W20 2025: Strawberry Weekly Update

In W20 in the strawberry landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Brazil has maintained stable strawberry prices, supported by steady harvests and new bioplastic technology that extends shelf life.
- China is expected to remain the global leader in strawberry production in 2025, with a projected annual output of 3.39 million tons across 202.34 thousand ha, supported by advanced technologies and strong infrastructure investment.
- Kashmir experienced good strawberry yields in 2025. However, prices fell sharply due to reduced tourism following a terror attack, significantly affecting local farmers' profits.
- Lithuania began its 2025 strawberry season early in May-25. Cooler spring weather led to lower yields and higher prices, especially in regions relying on greenhouse production.
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Strawberry Prices in Brazil Stable as Production Advances and New Preservation Technology Emerges
Strawberry prices in Brazil have been stable in recent weeks, with direct-to-consumer rates ranging from USD 3 to 5.60 per kilogram (kg) and wholesale prices between USD 3 and USD 4/kg. In the Pelotas region, neutral-day varieties continue to be harvested steadily, despite producing smaller fruits, as demand increases and imported seedlings are introduced. Meanwhile, early short-day varieties have begun to flower in Santa Rosa, while neutral-day types remain in the vegetative stage. In Caxias do Sul, favorable weather is supporting healthy crop development, although effective disease management, particularly against powdery mildew, remains crucial. Moreover, researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in São Paulo have created a bioplastic made from bacterial cellulose, pectin, and coconut oil, which extends strawberry shelf life from three to eight days, potentially reducing refrigeration needs and post-harvest losses.
China
China Leads Global Strawberry Production with Technological Innovations
In 2025, China is expected to maintain its position as the world’s leading strawberry producer, with 202.34 thousand hectares (ha) under cultivation and an annual output of 3.39 million tons. This places China significantly ahead of the United States (US) with 1.21 million tons and Turkey with 669.19 thousand tons. This leadership is driven by strong state investment, well-developed infrastructure, and the widespread adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, drones, and sensors for crop monitoring and pest control. These innovations have improved yield, quality, and operational efficiency, positioning China as a global benchmark in strawberry cultivation. While countries like Mexico and Spain continue to dominate strawberry exports, and others like Egypt and France contribute steadily, China’s unmatched scale and technological advancements are reshaping the global landscape of strawberry production.
India
Security Tensions Impact Strawberry Production in Kashmir
Strawberry farmers in Kashmir experienced a relatively good harvest in 2025, producing between 2.5 thousand metric tons (mt) and 3.5 thousand mt across 300 to 350 ha. Notably, areas like Gussu village saw increased production, as many growers have recently shifted from vegetable and paddy farming to strawberries. Despite strong yields and potential earnings of USD 2.3 million to 3.4 million (INR 200 to 300 million), profits were significantly impacted by a sharp price drop. This decline followed a terror attack in Pahalgam and ensuing military tensions between India and Pakistan, which led to a steep fall in tourism and local demand. Before the attack, prices reached USD 5.82 per 2.5-kg tray (INR 500 per 2.5-kg tray). Afterward, they fell to USD 2.68 to 2.91 per 2.5-kg tray (INR 230 to 250 per 2.5-kg tray), later stabilizing around USD 3.49 to 4.07 per 2.5-kg tray (INR 300 to 350 per 2.5-kg tray) by the end of the harvest. Most of the crop is consumed locally, and although minor hailstorms occurred, officials confirmed that overall production remained strong, with fruits carefully stored in cold facilities to help manage distribution amid the disruptions.
United States
Fungal Disease Threatens Ohio's Strawberry Supply in 2025
Strawberry production in Ohio faces significant challenges in 2025 due to the rapid spread of Neopestalotiopsis (Neo-P), a fungal disease. This disease has restricted access to healthy transplants and lowered crop yields. This situation will result in fewer Ohio-grown strawberries and make the prices higher. The disease poses a particular challenge for greenhouse and high tunnel growers, as fungicide options are limited and resistant strawberry varieties are not available. Supported by internal and state grants, Ohio State University Extension is actively collaborating with growers to provide early detection tools and effective disease management strategies. They conduct ongoing research to better understand the pathogen’s behavior and impact. The problem is compounded by last year’s shortage of clean planting material, which has disrupted both commercial production and academic research, given the critical role of fall transplanting for spring harvests.
Lithuania
Lithuania’s 2025 Strawberry Season Starts Early Amid Low Yields and High Prices
Lithuania’s 2025 strawberry season began in early May, with the first harvests from heated greenhouses starting about a week earlier than in 2024. However, cooler spring temperatures have reduced yields and caused prices to rise. In Anykščiai, farms produce around 1 ton of strawberries daily by carefully managing temperature and irrigation to improve fruit quality. Meanwhile, growers in northern areas like Joniškis rely exclusively on greenhouse cultivation to manage unpredictable spring weather, allowing for year-round production with two harvests each season.
2. Weekly Pricing
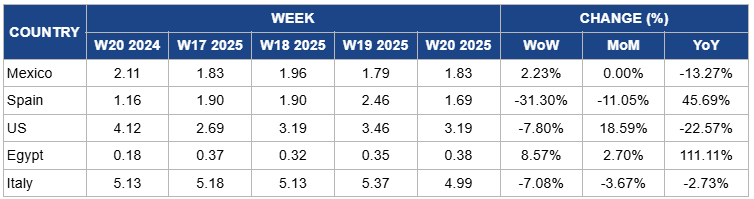
Weekly Strawberry Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Strawberry Pricing Important Exporters (W20 2024 to W20 2025)
Mexico
Mexico's strawberry prices increased by 2.23% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 1.83/kg in W20, with no month-on-month (MoM) change due to improving weather conditions that enhanced crop quality and a slight reduction in local supply as farmers adjusted harvest volumes to market demand. Additionally, stronger demand from export markets, especially the US, supported the recent price increase. However, year-on-year (YoY) prices dropped by 13.27% due to increased competition from other major strawberry-producing countries like the US and Spain, and overall higher production volumes in Mexico compared to the previous year, which contributed to downward pressure on prices over the longer term.
Spain
In W20, strawberry prices in Spain dropped by 31.30% WoW to USD 1.69/kg, marking an 11.05% MoM decrease. This decline is due to a surge in supply from the Huelva region, where favorable weather conditions accelerated the ripening process, leading to an influx of strawberries into the market. The increased availability and intensified competition from other European producers, such as Italy and the Netherlands, exerted downward pressure on prices. However, YoY prices rose by 45.69%, reflecting the lingering effects of the previous year's unusually cold weather that disrupted the biological cycle of strawberry plants, leading to reduced productivity and smaller fruit sizes. Despite a projected recovery in production for 2025, concerns over potential weather anomalies may limit growth, keeping prices relatively low in the short term.
United States
US strawberry prices dropped by 7.80% WoW to USD 3.19/kg in W20, marking a 22.57% YoY decrease due to a seasonal increase in local production from key growing regions such as California and Florida, which led to higher supply and downward pressure on prices. Additionally, favorable weather conditions supported larger harvests, contributing to the weekly price drop. However, MoM prices increased by 18.59% due to the transition period between peak and off-peak seasons, where supply tightens slightly, and growing demand from both local consumers and export markets helps support a moderate price rebound over the month.
Egypt
In Egypt, strawberry prices increased by 8.57% WoW to USD 0.38/kg in W20, marking a 2.70% MoM increase and a 111.11% YoY increase due to a combination of reduced local supply caused by adverse weather conditions affecting early-season crops and stronger demand from both local markets and export destinations in the Middle East and Europe. Additionally, improvements in post-harvest handling and increased investment in strawberry cultivation have helped boost quality, supporting higher prices year over year despite seasonal fluctuations.
Italy
Strawberry prices in Italy dropped by 7.08% WoW to USD 4.99/kg in W20, with a 3.67% MoM decrease and a 2.73% YoY decline. The price drop is due to increased early-season harvest volumes from key growing regions like Emilia-Romagna and Sicily, leading to higher local supply. Additionally, favorable weather conditions boosted yields, while competition from imports and moderated consumer demand amid economic uncertainties further pressured prices downward.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Expand Cold Chain Reach and Offload to Distant Markets
Strawberry producers in India, especially in regions like Kashmir, should partner with logistics and distribution firms to widen cold chain access and redirect produce to distant urban markets during local demand shocks. For example, growers can work with private cold storage and reefer truck operators to move fresh strawberries to high-demand cities like Delhi, Mumbai, or Bengaluru, where tourism-linked demand remains stable. Establishing forward contracts with retailers and e-commerce platforms in these areas can also help secure better pricing during volatile local market conditions.
Source Certified Disease-Free Transplants Through Regional Grower Networks
Strawberry producers in the US, including those in Ohio, should form or join regional grower networks to collectively source certified disease-free transplants from vetted nurseries in unaffected states like California or North Carolina. For instance, Ohio growers facing Neo-P outbreaks can pool orders with nearby states to secure cleaner, traceable plant stock and reduce per-unit costs. Producers should also coordinate with trusted suppliers who offer lab-tested planting material and maintain transparent disease management records to prevent recurring infection cycles.
Sources: Tridge, Abrafrutas, Freshplaza, Hindustantimes, LRT, IDR, News OSU





