markets for Colombian beef in 2024 were Russia (9.92 thousand mt), China (3.16 thousand mt), and Chile (1.4 thousand mt). Fedegan also highlighted the importance of exploring new markets, as Colombia’s cattle herd ranks eleventh globally, and it continues to expand its presence in regions such as Curaçao, Egypt, and Turkey. The diversification of markets underscores the competitiveness of Colombia’s livestock industry on the international stage.
Paraguay
Paraguay Set to Expand Beef Export Markets in 2025
Paraguay is set to expand its beef exports by 2025, with new markets such as South Korea, Singapore, the Philippines, and Mexico on the horizon. This progress is the result of years of strategic efforts, including diplomatic visits and documentation exchanges, according to the National Service of Quality and Animal Health (Senacsa). Paraguay has already completed audits for South Korea and the Philippines in 2024 and is awaiting a mission from Singapore. Additionally, it began exporting to the United States (US), Canada, and confirmed Mexico's opening, pending health certificate approval. Through the Mercosur-European Union (EU) free trade agreement, Paraguay will gain a preferential tariff quota for chilled and frozen meat. Despite successes, progress with Japan has been slower than anticipated, with no responses received six months after submitting the necessary documents. In 2024, Paraguay exported beef to 59 markets, with key destinations including Chile, Taiwan, the US, Brazil, and Israel.
South Korea
Smart System Enhances Efficiency in Hanwoo Beef Processing
In collaboration with the Korea Agricultural Cooperative Federation, the National Institute of Animal Science has developed a real-time production management system for Hanwoo beef processing plants, enabling efficient monitoring from slaughter to export. This smart system automates previously manual tasks such as meat intake, packaging, and export reporting, improving efficiency and reducing labor. Features include real-time verification of production yields, prevention of part mixing, and integration with the livestock product traceability system. Plans are underway to merge this with the "Hanwoo Slaughterhouse Smart History Management System" and conduct field verification, aiming to enhance operational accuracy and reporting efficiency in Hanwoo processing facilities.
Korean Beef Industry Advocates Strong Legislative Action Despite Budget Conflicts
The push to establish the Korean Beef Association and pass the Hanwoo Act is gaining momentum, with the Democratic Party introducing several bills after 2024’s veto of the 'Support Act for Sustainable Hanwoo Industry.' The National Hanwoo Association is strongly advocating for the Hanwoo Act to stabilize the industry, particularly in response to corporate capital's entry into the sector. Concerns have been raised about the misapplication of laws meant for short-cycle livestock to Korean cattle, which require longer cycles. With the Democratic Party holding a majority in the National Assembly, the enactment of the Hanwoo Act is increasingly likely, though conflicts over budget allocation between livestock sectors remain a challenge.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
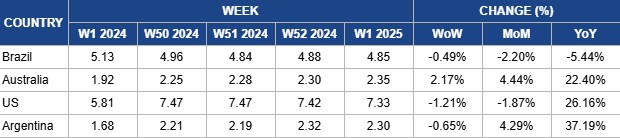
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W1 2024 to W1 2025)
Brazil
In W1, Brazil's wholesale price for boneless rear beef declined by 0.49% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 4.85 per kilogram (kg). This also marked a 2.20% month-on-month (MoM) drop and a 5.44% YoY decrease. Despite the decline in USD terms, prices in Brazilian real remained stable at BRL 30/kg for the eighth consecutive week, with exchange rate fluctuations being the main factor affecting the price in USD. According to Safras and Mercado, market players are adjusting expectations for the wholesale-to-retail price transition in the first half of Jan-25 following a holiday season. The consumption pattern is expected to shift after the New Year, with the demand for premium cuts likely to decrease. Additionally, substitutes like chicken meat are offering competitive prices, further influencing the beef market.
Australia
Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator averaged USD 2.35/kg in W1, marking a 2.17% WoW increase and a steady rise since W46. This price also reflects a 4.44% MoM increase and a 22.40% year-on-year (YoY) uptick. The consistent growth was largely driven by the Christmas and New Year 2025 celebrations when demand for beef surged as retailers stocked up on premium cuts. This holiday season coincides with summer, further boosting consumption through outdoor barbecues and gatherings.
United States
In W1, the price for lean beef (92% to 94%) in the US averaged USD 7.42/kg, reflecting a slight 1.21% WoW decline. This marks a continued decrease since W36 2024, reaching their lowest point since W12 2024, with prices stabilizing in W52 2024. Additionally, lean beef prices dropped 1.87% MoM. Despite this, prices remain 26.16% higher YoY, driven by a tightening domestic supply due to a shrinking cow herd. The decline since W36 aligns with the seasonal dip in winter demand following the peak summer consumption period. However, limited production continues to support relatively high lean beef prices.
Argentina
Argentina's average steer beef price dropped to USD 2.30/kg in W1, reflecting a 0.65% WoW decline. However, the price marked a 4.29% MoM increase and a notable 37.19% YoY rise. Despite the weekly dip, this figure represents the second-highest price recorded since the start of 2024, just behind W52 at USD 2.32/kg, driven by strong holiday demand during Christmas and New Year celebrations. It is worth noting that Argentina's beef consumption in 2024 faced significant challenges due to economic pressures. According to the Chamber of Industry and Commerce of Meat and Derivatives of the Argentine Republic (CICCRA), beef consumption fell by 12% YoY in 2024, marking the worst year for beef sales in two decades. Per capita consumption dropped to 47.4 kg, an 11.1% decrease compared to the same period in 2023. CICCRA also reported that the 12-month moving average until Nov-24 was 47 kg per person, reflecting a 12.4% YoY decline. Apparent domestic beef consumption for 2024 totaled 2.038 million metric tons (mmt), 10.1% less than in 2023, reaching its lowest levels in 22 years.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strengthen Competitiveness Amidst Challenges
In response to Argentina’s beef sector challenges, the government should prioritize fully eliminating export duties on all meats and by-products to ensure sustained growth and competitiveness. Tackling informal market practices is also essential to protect formal businesses. Strengthening regulations to ensure labor, tax, and health obligations are met can curb unfair competition and bolster industry stability. Moreover, targeted investment in infrastructure and economic reforms would enhance the sector's long-term sustainability, fostering growth and supporting small agro-industrial players.
Prepare for Potential Safeguards and Trade Disruptions
With China launching an investigation into beef imports, global exporters must prepare for potential tariffs or quotas, which could disrupt global trade flows. Countries like Brazil and Argentina, which rely heavily on exports to China, should diversify their export markets to reduce dependency on the Chinese market. Building relationships with emerging markets and strengthening domestic production capabilities will help cushion any trade disruptions. Additionally, exporters should engage in proactive communication with Chinese authorities to ensure compliance with new regulations, which may shape the future of the global beef trade.
Capitalize on Export Growth and Market Diversification
Colombia’s beef export success should be leveraged by further diversifying export markets, especially in regions such as Africa and the Middle East. Strengthening trade relations with emerging markets will reduce over-reliance on major destinations like Russia and China. To maintain competitiveness, Colombia should continue promoting the sustainability of its beef production from natural pastures and focus on improving meat quality. Additionally, investing in marketing and certifications for new markets will solidify Colombia's position as a leading supplier of high-quality beef while supporting its export growth trajectory.
Advance Innovation and Legislative Support for Hanwoo Beef
South Korea should continue investing in innovative solutions, like the real-time production management system for Hanwoo beef processing plants, to improve operational efficiency. This technology will streamline production, reduce labor costs, and ensure traceability from slaughter to export. Additionally, the country’s beef industry would benefit from the successful passage of the Hanwoo Act, which would provide legislative backing to stabilize the industry. Advocating for clear policies that address the unique requirements of Hanwoo cattle and aligning them with sustainable practices will support long-term sector growth and protect local producers from corporate pressures.
Sources: Tridge, Aflnews, Agrinet, Agromeat, Bichos de campo, Elagro



