W27 2024: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
1. Weekly News
European Union
EU Witnesses Stable Beef Cattle Prices
The European Union (EU) Commission reported that the average prices for slaughter cattle have remained relatively stable in recent weeks. For young bulls in the R3 trade class, the weighted average price was USD 552.28 per 100 kilograms (EUR 507.98/100 kg) in the last week of Jun-24, marking a modest 0.2% increase from the previous week. Specifically, Italy saw a significant recovery with a 7.7% week-on-week (WoW) increase, while Ireland, Denmark, and Belgium experienced WoW increases of 1.1%, 0.7%, and 0.4%, respectively. Germany and Spain each recorded a 0.2% WoW price increase. In contrast, France experienced price fluctuations, while Poland and Austria saw WoW decreases of 0.1% and 0.2%, respectively.
The EU Commission also noted a slight rise in cow slaughter prices, which averaged USD 467.68/100 kg (EUR 467.68/100 kg) for animals in the O3 trade class, a 0.3% WoW increase. Austria led with a 5.2% WoW increase, followed by Denmark (+0.9%), Poland (+0.8%), Italy (+0.7%), and Germany (+0.1%). Meanwhile, Belgium, Ireland, and Spain recorded WoW decreases of 0.1%, 0.2%, and 3.4%, respectively.
Additionally, the EU Commission reported that heifer slaughter prices averaged USD 565.87/100 kg (EUR 520.48/100 kg), remaining unchanged from the previous week. Despite the overall stability, Denmark (+1.4%), Poland (+1.3%), Austria (+1.0%), France (+0.9%), Germany (+0.3%), and Italy (+0.2%) saw slight WoW increases. Conversely, Ireland and Spain experienced WoW reductions of 0.1% and 3.1%, respectively, while Belgium's prices remained unchanged.
Brazil
Brazil’s Beef Exports Drop in Jun-24
According to the Secretariat of Foreign Trade (SECEX), Brazil's exports of fresh, chilled, and frozen beef totaled 195.5 thousand metric tons (mt) in Jun-24, representing a 9.16% drop in volume compared to May-24, which saw shipments of 211.9 thousand mt. However, it depicts a 1.51% increase compared to Jun-23, which had 192.6 thousand mt.
The daily average exports in Jun-24 were 9.6 thousand mt, marking a 4.94% rise compared to the average in Jun-23. However, the average price per mt in Jun-24 was USD 4,466, an 11.63% decrease from Jun-23's price of USD 5,054/mt. The export value for Jun-24 amounted to USD 860 million, marking an 11.7% drop compared to Jun-23.
Brazil’s Beef Production Expected to Rise Bolstered by Female Cattle Slaughters
According to Safras and Mercado, Brazil’s cattle slaughter reached 18.9 million heads in the first half of 2024, an increase of 17.77% compared to the same period in 2023. This growth is attributed to a rise in the slaughter of female cattle, which reached 5.39 million heads, a 17.9% increase over the same period in 2023. Safras and Mercado expect the slaughter of female cattle to reach 9.4 million heads by the end of 2024, representing an 8.5% year-on-year (YoY) increase. Consequently, Brazil’s total slaughter is anticipated to increase by 4.8% YoY to 35.93 million heads in 2024. This is expected to result in a total beef production of around 10 million metric tons (mmt) in 2024, a 5.08% YoY rise.
China
China’s Beef Market Faces Price Declines Due to Oversupply
The beef market in China has recently experienced significant price drops, with wholesale prices falling by 18% from their peak in 2023 to around USD 8.53/kg (CNY 62/kg). This marks the lowest value in five years, rendering the cattle industry unprofitable. The price decline is attributed to an oversupply of meat in the market amid a slowing economy. In response, China’s Ministry of Agriculture has urged local authorities to support farmers with subsidies and feed to prevent a crisis.
This situation poses a threat to the country’s food security despite the government's efforts to achieve self-sufficiency in key markets, including beef. With deflationary pressures affecting the economy, China has been compelled to intervene and support various sectors ranging from livestock to crops. The meat oversupply is partly due to China’s encouragement of imports, with shipments increasing by 23% in the first five months of 2024. This trend is evidenced by China’s initiatives to open its market to other countries such as Brazil, Spain, and most recently, Australia. The Chinese government is also promoting domestic production.
Demand for beef has grown alongside the country’s increasing prosperity despite being relatively more expensive than other types of meat. However, with the current economic downturn, beef demand is declining, creating additional challenges for producers and the Chinese government.
2. Weekly Pricing
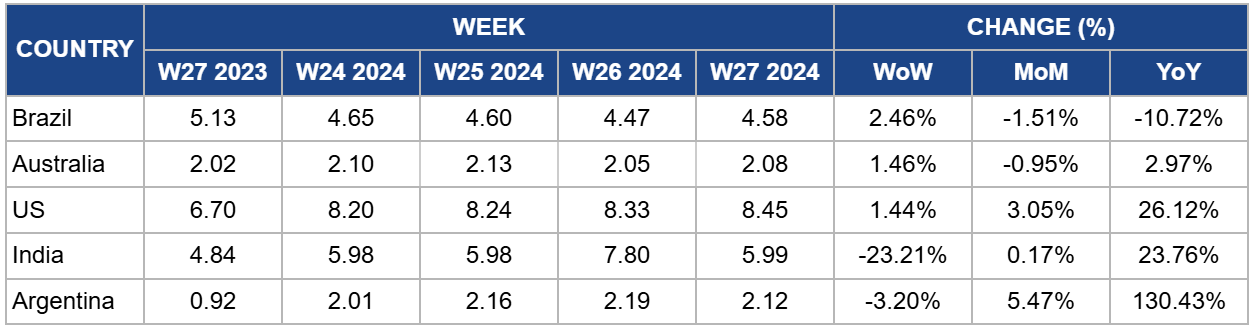
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
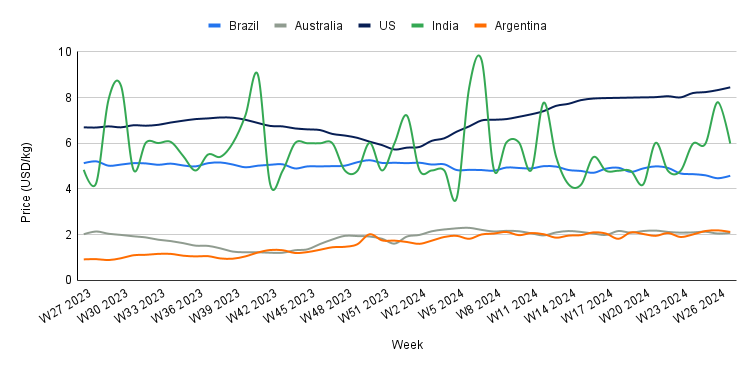
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W27 2023 to W27 2024)
Brazil
The wholesale price of boneless rear beef in Brazil averaged USD 4.58/kg in W27. This marks a 2.46% WoW increase but a 10.72% YoY decline. Despite the WoW increase in USD, the price in Brazilian real (BRL) remained unchanged at BRL 25.00/kg for the fifth consecutive week. This stability in real suggests that the weekly increase in USD was influenced by the exchange rate, where the real strengthened against the United States (US) dollar. However, the substantial YoY decline is primarily attributed to the abundant supply of beef in the market, driven by increased production. Safras and Mercado forecast that beef production may reach 10 mmt, supported by elevated slaughter rates, particularly of female cattle.
Australia
In W27, Australia's national young cattle indicator averaged USD 2.08/kg, a 1.46% WoW increase, a 0.95% month-on-month (MoM) decline, and a 2.97% YoY rise. The WoW price increase can be due to limited supply and heightened demand in the market. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), cattle yardings totaled 45.04 thousand heads in W27, a decrease of 10.1 thousand heads from W26. MLA also noted that demand from processors drove prices higher in Queensland, with most cows at Dalby being sold to southern states. Additionally, increased competition for quality-conditioned cattle boosted the overall market.
United States
In W27, the average price of lean beef (92% to 94%) in the US was USD 8.45/kg, marking a 1.44% WoW increase and a significant 26.12% YoY rise. These price hikes are attributed to a reduced beef supply in the market, driven by a decrease in US beef production due to prolonged droughts. According to Farm Progress, US beef production dropped by 1.6% YoY in the first half of 2024, primarily due to a 12.5% YoY decline in non-fed cattle slaughters during this period. Consequently, US beef production is expected to drop by 3.0% to 3.5% by the end of 2024 compared to 2023.
India
The average price of beef (cow) in India was USD 5.99/kg in W27, reflecting a significant 23.21% WoW drop but a substantial 23.76% YoY increase. These varying price movements highlight the volatility of the Indian beef market, which has been notably pronounced over the past 12 months. This volatility is primarily driven by both domestic and international regulations, as well as fluctuations in the supply within the Indian market.
Argentina
The average price of beef (steer) in Argentina reached USD 2.12/kg in W27, marking a 3.20% WoW drop, and a 5.47% MoM rise. The WoW decline suggests that the recent resurgence in beef demand has started to subside following the completion of a series of holidays observed in Argentina. This trend is likely to continue, leading to further price drops in the coming weeks, as Argentina is currently experiencing its lowest beef consumption in years due to economic downturn and inflation. According to the Rosario Exchange, each person in Argentina is expected to consume approximately 44.8 kg of beef in 2024, the lowest since 1914.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Optimizing Production and Market Strategies Amid Stable Prices
Given the stable beef cattle prices in the EU, producers should focus on optimizing their production efficiency and cost management to maintain profitability. Exploring value-added products and niche markets, such as organic or premium beef, can help capture higher margins. Strengthening relationships with key buyers in countries experiencing price increases, such as Italy, Ireland, and Denmark, can secure more favorable contracts. Additionally, monitoring regulatory changes and adapting swiftly can prevent disruptions.
Diversifying Markets and Enhancing Export Quality
With a drop in beef exports in Jun-24, Brazilian beef exporters should diversify their markets to reduce dependence on traditional buyers and mitigate risks. Strengthening marketing efforts in emerging markets and negotiating trade agreements can open new opportunities. Enhancing product quality and certification to meet varying international standards will increase market access. Domestically, focusing on sustainable and ethical farming practices can improve brand image and attract conscientious consumers. Leveraging technology to improve supply chain efficiency and reduce costs will be crucial in maintaining competitiveness amidst fluctuating export volumes and prices.
Addressing the Oversupply Situation through Product Diversification and Promotion
To address the oversupply and price declines in China's beef market, producers should diversify their product offerings and develop value-added beef products to maintain profitability. Forming partnerships with local authorities to secure subsidies and feed will help alleviate short-term financial pressures. Additionally, investing in marketing strategies that promote beef consumption and highlight their health benefits can stimulate domestic demand. Exploring export opportunities to offset domestic oversupply and participating in government-led initiatives to stabilize the market are also essential. Implementing efficient production practices to reduce costs will enable producers to withstand the economic downturn and navigate price volatility more effectively.
Sources: Proplanta, Elagro, Canal Rural, and UkrAgroConsult

