
In W3 in the orange landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Adverse conditions, such as drought in São Paulo and Florida, have led to reduced orange harvests and tighter global supplies. In contrast, Morocco and Egypt benefited from favorable weather and irrigation improvements.
- Morocco and South Africa increased exports to the US and Europe, filling gaps left by lower production in traditional markets. The EU saw a surge in imports, primarily from South Africa and Egypt.
- South African orange prices rose sharply due to limited supply and export demand, while Egypt's prices remained stable, supported by high-quality production. Spain’s juice orange prices remain below production costs, sparking calls for market intervention.
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Brazil's 2024/25 Orange Harvest Expected to Rise
Brazil's orange harvest for the 2024/25 season is projected at 223.14 million 8.2-kilogram (kg) boxes, a 3.4% increase from the Sep-24 estimate, driven by favorable rains. However, the projected volume still represents a 27.4% year-on-year (YoY) decline compared to last year’s harvest. Adverse conditions, such as reduced stocks and a smaller harvest, are expected to keep juice exports below last year’s levels. This reduction in supply is expected to benefit local fruit prices in Brazil, as consumers may turn to alternative fruits like apples, mangoes, and bananas, driving up demand and prices for these products.
Irregular 2024/25 Orange Harvest in São Paulo Due to Drought
The 2024/25 orange harvest in São Paulo, Brazil, has faced challenges due to high temperatures and droughts lasting over 15 days in some regions, leading to irregular fruit development. While growers remain hopeful for rainfall in the coming months, the harvest is expected to be regular to good overall. Despite the prolonged drought, certain areas experienced a more balanced rainfall pattern, which benefited the fruit set. However, the harvest remains uneven, particularly affecting varieties such as the pear orange. Growers are closely monitoring the situation, awaiting further flowering to assess the full extent of the harvest.
Europe
EU Orange Imports Surged in Late 2024 with Price Variations Across Member Countries
From Oct-24 to Dec-24, the European Union’s (EU) orange imports reached 187.1 thousand metric tons (mt), marking a 41% increase compared to the five-year average. South Africa was the largest exporter, supplying 154.6 thousand mt, followed by Egypt, and Turkey. The average price of oranges in the EU fell to USD 96.88 per 100 kg (EUR 93/100 kg) in Dec-24, down from USD 102.08/100 kg (EUR 98/ 100 kg) in Nov-24, with notable price variations across member countries: Spain at USD 79.17/100 kg (EUR 76/100 kg), Italy at USD 148.96/100 kg (EUR 143/100 kg), and Greece at USD 55.21/100 kg (EUR 53/100 kg). These price variations reflect differences in local supply, regional demand, and import reliance across the region.
Spain
ASAJA Condemns Low Orange Prices in Spain’s Citrus Industry
In Andalusia, Spain, the agricultural organization Agrarian Association of Young Farmers (ASAJA) has condemned the citrus industry's pricing practices. Oranges, especially those for juice production, are being bought from farmers at prices well below market value, putting the viability of orange cultivation at risk. Asaja has pointed out that oranges for juicing, comprising about 20% of the total crop, are sold at prices below production costs, heightened by cheaper imports from countries like Egypt. The situation is further compounded by a significant drop in local orange consumption in Spain, which has fallen from 21 kg per person annually in 2013 to just 11.88 kg in 2023, driven by changing consumer preferences and competition from other fruits. Asaja urges public authorities to intervene, promote Andalusian oranges, and bolster consumption to stabilize the market. Despite Spain's position as the largest citrus producer in the EU and a global leader in orange exports, adverse weather conditions have still impacted the sector. For the 2024/25 campaign, national production is projected at 5.84 million tons, including 2.97 million tons of oranges.
Morocco
Moroccan Orange Production and Export Outlook for 2024/25 Campaign
For the 2024/25 campaign, Morocco's orange production is expected to increase by 17%, reaching 960 thousand tons, due to improved climatic conditions and the greater adoption of advanced irrigation techniques. Although still below the record high of the 2018-2019 season, this growth is a positive development compared to the previous year. Moroccan orange exporters are facing strong competition from Egypt and Turkey, but have seen a significant rise in exports to the United States (US), driven by reduced production in California. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) forecasts Moroccan orange exports to reach 90 thousand tons, a 50% YoY increase, reflecting the country’s capacity to meet growing demand.
United States
Florida's Orange Production Revised Down by 20% Due to Drought and Unfavorable Weather
Florida's orange production in the US has been revised down by 20%, reaching its lowest point in nearly a century due to drought and unfavorable weather. This significant drop in supply, combined with reduced harvests in Brazil, is expected to drive higher juice prices and industry margins globally, particularly in New York.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Orange Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
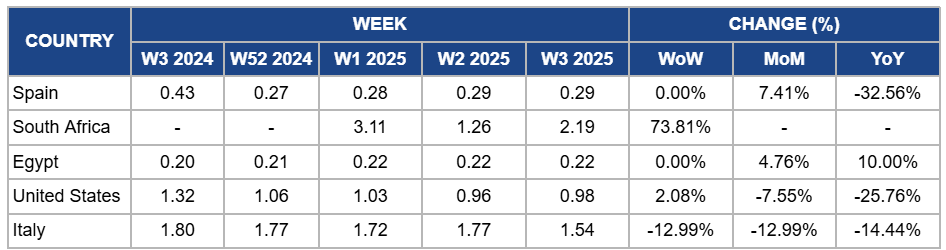
Yearly Change in Orange Pricing Important Exporters (W3 2024 to W3 2025)
Spain
Orange prices in Spain held steady at USD 0.29/kg in W3, with a 7.41% month-on-month (MoM) increase due to heightened demand for juice oranges amidst limited local production caused by adverse weather conditions earlier in the season. Additionally, increased efforts by producers to stabilize supply levels and tap into export markets supported the modest price rise. However, there is a 32.56% YoY drop in orange prices due to persistent pricing pressures from cheaper imports, particularly from countries like Egypt, and declining domestic consumption, which has significantly reduced demand for locally produced oranges. The ongoing challenges faced by farmers, including selling at prices below production costs, have further constrained the market, keeping overall price levels subdued despite Spain’s dominant position in the EU citrus market.
South Africa
South Africa's orange prices surged by 73.81% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 2.19/kg in W3 due to limited availability of fresh oranges during the off-season, creating upward pressure on prices. The increase was also influenced by strong demand in both domestic and export markets, particularly as international buyers sought high-quality South African produce amidst tighter global supplies. Additionally, the recent rainfall in key growing regions like Limpopo and Mpumalanga has raised expectations of a strong upcoming harvest, contributing to speculative market activity. Combined with reduced market activity for alternative citrus fruits, this further supported the price recovery.
Egypt
In W3, orange prices in Egypt remained stable at USD 0.22/kg, showing a 4.76% MoM increase and a 10% YoY increase due to strong domestic demand during the peak winter production season and consistent export opportunities to primary markets. Favorable weather conditions have supported high fruit quality, strengthening competitiveness in the international market. Additionally, heightened consumer interest in oranges as a seasonal staple has sustained elevated price levels compared to the previous year, even with high supply ensuring price stability weekly.
United States
Orange prices in the US increased slightly by 2.08% WoW to USD 0.98/kg in W3. This is due to a reduced supply following the 20% revision in Florida's orange production caused by drought and unfavorable weather. This supply constraint, coupled with similar challenges in Brazil, has driven marginal price increases as the market adjusts to limited availability. However, MoM and YoY prices dropped by 7.55% and 25.76%, respectively, due to sustained effects of oversupply from previous harvests and subdued demand for fresh oranges amid higher consumer focus on processed orange products like juice. The global market’s adjustment to lower supply levels is yet to fully offset the downward price pressures seen earlier.
Italy
Italy's orange prices dropped by 12.99% WoW and MoM, showing a 14.44% YoY decline due to increased competition from imported oranges, particularly from South Africa, which continues to saturate the European market. This oversupply has weakened demand for locally produced oranges, despite steady consumption among Italian households. Additionally, production challenges in Sicily, including drought and torrential rains, have limited the availability of premium-quality oranges, further pressuring prices as consumers opt for more competitively priced imports. The growing, yet still limited, market share of organic oranges has not been sufficient to offset the overall decline in pricing, reflecting ongoing challenges in stabilizing the domestic orange market.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Leverage Orange Juice Price Trends Amid Supply Shortages
Florida and Brazilian orange growers should focus on maximizing fruit quality from the limited harvests, ensuring they meet the premium standards expected amid rising juice prices. Exporters should explore diversifying markets and strengthening relationships with juice processors to capitalize on the anticipated price increases. In parallel, investing in water-efficient irrigation technologies could help mitigate the impact of irregular weather patterns in future harvests.
Capitalize on Growing US Demand for Moroccan Oranges
Moroccan orange exporters should focus on expanding their presence in the US market, where demand is rising due to reduced production in California. With an export increase to the US, exporters can leverage this growth opportunity by strengthening marketing efforts and building partnerships with US distributors. This strategic focus will help maintain a competitive advantage despite the competition from Egypt and Turkey.
Address Low Pricing and Declining Consumption of Andalusian Oranges
ASAJA should push for more transparent pricing models that reflect the true cost of production for juice oranges, while also exploring new marketing strategies to boost local consumption. ASAJA can collaborate with retailers and promote the quality and sustainability of Andalusian oranges to counter the effects of cheaper imports and declining domestic demand.
Sources: Tridge, Agraria, Elconfidencial, Freshplaza, NoticiasAgricolas, Simfruit





