
1. Weekly News
Germany
Germany's Apple Harvest Hits Lowest Level Since 2017
According to the World Apple and Pear Association (WAPA), Germany's apple harvest is projected to be below 800 thousand tons in the 2023/24 season, marking a 15% year-on-year (YoY) decrease and the lowest yield since the frost-affected season of 2017. This significant reduction highlights the need for more efficient apple trade across the European market. Despite the challenging harvest, exporters gradually increased their presence in the German market, exporting 87 thousand tons this season, excluding Jul-24 and Aug-24.
Hungary
Hungary's Apple Harvest Expected to Fall Sharply in 2024
Hungary's 2024 apple harvest is expected to be around 330 thousand tons, a significant decrease from last year's 472 thousand tons. This would mark the second weakest crop in the past decade. The reduced yield is due to several factors, including the stress from last year's large crop and adverse weather conditions such as cold spells, drought, heat shocks, and hail. While the number of edible apples will be slightly lower than last year, with an estimated 90 thousand to 100 thousand tons available, the apple juice supply is expected to be notably reduced. Apple juice comprises two-thirds of the harvest. Hungary's processing capacity, which can handle about 400 thousand tons, will see only 60% utilization due to the domestic shortfall. This shortage may impact acceptance prices and reflect broader international apple supply issues.
India
High-Density Apple Farming Boosts Jammu and Kashmir's Apple Industry
High-density apple farming is revolutionizing the apple industry in Jammu and Kashmir by delivering impressive returns and overcoming challenges associated with traditional apple varieties. Growers in the region have reported significant benefits from this method, including reduced input and labor costs, superior fruit quality, and early yields that mitigate risks from untimely snowfall. Prices for high-density apples, such as Jeromine, King Roat, and Gala Scarlet, stood at USD 1.19 to 1.67 per kilogram (INR 100 to 140/kg), nearly double the rate for traditional varieties. Approximately 800 hectares (ha) of land in Jammu and Kashmir are converted to high-density farming, with plans to expand to 5.5 thousand ha, supported by a 50% government subsidy. This farming approach, introduced in 2015, has become a key part of the region's apple industry, which supports half of Kashmir's population and contributes around 9.5% to the state's gross domestic product (GDP).
Poland
Polish Apple Season Starts Early Amid Weather Challenges and Decreased Production
The Polish apple season started earlier in 2024, with Gala apples beginning to be harvested about ten days ahead of schedule. In 2023, Gala apple varieties were picked starting around September 28, highlighting the shift. The weather in Poland has been erratic, with previous heat waves followed by recent heavy rains that have caused flooding in some regions. Despite these challenges, cooler temperatures and sunny days are benefiting apple ripening. This year’s apple production in Poland is expected to decrease by 20% YoY, with notable difficulties anticipated for apple varieties like Jonagold and Idared due to uneven tree growth. While European apple production overall is decreasing, demand from Germany, the Czech Republic, and the processing industry may remain strong, potentially driving up prices. Growers also invest in new technologies and water management solutions to cope with rising production costs and changing climate conditions.
Ukraine
Ukrainian Apple Exports Face Growing Competition in Global Market
The increase in Ukrainian apple exports is primarily driven by domestic exporters capturing market share from other exporting countries. This trend is influenced by a global shift in fruit consumption, where other fruits are increasingly replacing apples. As a result, Ukrainian exporters face higher costs and reduced margins than in previous years. Despite these challenges, Ukrainian apples are well-received internationally, mainly due to their high quality at competitive prices. Moldova, Serbia, and Poland remain Ukraine's main competitors in the global apple market.
United States
US Apple Production Anticipates High Yields Amid Slight Decline
According to the United States Apple Association (USApple), apple growers in the country are anticipating another strong harvest for the 2024/25 marketing year (MY) despite a projected 10.1% decrease in total production to 259.5 million bushels. Moreover, Gala apple varieties are expected to continue leading in production, with Red Delicious, Granny Smith, Honeycrisp, and Fuji being prominent. Fresh apple exports have surged by 44% YoY due to a robust domestic supply, competitive pricing, and favorable trade policies, including removing tariffs on US apples in India.
Michigan's Apple Harvest Expected to Surpass Average Despite Slight Decline
In 2024, Michigan is expected to harvest 30.5 million bushels of apples, equivalent to 1.3 billion pounds (lbs), slightly down from last year's 31.9 million bushels but still above the state's average annual crop of 25.9 million bushels. The Michigan Apple Committee attributes this strong performance to high-density orchards and innovative growing practices. Despite a smaller forecast, the 2024 apple crop remains one of the more significant recent harvests, aided by favorable weather conditions, including a lack of substantial frost after an early bloom in May-24. Michigan's apple industry, the state's largest fruit crop, continues to thrive with a commitment to producing high-quality apples.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
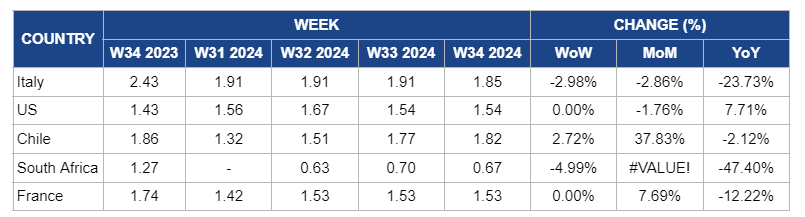
* Varieties: US and Italy (Gala), Chile, South Africa, and France (Granny Smith)
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W34 2023 to W34 2024)
* Varieties: US and Italy (Gala), Chile, South Africa, and France (Granny Smith)
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
Italy
In Italy, apple prices in W34 decreased by 2.98% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 1.85/kg, with a 2.86% month-on-month (MoM) and a 23.73% YoY decline. Despite the severe drought and heatwave conditions affecting production, this price drop may result from a temporary market adjustment. Traders and distributors might be lowering prices in the short term, anticipating the eventual impact of reduced supply in the coming weeks. As the effects of the poor harvest become more apparent, prices are likely to experience upward pressure.
United States
In W34, apple prices in the US remained steady at USD 1.54/kg, with a 1.76% MoM increase. However, YoY prices decreased by 7.71%, reflecting the impact of a strong harvest despite a projected 10.1% decline in total production for the 2024/25 MY. The stable prices are supported by the continued availability of popular varieties and a robust export market, which has seen a 44% YoY increase due to competitive pricing and favorable trade policies. This balance between supply and demand has helped maintain price stability despite the overall production drop.
Chile
Chilean apple prices increased slightly by 2.72% WoW to USD 1.82/kg in W34, with a significant 37.83% MoM rise. This price surge reflects the impact of decreasing production and exports as growers transition to more profitable crops and the planted area continues to contract. With production expected to drop to 870 thousand metric tons (mt) and exports declining to 463 thousand mt, the lowest since the 1999/2000 season, the reduced apple supply is driving prices upward. The constrained availability in domestic and international markets further contributes to the upward price pressure.
South Africa
South Africa's apple prices declined by 4.99% WoW to USD 0.67/kg, with a significant decline of 47.4% YoY. This drop is primarily due to the anticipated increase in apple production, which is expected to reach 1.2 million metric tons (mmt)due to favorable weather conditions and a larger harvested area. The recovery from last year's hail damage and the projected rise in production are contributing to a greater supply in the market, exerting downward pressure on prices. Additionally, while expanding market reach, the export increase to India and the European Union (EU) has not fully offset the higher domestic supply. As a result, abundant local production and strong export performance have led to a substantial decrease in apple prices YoY.
France
Apple prices in France remained steady at USD 1.53/kg in W34, reflecting a 7.69% increase MoM. The price stability is due to a harvest consistent with last year and shows a 2.5% increase compared to the three-year average, maintaining supply levels. The MoM increase is driven by decreased production of certain international varieties like Granny Smith and Fuji, which saw declines of 26.3% and 27%, respectively, alongside reduced yields for Gala and Pink Lady apples. Despite the MoM rise, there is a 12.22% YoY price decline indicating that prices are still adjusting from higher levels in previous years, influenced by an oversupply from earlier seasons and shifts in consumer demand.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Optimize Apple Trade Efficiency to Compensate for Low Harvest
To address Germany's projected apple harvest decrease and maintain a strong market presence, exporters should optimize trade efficiency by streamlining logistics and reducing transport costs. This involves improving coordination between suppliers and distributors, investing in efficient supply chain management, and adopting technologies to enhance operational processes. Simultaneously, Germany can enhance competitive pricing strategies by analyzing market trends and adjusting prices to offer attractive rates to buyers despite the reduced supply. Strengthening relationships with German importers and exploring alternative distribution channels within Europe will help secure market position and mitigate the impact of the lower harvest.
Invest in Technology and Water Management for Apple Production
Polish apple growers should accelerate investment in new technologies and advanced water management systems to adapt to changing climate conditions and offset a 20% expected decrease in apple production. Precision irrigation systems will optimize water use, reducing the impact of erratic weather and improving water efficiency. Adopting climate-resilient cultivation technologies, such as weather sensors and automated climate control, will enhance apple quality and yield consistency. These measures will help growers meet strong demand from key markets like Germany and the Czech Republic, stabilize prices, and ensure sustainable production despite challenging conditions.
Optimize Processing Capacity and Diversify Supply Channels
Hungary's apple processors should enhance their processing capacity and diversify supply channels to address the anticipated shortfall in apple juice production. With the domestic apple harvest expected to meet only 60% of the processing capacity, seeking international partnerships to fill the supply gap is crucial. Investing in advanced processing technologies will improve efficiency by enabling better utilization of available apples, reducing waste, and increasing overall output. These measures will help stabilize apple juice prices and effectively address broader international supply issues.
Sources: Tridge, Sad24, Fruitgrowersnews, Agrotimes, Agraria, Kashmirobserver, Eastfruit, Freshplaza, Producereport, Ofimagazine





