
In W3 in the banana landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Many banana producers, including the Philippines, India, and Guatemala, are facing production declines due to extreme weather, disease outbreaks (like Foc TR4), and logistical issues, leading to market instability.
- Ecuador and Colombia have seen price increases due to reduced local supply and higher export demand, while the Philippines and Guatemala have experienced price drops due to lower demand and production challenges.
- There’s growing interest in sustainable farming, with Italy successfully growing bananas in non-tropical climates and Peru working on disease-resistant banana varieties to combat Foc TR4.
- While some regions are recovering with improved prices, the global market remains volatile, impacted by competition, rising costs, and climate-related factors.
1. Weekly News
India
Banana Farmers in India’s Kalaburagi District Face Price Declines and Financial Struggles
In Kalaburagi district, more than 1 thousand banana farmers face financial challenges due to declining market prices, resulting in significant losses and increased debts. Banana cultivation requires a year-long effort and substantial investment, with profitability heavily dependent on favorable market rates. However, prices have dropped sharply, declining from around USD 22–24/ton in Sep-24 and Oct-24 to USD 12–15/ton in Dec-24 and Jan-25, making it difficult for farmers to recover their production costs. Afzalpur taluk, a major banana-growing area, is further impacted by declining groundwater levels due to inadequate rainfall, forcing some farmers to reconsider their crops. In response, farmers are calling for government intervention, including price support schemes, free saplings, and purchases through state-run outlets, while stakeholders are urging financial assistance in the national budget to help sustain banana farming in the region.
Cold Weather Threatens Banana Harvest in Karnataka, India
Banana farmers in Karnataka, India, are facing significant crop damage due to extreme cold weather this winter, with temperatures falling below 12 degrees Celsius (°C) and affecting over 25% of the crop, particularly those in early growth stages. This has led to issues including discoloration and reduced market quality, resulting in decreased export demand. As the third-largest banana producer in India, Karnataka, especially in regions like Chikkamagaluru, Shivamogga, and Kalaburagi, is particularly vulnerable. Farmers are struggling to recover from the weather-related damage and are calling for government intervention to support prices and establish a dedicated board to protect their interests. While cold-related crop damage is common, officials believe recovery is possible with warmer weather.
Italy
Sicilian Farm Successfully Grows Cavendish Bananas Using Sustainable Methods
In Marina di Ragusa, Sicily, Italy, the Alba Bio OP, a cooperative specializing in organic farming, has successfully cultivated Cavendish bananas in an unheated greenhouse, demonstrating the potential for banana farming in non-tropical climates. This innovative project capitalizes on Sicily's favorable weather and low-carbon cultivation methods, producing organic, sustainable bananas with a minimal environmental footprint. The locally grown bananas, marketed for their sustainability and health benefits, have attracted interest in European markets, with retail prices expected to range from USD 1.36 to 1.78 per kilogram (EUR 1.30 to 1.70/kg). This initiative not only aligns with Alba Bio's diversification strategy but also represents a significant milestone for Italian agriculture in promoting sustainable, locally produced bananas.
Philippines
Philippines Drops to Fourth Place Among Global Banana Exporters
In 2024, the Philippines dropped to fourth place among the world’s top banana exporters, behind Ecuador, Guatemala, and Colombia, following a 3% decrease in shipments due to adverse weather and the spread of Banana Fusarium Wilt Tropical Race 4 (Foc TR4). Exports from the country fell to 2.278 million tons, down from 2.35 million tons in 2023. TR4 continues to devastate crops in Mindanao, the Philippines' main banana-producing region, with only 51 thousand hectares (ha) remaining productive out of an original 89 thousand ha. Despite these challenges, the Philippines remains Asia's leading banana exporter. Rising geopolitical tensions, high input costs, and logistical issues have further impacted the industry.
Peru
Experimental Project in Peru Aims to Combat Banana Pest Threat
In Peru's Chira Valley, the Regional Directorate of Agriculture, in collaboration with local banana producers, has launched an experimental project. The project aims to test three subvarieties of bananas that are resistant to Foc TR4, a pest threatening the banana crops of over 10 thousand farming families in the region, jeopardizing their livelihoods. The initiative includes the construction of a tubular well for irrigation in experimental plots and receives technical support from key institutions such as the National Agrarian Health Service (SENASA), the National Institute of Agrarian Innovation (INIA), and the National University of Piura. The project, which also benefits from international collaboration, aims to address the pest issue and provide a viable solution, potentially strengthening local and global banana markets.
Spain
Recovery Despite Challenges for the Canary Islands Banana Industry in 2024
The Canary Islands banana industry began showing signs of recovery in 2024 after a challenging 2023, which saw record production and historically low prices. Export volumes fell by 23.5 million kg to 373 million kg in 2024, with mainland Spain and the Balearic Islands receiving the majority at 360.3 million kg, while smaller volumes were shipped to Morocco, Switzerland, Belgium, Poland, and Portugal. Despite this decline, export value rebounded by over 25%, reaching nearly USD 418.1 million (EUR 400 million), driven by stabilization in average prices. However, the industry continues to face challenges, including a 24% rise in production costs over the past three years, weather-induced variability, declining fruit consumption in Spain, intensified competition, and climate-related production fluctuations, all contributing to an uncertain yet cautiously optimistic outlook.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Banana Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Banana Pricing Important Exporters (W3 2024 to W3 2025)
* Varieties: Ecuador and the Philippines (overall banana average), Colombia (Uraba), and Guatemala (Criollo)
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
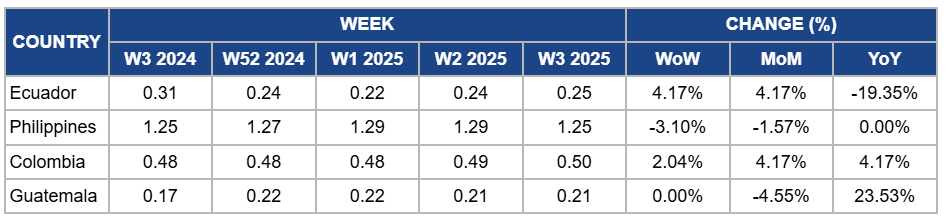
Ecuador
In Ecuador, banana prices increased by 4.17% week-on-week (WoW) and month-on-month (MoM) to USD 0.25/kg in W3 due to a temporary reduction in local supply as harvests slowed, allowing for market stabilization and better price conditions. This price uptick reflects ongoing adjustments in supply to meet current demand. However, there is a big drop of 19.35% year-on-year (YoY) in banana prices due to the lingering oversupply effects which have kept pressure on prices. Additionally, competition from other banana-exporting countries offering more competitive pricing, logistical challenges, and unfavorable global market conditions in key export destinations, has constrained price recovery, resulting in a significant YoY decline.
Philippines
Banana prices in the Philippines dropped by 3.10% WoW to USD 1.25/kg in W3. This reflects a 1.57% MoM decrease despite ongoing challenges posed by Foc TR4, which continues to affect production in Mindanao. While Foc TR4 has hindered production, the slight drop in export demand has contributed to the overall price decrease. On the other hand, YoY prices show no change, which means that according to seasonality pricing seems stable. Despite some weather improvements, the impact of the disease and logistical issues has slowed down the expected production recovery, which could have otherwise pushed prices higher. Additionally, geopolitical tensions and rising input costs have increased operational challenges, but their effects on pricing have been somewhat mitigated by the steady demand from both local and international markets, which has helped maintain price stability.
Colombia
Colombia's banana prices increased by 2.04% WoW to USD 0.50/kg in W3, showing a 4.17% MoM and YoY increase due to a rebound in export demand following the post-holiday dip, particularly from key markets like the United States (US) and Europe. The seasonal recovery in demand has supported higher prices, alongside steady production and favorable weather conditions. Additionally, reduced competition from other banana-exporting countries, and efforts to mitigate logistical challenges, helped stabilize the market and contribute to the price growth. The YoY increase also reflects improved market conditions compared to the same period in 2024.
Guatemala
In W3, banana prices in Guatemala remained stable at USD 1.21/kg, with a 23.53% YoY increase due to reduced production levels compared to the previous year, driven by early-month weather challenges such as scattered showers and rainy conditions that impacted harvesting and logistics. These constraints led to tighter supply and supported higher prices YoY. However, there is a slight decrease in MoM banana prices by 4.55% due to higher supply levels during the low production season, which temporarily led to price reductions despite stable demand.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Address Challenges to Increase Banana Exports in the Philippines
Philippine banana exporters should focus on disease management by investing in Foc TR4-resistant banana varieties like Cavendish hybrids. Implementing sustainable farming techniques such as integrated pest management (IPM), soil health management, and crop rotation can reduce disease impacts and improve productivity. Expanding logistics infrastructure, diversifying export markets, and enhancing international partnerships will help mitigate geopolitical tensions and rising costs, securing the country's position as a global leader in banana exports.
Mitigate Cold Weather Impact on Banana Production in Karnataka
Banana farmers in Karnataka should adopt frost protection measures like windbreaks, frost covers, and improved irrigation to minimize cold damage. Exploring cold-tolerant banana varieties and diversifying with intercropping can help mitigate the impact of extreme temperatures. Providing technical training on recovery practices will support farmers in restoring crop health and market quality.
Sources: Tridge, AgroPeru, Asprocan, Freshplaza, India Times, Inquirer, Hortidaily, Varthabharati






